Creating a Stack¶
Log in to the management console.
In the upper left corner of the page, click
 , and then click Management & Deployment > Resource Formation Service.
, and then click Management & Deployment > Resource Formation Service.The Dashboard page is displayed.

Figure 1 RFS Dashboard¶
There are several ways to start creating a stack
On the Dashboard page:
click Create Stack in the upper right corner.
click Create Stack in the Select Template tile of the Guide to Create a Stack flow chart.
On the Stacks page, click Create Stack in the upper right corner.
Figure 2 Creating a stack on Stacks page
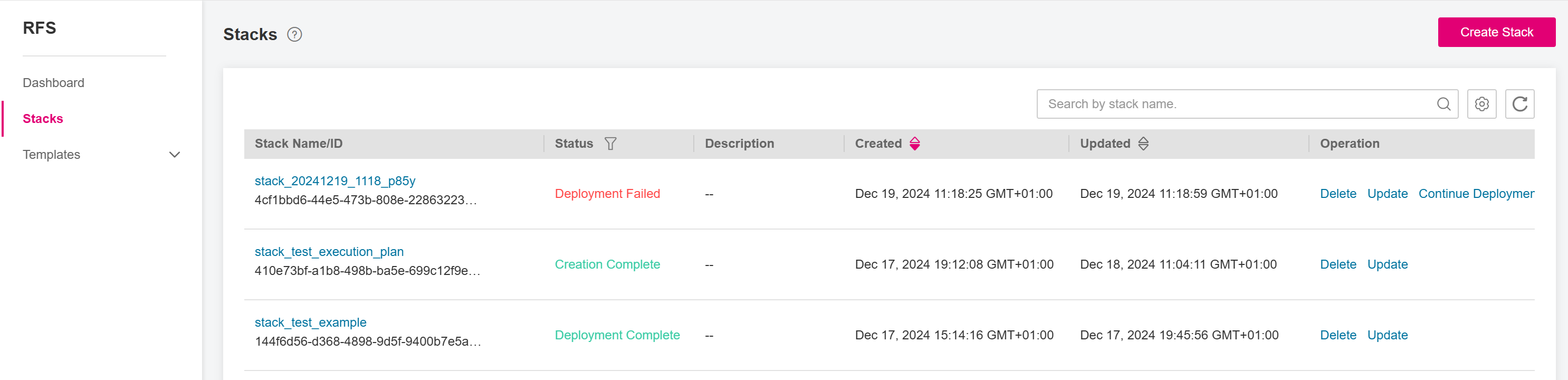
On the Templates -> Private Templates page:
click Create Stack under the Operation column associated with an existing template.
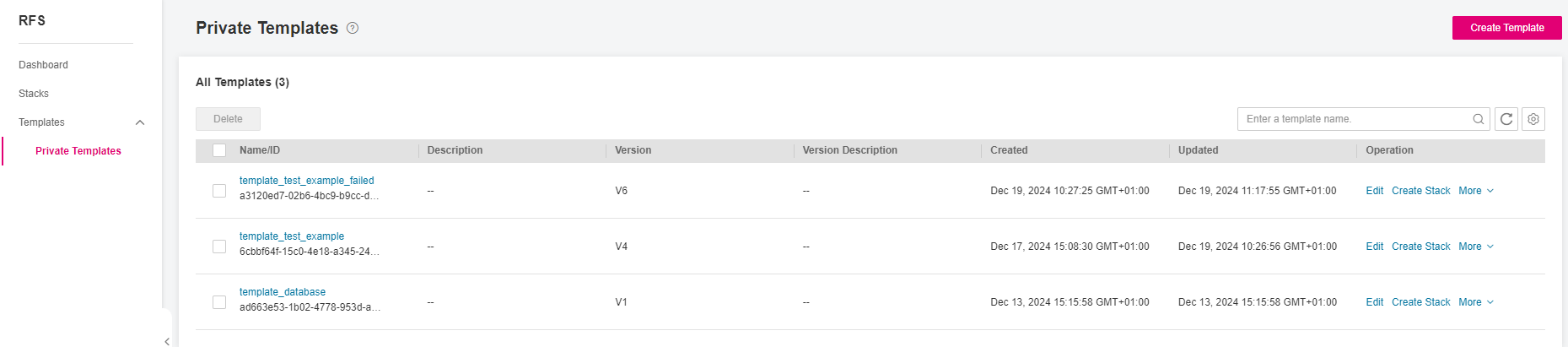
Figure 3 Creating a stack on Private Templates page¶
click the name of the desired template to navigate to its details page, and then click Create Stack under the Operation column associated with a specific template version.
