OS Partitioning Recommendations¶
Scenario 1: BIOS Boot¶
If a BMS is booted in BIOS mode, BIOS needs to be configured for the image used to create the BMS and MBR partitioning is also required.
If the primary partition meets your requirements:
A: If the boot and swap partitions are independent, use the following partitioning:
boot-swap-root partition
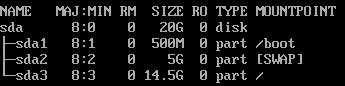
B: If the boot and swap partitions are not independent, use the following partitioning:
swap-root partition
root partition
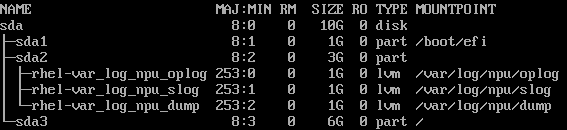
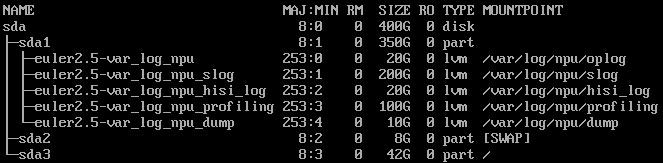
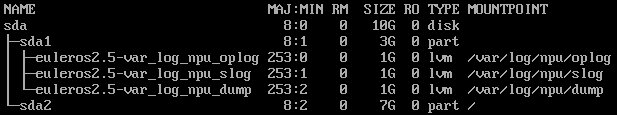
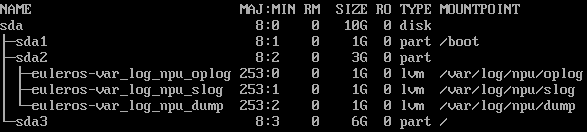
If an extended partition (for example, lvm) is required, use the following partitioning:
Extended partition (lvm)-swap-root partition
Extended partition (lvm)-root partition
boot-extended partition (lvm)-root partition
Scenario 2: UEFI Boot¶
If a BMS is booted in UEFI mode, UEFI needs to be configured for the image used to create the BMS. For an x86 BMS with the UEFI boot mode, MBR partitioning is required and the boot_efi partition is mandatory.
If the primary partition meets your requirements:
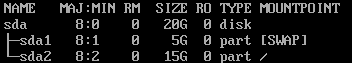
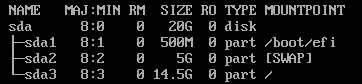
A: If the swap partition is independent, use the following partitioning:
boot_efi-swap-root partition
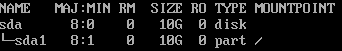
B: If the swap partition is not independent, use the following partitioning:
boot_efi-root partition
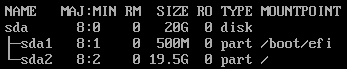
If an extended partition is required, use the following partitioning:
boot_efi-extended partition (lvm)-root partition