Configuring Precise Protection Rules¶
This section describes how to configure precise protection rules.
With these rules, WAF allows you to customize combinations of HTTP headers, cookies, URLs, request parameters, and IP addresses, improving defense accuracy.
Prerequisites¶
Login credentials have been obtained.
The domain name to be protected has been created.
Procedure¶
Log in to the management console.
Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.Click Service List at the top of the page and choose Security > Web Application Firewall. In the navigation pane, choose Domains. Figure 1 shows an example.
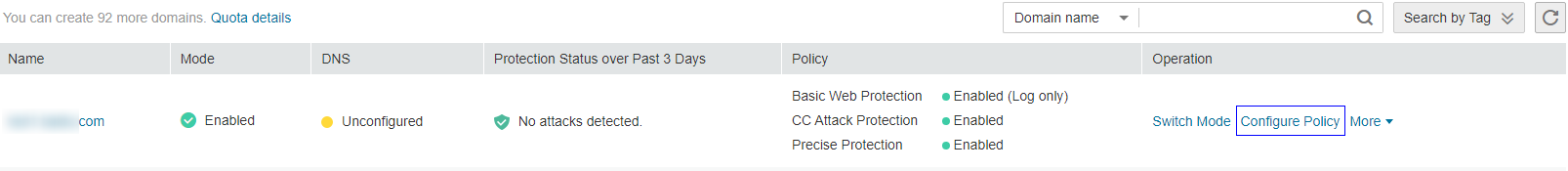
Figure 1 Entrance to the domain configuration page¶
Note
In the upper part of the domain name list, click Quota details to view the domain name quota.
Locate the row that contains the desired domain name. In the Operation column, click Configure Policy. Figure 2 shows an example.
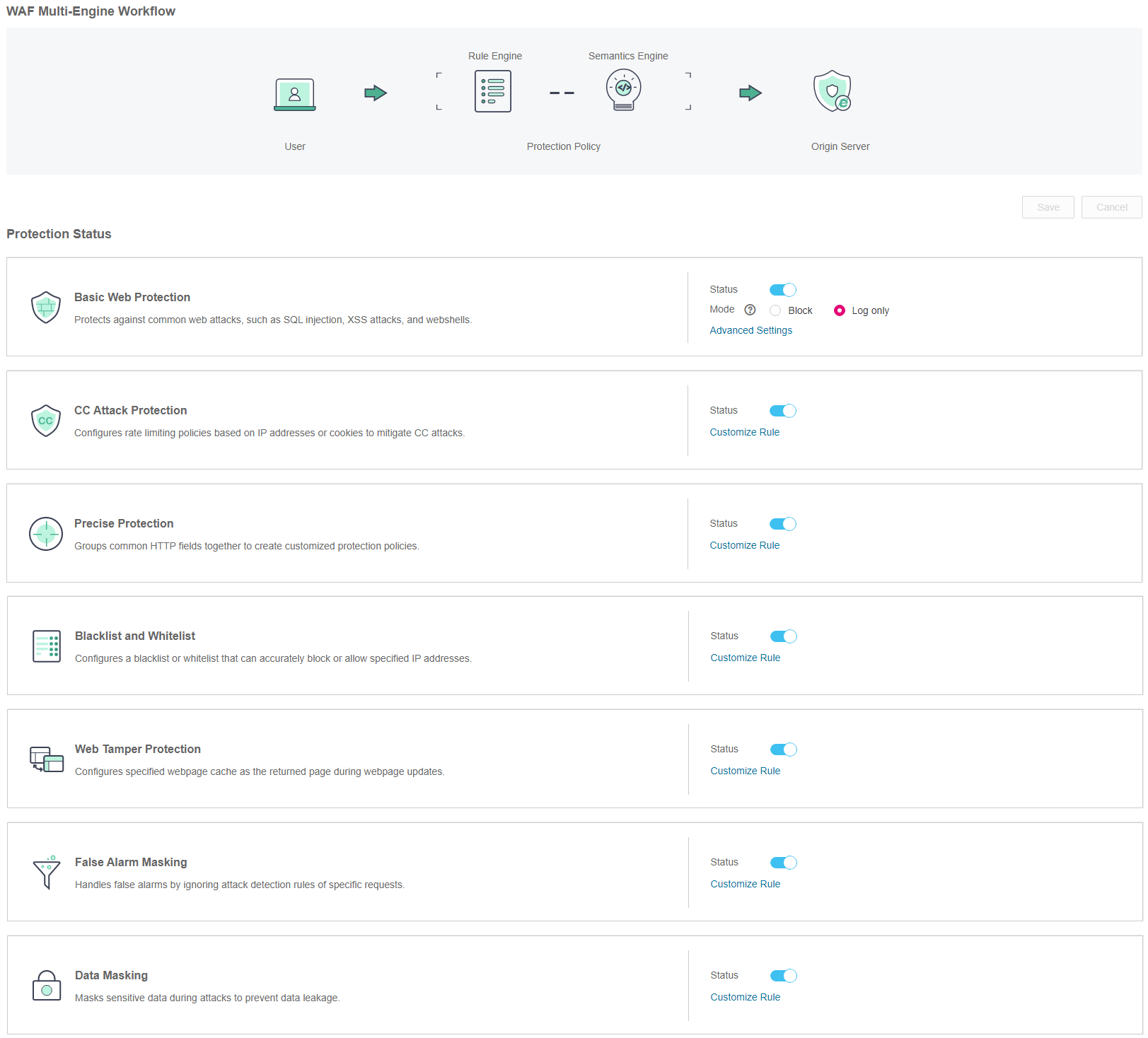
Figure 2 Protection configuration page¶
In the Precise Protection area, specify Status. After the configuration completes, in the upper right corner of the Protection Status list, click Save. In the displayed dialog box, click Yes to save the settings. If you do not want to save the settings, click Cancel. Figure 3 shows an example.

Figure 3 Precise Protection configuration area¶
Click Customized Rule. On the displayed page, specify Detection Mode. Figure 4 shows an example.
Note
If you do not click Save after changing Status in Step 5, a Warning dialog box is displayed when you click Customize Rule.
Click Yes to cancel the previous settings.
Click No and then Save to save the settings.
Two detection modes are available:
Instant Detection: WAF immediately ends threat detection and blocks the request that hits the configured precise protection rule.
Full Detection: WAF blocks all requests that hit the configured precise protection rule when it finishes all threat detections.
The default detection mode is Instant Detection. After changing the detection mode, click Save.

Figure 4 Setting Detection Mode¶
In the upper left corner of the Precise Protection page, click Add Rule. Figure 5 shows an example.

Figure 5 Add Rule (Precise Protection)¶
Note
In the upper part of the protection rule list, click Quota details to view the quota of protection rules.
In the displayed dialog box, specify the parameters by referring to Table 1. Figure 6 shows an example.