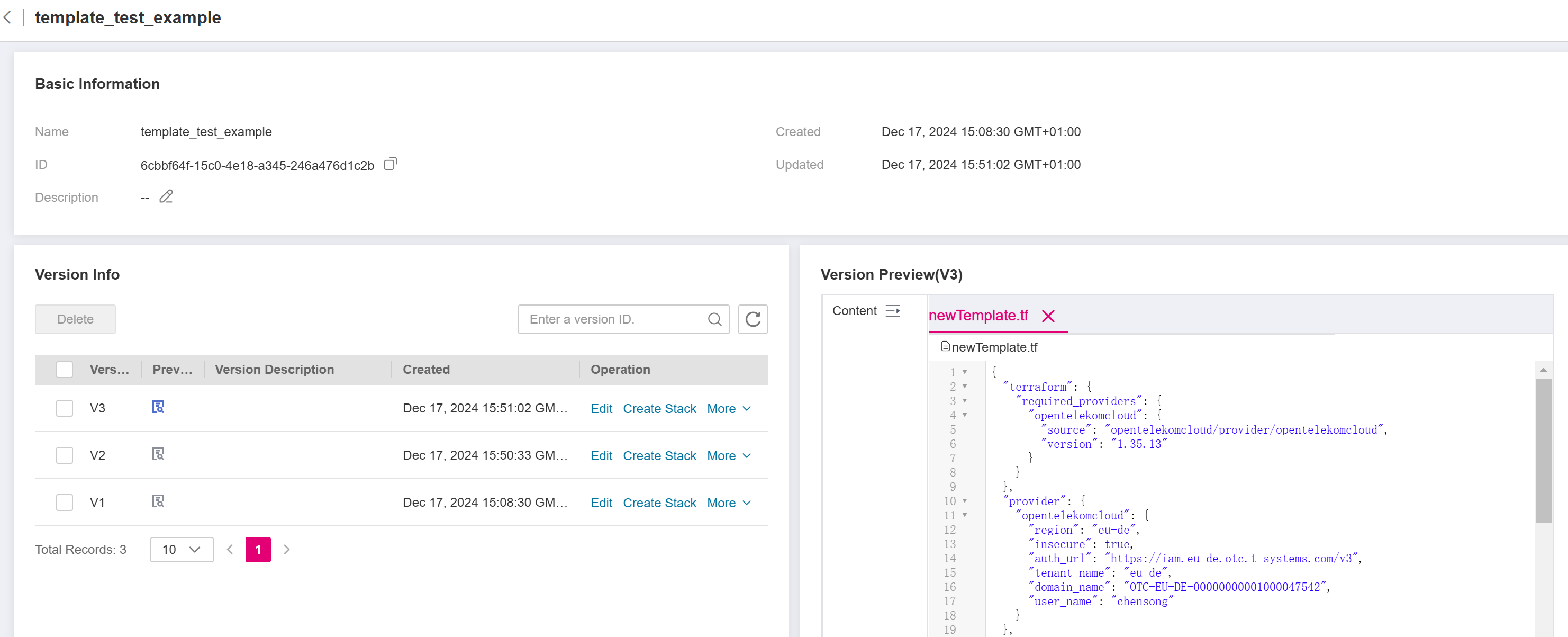
Figure 4 Creating a stack on Template Details page¶
There are three ways to select a template.
