WAF Operation Guide¶
To use Web Application Firewall (WAF) to protect your web services, the services must be connected to WAF. WAF provides two access modes for you to connect web services to WAF: ELB load balancer access and dedicated access modes. You can select the access mode that best fits your web services.
Application scenarios¶
WAF provides the following access modes for you to connect websites to WAF.
ELB load balancer access mode:
Service servers are deployed on the cloud.
This mode is suitable for large enterprise websites having high security requirements on service stability.
Protected object: domain names and IP addresses (public or private IP addresses)
Access method: Connecting a Website to WAF (Cloud - ELB Load Balancer Access Mode)
Dedicated mode
Service servers are deployed on the cloud.
This mode is suitable for large enterprise websites that have a large service scale and have customized security requirements.
Protected object: domain names and IP addresses (public or private IP addresses)
Access method: Connecting a Website to WAF (Dedicated Mode)
Procedure for Using WAF¶
Figure 1 shows the procedure. Table 1 describes the procedure.
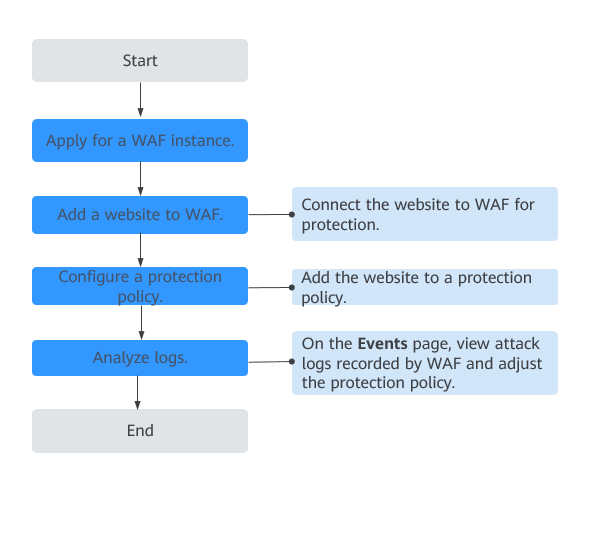
Figure 1 Process of using WAF¶
Operation | Description |
|---|---|
Apply for a dedicated WAF instance. | |
Add websites you want to protect to your WAF instance.
Note
| |
A policy is a combination of rules, such as basic web protection, blacklist, whitelist, and precise protection rules. A policy can be applied to multiple domain names, but only one policy can be used for a domain name. | |
WAF displays blocked or logged-only attacks on the Events page. You can view and analyze protection logs to adjust your website protection policies or mask false alarms. |