Overview¶
Before using WAF, you need to connect your domain name to it and enable it for protection to take effect.
Table 1 describes the procedure to use WAF.
Step | Description |
|---|---|
Creating a domain name | Add a website to be protected. For details, see Creating a Domain Name. |
Enabling WAF protection | Enable WAF protection to protect your web services. For details, see Enabling WAF Protection. Note
|
Configuring rules | In addition to the built-in protection rules, WAF provides a rich set of custom rules. For details, see Rule Configurations. |
Enabling alarm notification | Once the function is enabled, users can receive attack logs at the earliest moment. For details, see Enabling Alarm Notification. |
Handling false alarms | If the attack events blocked or logged are false positives, mask them. For details, see Handling False Alarms. |
Viewing Dashboard | View the request and attack statistics, event distribution, and top 5 attack resource IP addresses of yesterday, today, past 3 days, past 7 days, or past 30 days. For details, see Dashboard. |
For details about how to connect your website to WAF, see Figure 1.
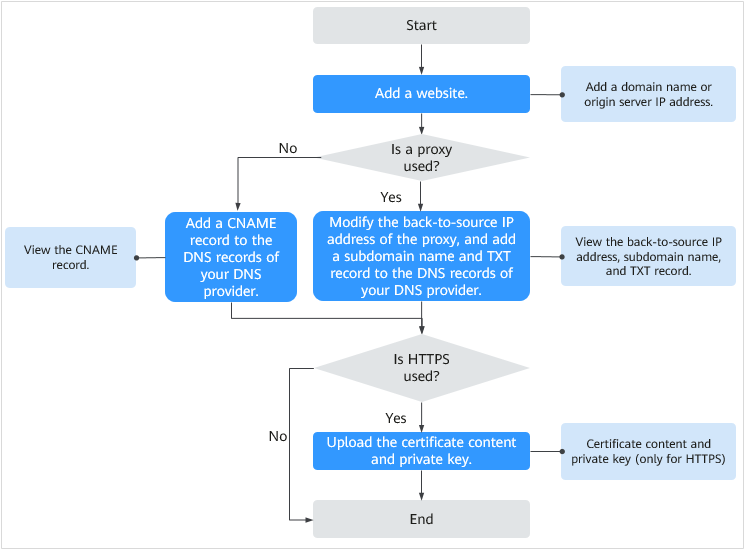
Figure 1 Flowchart for connecting your website to WAF¶