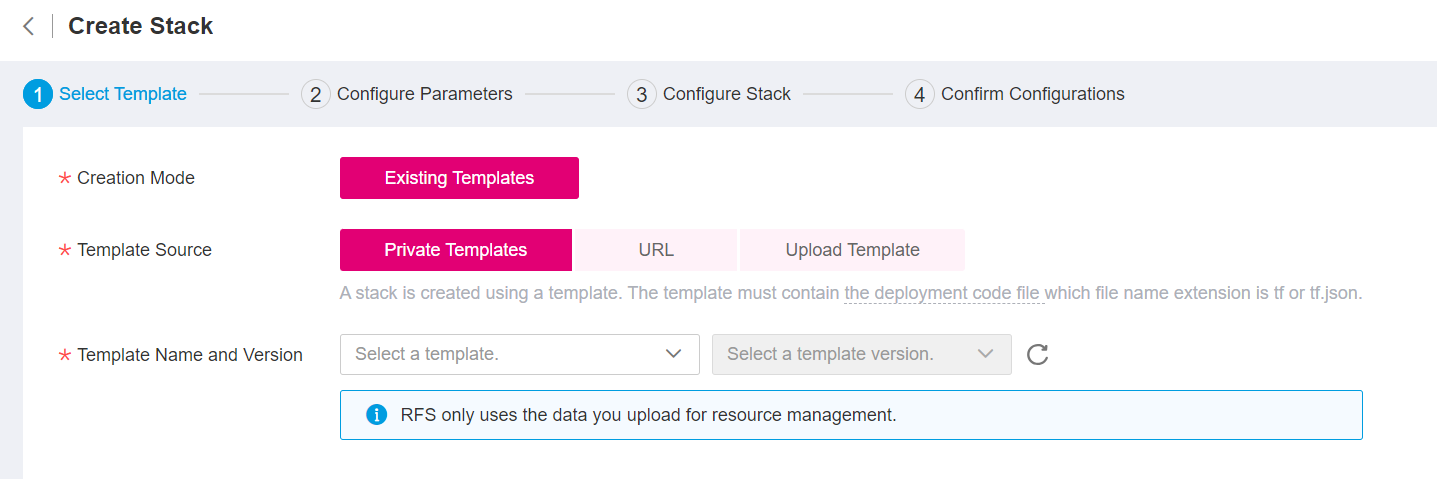
Figure 5 Selecting a template¶
Select a template from Private Templates: Template name and version selector dropdowns.
Enter a URL of an OBS template: Template URL dropdown. (The URL must contain at least the deployment code file, and the file size cannot exceed 1 MB.)
Example: https://test-stack-template.obs.eu-de.otc.t-systems.com/main.tf
Upload a local template file or zip by clicking Add File button.
Important
The .tf, .tf.json, and .zip files are supported.
At least the deployment code file needs to be uploaded.
The size of a file cannot exceed 50 KB.
The size of a decompressed .zip file cannot exceed 1 MB.
Then click Next to go to the parameter configuration page.
Caution
A stack is created using a template. The template must contain the deployment code file which file name extension is tf or tf.json.
The deployment code file must use the open source HCL syntax. After the file is imported, the corresponding resource configuration table is generated for users to configure resource parameters. This file must be provided in URL or via template upload.
When using the RFS service, users do not need to specify the "access_key" and "secret_key" fields under the provider block in the template.
RFS only uses the data you upload for resource management.