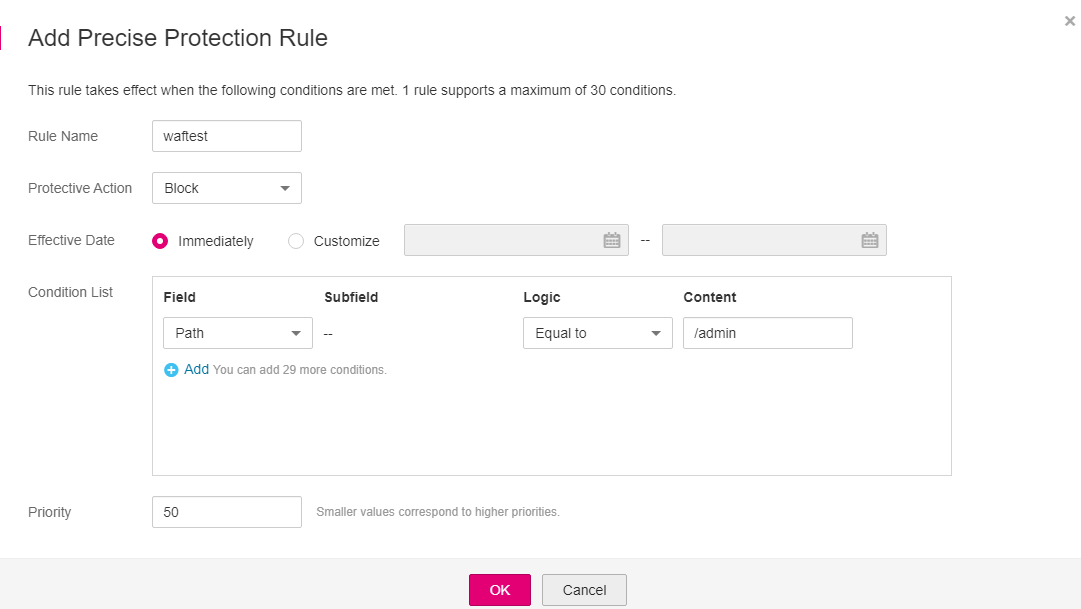
Figure 6 Adding a precise protection rule¶
Table 1 Rule parameters¶ Parameter
Description
Example Value
Rule Name
Customizable rule name
waftest
Protective Action
Its value is Block or Allow. The default value is Block.
Block
Effective Since
Select Immediately or select Customize to set a period. This period can only be a time segment in the future.
Immediately
Condition List
Click Add to add conditions. You must add one to thirty conditions to a protection rule. If more than one condition is added, all the conditions must be met simultaneously for the rule to take effect.
Field
Subfield: Configure this field only when Params, Cookie, or Header is selected.
Important
NOTICE: The length of a subfield cannot exceed 2048 bytes. Only digits, letters, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed.
Logic: Select the desired logical relationship from the drop-down list.
Content: Enter or select the content of condition matching.
Note
For detailed configurations, see Table 2.
Path Include /admin
User Agent Prefix is not mozilla/5.0
IP Equal to 192.168.2.3
Cookie key1 Prefix is not Nessus
Priority
Priority of a rule being executed
Smaller values correspond to higher priorities. If two rules are assigned with the same priority, the rule added earlier has higher priority.
50
Table 2 Condition list configurations¶ Field
Example Subfield
Logic
Example Content
Path: URL excluding a domain name. This value supports exact match only. For example, if the path to be protected is /admin, set Path to /admin.
None
Include, Exclude, Equal to, Not equal to, Prefix is, Prefix is not, Suffix is, or Suffix is not
/buy/phone/
User Agent: A user agent of the scanner to be protected
None
Include, Exclude, Equal to, Not equal to, Prefix is, Prefix is not, Suffix is, or Suffix is not
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1)
IP: An IP address of the visitor to be protected
None
Equal to or Not equal to
192.168.2.3
Params: A request parameter to be protected
sttl
Include, Exclude, Equal to, Not equal to, Prefix is, Prefix is not, Suffix is, or Suffix is not
201901150929
Cookie: A small piece of data to identify web visitors
name
Include, Exclude, Equal to, Not equal to, Prefix is, Prefix is not, Suffix is, or Suffix is not
Nessus
Referer: A user-defined request resource
For example, if the protected path is /admin/xxx and you do not want visitors to access the page from www.test.com, set Content to http://www.test.com.
None
Include, Exclude, Equal to, Not equal to, Prefix is, Prefix is not, Suffix is, or Suffix is not
http://www.test.com
Header: A user-defined HTTP header
Accept
Include, Exclude, Equal to, Not equal to, Prefix is, Prefix is not, Suffix is, or Suffix is not
text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
Click OK.
To modify the added rule, click Modify in the row containing the target rule.
To delete the added rule, click Delete in the row containing the target rule.