Preparing the Environment¶
Prepare a Linux physical server or VM as the host and install Linux on the host.
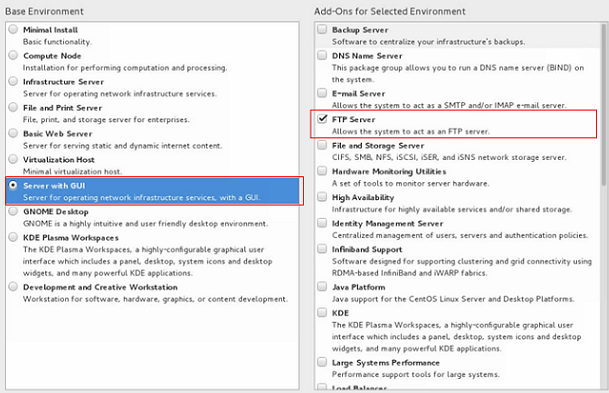
For example, if you are installing CentOS 7.3 64bit on the host, you must select the GUI and virtualization environment.
Select Server with GUI and then select FTP Server, Virtualization Client, Virtualization Hypervisor, and Virtualization Tools.
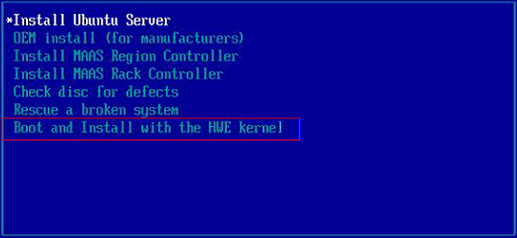
For example, if you are creating an Arm64 image and installing Ubuntu 16.04 Server-ARM64 on the host. Select the option containing the HWE kernel.
After the OS is installed on the host, run the following commands to install the Ubuntu desktop and virtualization software and then restart the host.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop
sudo apt-get install qemu
sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm
sudo apt-get install libvirt0
sudo apt-get install virt-manager
sudo apt-get install qemu-efi
Configure the host network and remote connection to the host.
Connect the host to the Internet so that you can install software on VMs online through the host.
Remotely connect to the host. If you are connecting from a Windows local server, additional configurations are needed.
Enable the vsftpd, SSHD, and VNC services and configure them.
These services allow you to remotely transmit software packages, ISO files, and scripts to the host, and remotely log in to the host. For details, see Configuring the SSH Service, Configuring the vsftpd Service, and Configuring the VNC Service.
For CentOS 7.x, disable the firewall so that you can log in to the host using VNC Viewer. Run the following commands to disable the firewall:
systemctl disable firewalld.service
systemctl stop firewalld.service
Transmit required files to the host.
After the host configuration is complete, use vsftpd to upload the required files to the host. After the preceding operations are performed, the host environment configuration is complete.
If you use Xftp to upload the files, click the icon shown in the red box in the following figure after you log in to the host through Xshell using SSH.