The following is an example of uploading a local template file. In this example, the ecs_test.tf.json file is uploaded. The template content is as follows:
{ "terraform": { "required_providers": { "opentelekomcloud": { "source": "opentelekomcloud/provider/opentelekomcloud", "version": "1.35.13" } } }, "provider": { "opentelekomcloud": { "region": "eu-de", "insecure": true, "auth_url": "https://iam.eu-de.otc.t-systems.com/v3", "tenant_name": "eu-de", "domain_name": "OTC-EU-DE-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "user_name": "xxxxxxxxxx" } }, "variable": { "vpc_name": { "type": "string", "description": "vpc name", "default": "rf_test_stack_example_vpc", "sensitive": true, "nullable": false }, "subnet_name": { "type": "string", "description": "subnet name", "default": "rf_test_stack_example_subnet" }, "ecs_name": { "type": "string", "description": "ecs name", "default": "rf_test_stack_example_ecs" }, "compute_keypair_name": { "type": "string", "description": "ecs compute key pair name", "default": "rf_test_stack_example_keypair" }, "storage_volume_name": { "type": "string", "description": "storage volume name", "default": "rf_test_stack_example_volume" } }, "resource": { "opentelekomcloud_vpc_v1": { "rf_doc_vpc": { "name": "${var.vpc_name}", "cidr": "192.168.0.0/16" } }, "opentelekomcloud_vpc_subnet_v1": { "rf_doc_subnet": { "name": "${var.subnet_name}", "vpc_id": "${opentelekomcloud_vpc_v1.rf_doc_vpc.id}", "cidr": "192.168.1.0/24", "gateway_ip": "192.168.1.1" } }, "opentelekomcloud_compute_keypair_v2": { "rf_doc_keypair": { "name": "${var.compute_keypair_name}" } }, "opentelekomcloud_compute_instance_v2": { "rf_doc_ecs": { "name": "${var.ecs_name}", "flavor_id": "s2.large.1", "image_id": "bf0f71bd-f08a-4cd0-9594-ca2caa00b9d7", "availability_zone": "eu-de-01", "key_pair": "${opentelekomcloud_compute_keypair_v2.rf_doc_keypair.name}", "security_groups": ["default"], "network": { "uuid": "${opentelekomcloud_vpc_subnet_v1.rf_doc_subnet.id}" } } }, "opentelekomcloud_blockstorage_volume_v2": { "rf_doc_volume": { "name": "${var.storage_volume_name}", "size": 4, "availability_zone": "eu-de-01" } }, "opentelekomcloud_compute_volume_attach_v2": { "rf_doc_volume_attach": { "instance_id": "${opentelekomcloud_compute_instance_v2.rf_doc_ecs.id}", "volume_id": "${opentelekomcloud_blockstorage_volume_v2.rf_doc_volume.id}" } } }, "output": { "ecs_address": { "value": "${opentelekomcloud_compute_instance_v2.rf_doc_ecs.access_ip_v4}", "description": "The ecs private address." }, "ecs_id": { "value": "${opentelekomcloud_compute_instance_v2.rf_doc_ecs.id}", "description": "The ecs resource id." } } }
Caution
The sample template contains charged resources. Check whether resources need to be enabled before using the template.
The template consists of eight parts:
opentelekomcloud_vpc_v1 in resource indicates VPC information.
opentelekomcloud_vpc_subnet_v1 in resource indicates information about a subnet defined in the VPC.
opentelekomcloud_compute_keypair_v2 in resource indicates information about compute keypair defined in the template.
opentelekomcloud_compute_instance_v2 in resource indicates information about an ECS defined in the template.
opentelekomcloud_blockstorage_volume_v2 in resource indicates information about an EVS storage volume defined in the template.
opentelekomcloud_compute_volume_attach_v2 in resource indicates the binding relationship between EVS storage volume and ECS.
variable indicates variables defined by users in templates during stack creation and deployment.
output defines the outputs of templates. After a stack is created, its output is generated based on the definition and displayed on the Outputs tab page.
For detailed usage of other resources, please refer to OpenTelekom Cloud Provider.
Configure parameters
On the parameter configuration page, you can modify the stack name and description and configure the template parameters.
Caution
The stack name must start with a letter and can contain a maximum of 128 characters, including letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-). The name must be unique.
