Condition Field Description¶
When setting a precise access, CC attack protection, or global protection whitelist rule, configure some fields in the condition list area. These fields together are used to define the request attributes to trigger the rule. This topic describes the fields that you can specify in conditions to trigger a rule.
What Is a Condition Field?¶
A condition field specifies the request attribute WAF checks based on protection rules. When configuring a CC attack protection rule, precise access protection rule, or global protection whitelist, you can define condition fields to specify request attributes to trigger the rule.
If a request meets the conditions set in a rule, the request hits the rule. WAF will then handle the request based on the action (Allow, Block, or Log only) configured for the rule.
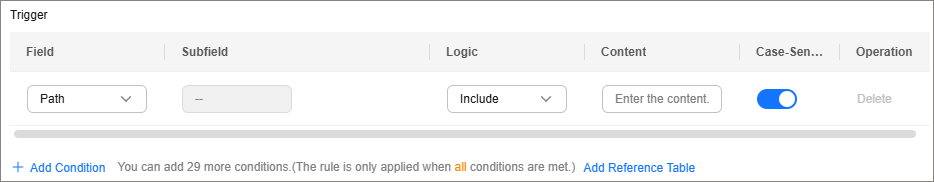
Figure 1 Condition field¶
A condition field consists of Field, Subfield, Logic, and Content. Example:
Example 1: If Field is set to Path, logic to Include, and Content to /admin, a request matches the rule when the requested path contains /admin.
Example 2: If Field is set to IPv4, Subfield to Client IP Address, Logic to Equal to, and Content to 192.XX.XX.3. When the client IP address is 192.XX.XX.3, the request hits the rule.
Supported Condition Fields¶
Field | Description | Subfield | Logic | Content (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Path | The path of a resource requested by the client. A path is part of a URL. Configuration description:
| -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| /buy/phone/ |
User Agent | The client type, for example, browser, crawler, and mobile app. | -- | Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) | |
Referer | The source from which the request is sent. If you do not want visitors to access the page from www.test.com, set Content corresponding to Referer to http://www.test.com. | -- | /admin/xxx | |
IP | -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| Client IP address to be matched, for example, XXX.XXX.1.1. | |
Params | The query parameter in the URL. The query parameter is the content following the question mark (?). |
| The following logical relationships are supported:
| 201901150929 |
Cookie | The cookie in the request. |
| jsessionid | |
Header | The request header content. |
| text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,/;q=0.8 | |
Method | The request method. | -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH |
Protocol | The request protocol. | -- | HTTP and HTTPS | |
Request Line | The request line length. The value must be an integer ranging from 0 to 65,535. | -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| 50 |
Request | The request length. The value must be an integer ranging from 0 to 2,147,483,647. The maximum value for cloud load balancer access mode is 4,000 bytes. If the value exceeds the maximum, the configuration does not take effect. | -- | 50 | |
Response Length | The response length. The value must be an integer ranging from 0 to 2,147,483,647.
| -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| 50 |
Response Time | The response time. The value must be an integer ranging from 0 to 60,000, in ms.
| -- | 100 | |
Response Code | The status code returned to the request. For requests sent after this rule is triggered, WAF stops checking their HTTP response code until the current traffic limit duration you configure in the rule ends. | -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| 404 |
Response Header | The response header. WAF checks responses after response headers are returned. If WAF needs to block responses, response headers cannot be changed. |
| The following logical relationships are supported:
| -- |
Response Body | The response message body. WAF checks responses after response headers are returned. If WAF needs to block responses, response headers cannot be changed. | -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| -- |
Request Body | The request message body. | -- | The following logical relationships are supported:
| -- |