A stack description can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
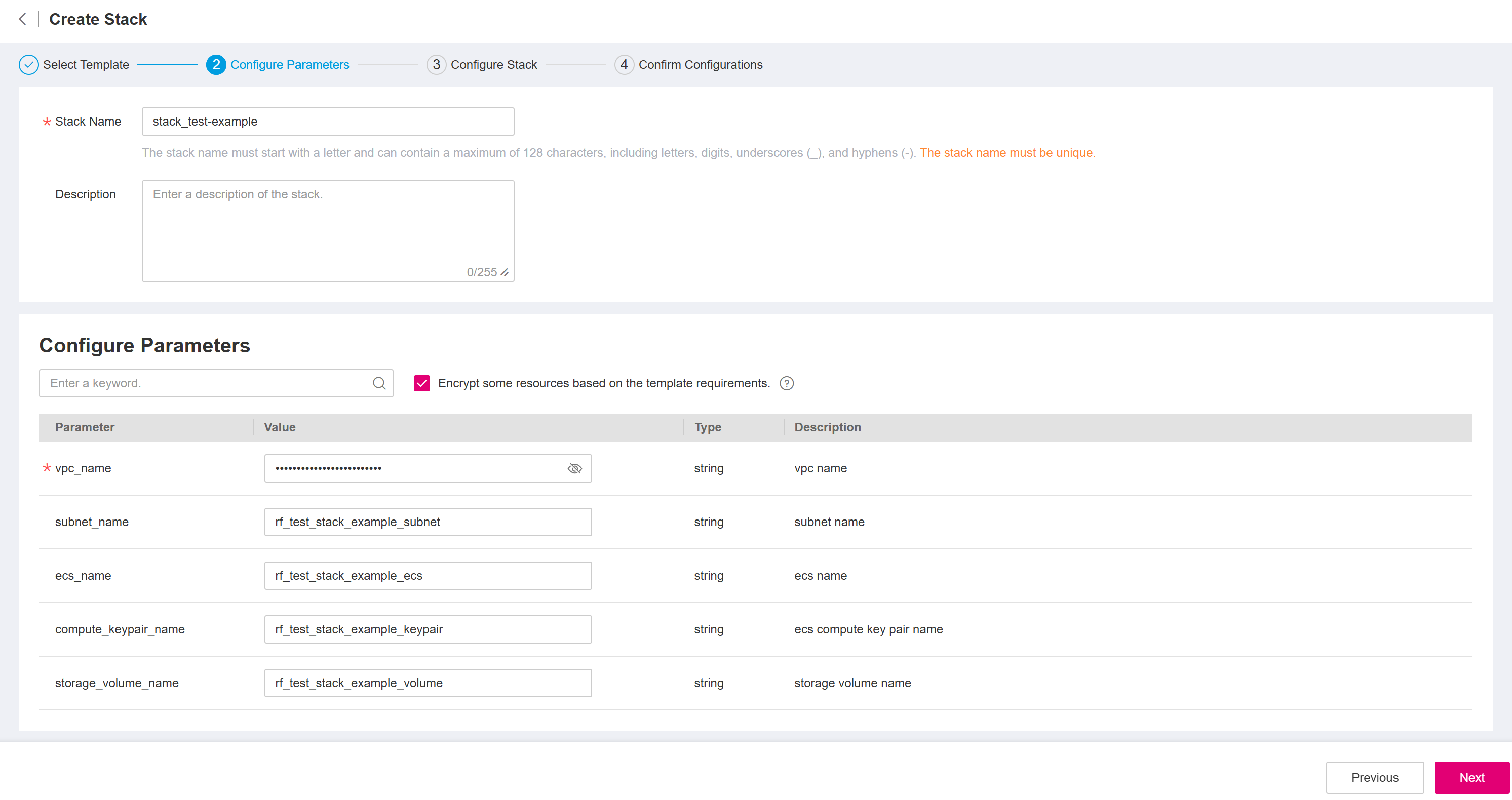
Figure 6 Configuring parameters¶
Parameters whose nullable field is set to false in template are marked with a red asterisk (
*) as mandatory. Valid values must be set to these parameters.If there are variables whose sensitive field is set to true in template, KMS encryption can be selected, as shown in Figure Encrypt requirements. If encryption is enabled, RFS will use KMS to encrypt those senstitive parameters to ensure their secure transmission and storage.
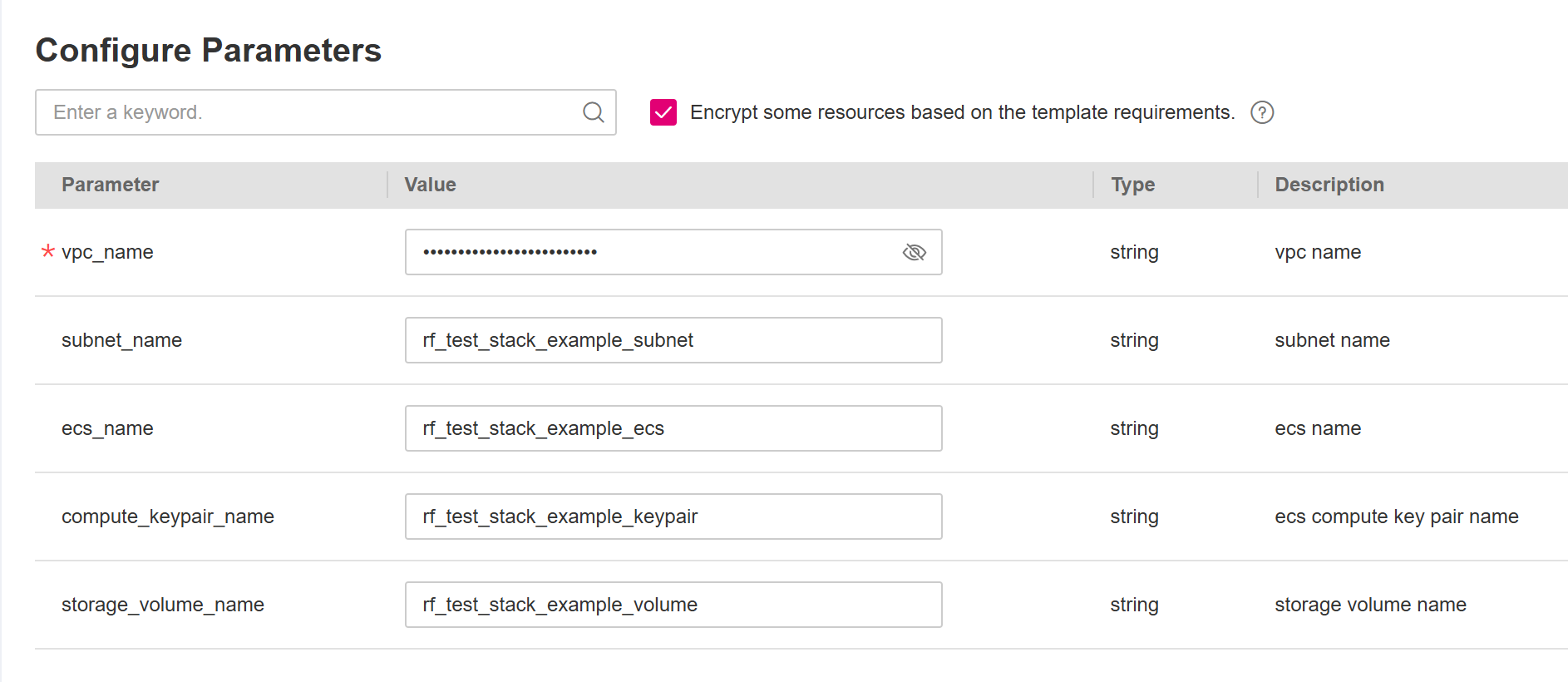
Figure 7 Encrypt requirements¶
If a value is invalid, the corresponding text box will turn red (as shown in Figure 8) and page redirection will not be triggered after you click Next.
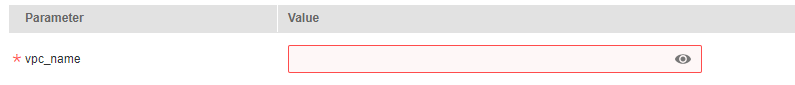
Figure 8 Text box with an invalid value¶
Check whether the default VPC, subnet, and ECS names used on this page already exist on the corresponding consoles. If the names already exist, change them to unique ones to prevent creation failures.
Then click Next and the Configure Stack page is displayed.
Configure the stack.
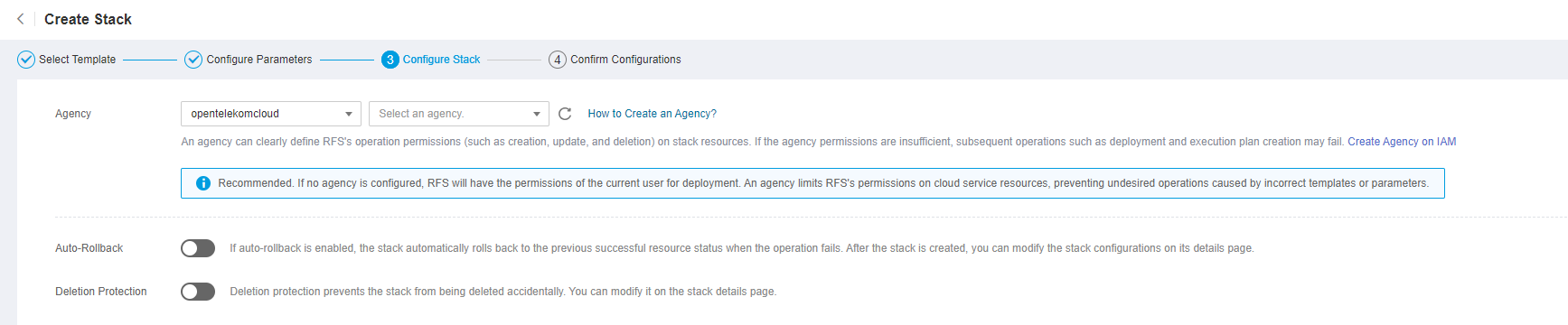
Figure 9 Configuring the stack¶
IAM Agency (Optional): An agency can clearly define operation permissions of RFS (such as creation, update, and deletion) on stack resources. If the agency permissions are insufficient, subsequent operations may fail. For more details of how to create agency, see create an agency.
Deletion Protection: prevents the stack from being deleted accidentally. After a stack is created, You can modify it on the stack details page.
Auto-Rollback: If auto-rollback is enabled, the stack automatically rolls back to the previous successful resource status when an operation fails.
After the stack is created, you can modify the stack configurations on its details page, see Modifying the basic parameters of a Stack.
Click Next to go to the Confirm Configurations page.
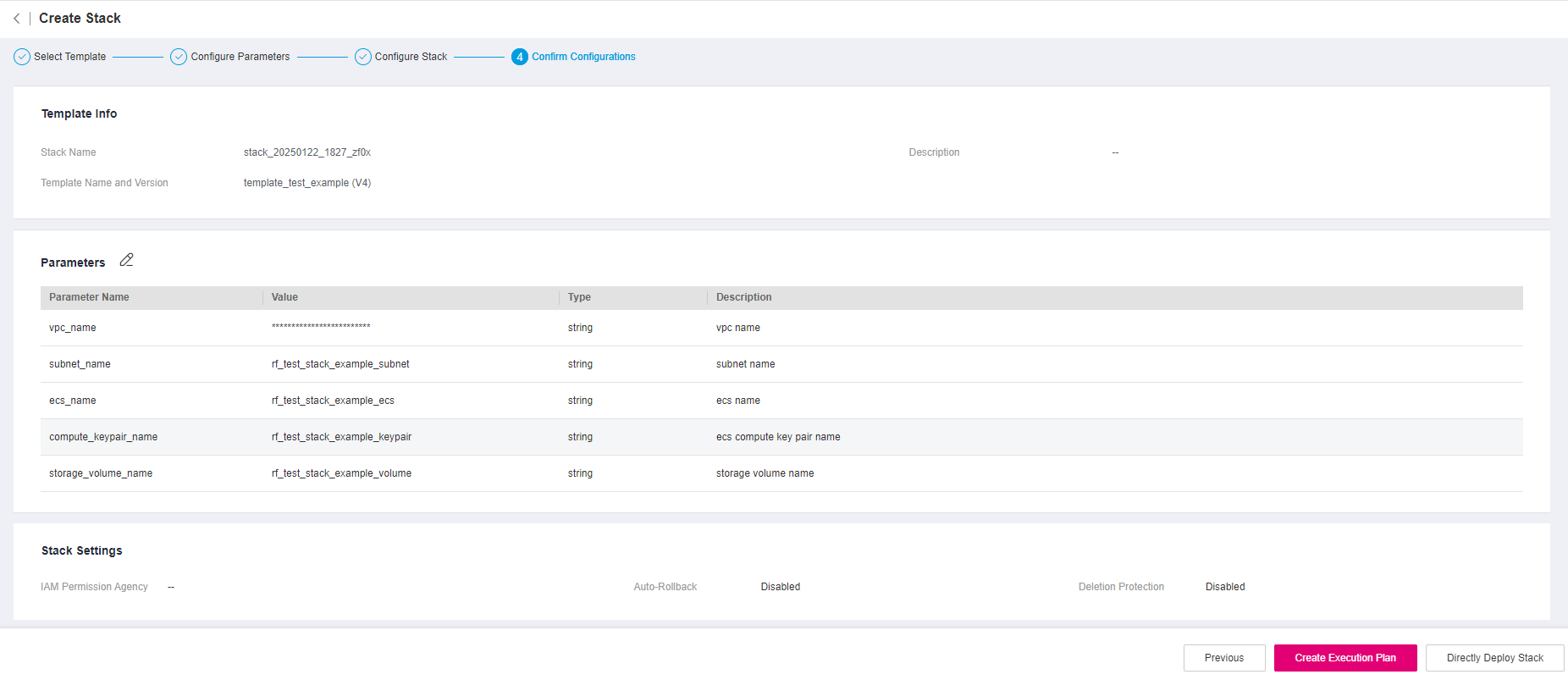
Figure 10 Confirm Configurations¶
Check the configuration and make sure everything is set correctly.
After you confirm the configurations, you can click either Create Execution Plan or Directly Deploy Stack.
If you click Directly Deploy Stack, a confirmation dialog box will be displayed.

Figure 11 Directly deploy stack¶
Click Yes. A new stack is generated and its status is Deployment In Progress, as shown in Figure 12. And it will redirect to the stack events page, as shown in Figure Stack Events.
Figure 12 Deployment in progress
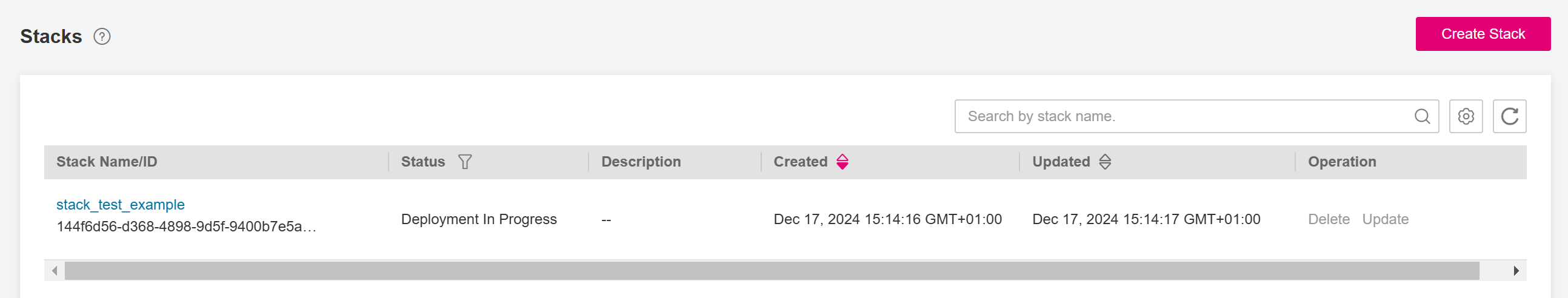
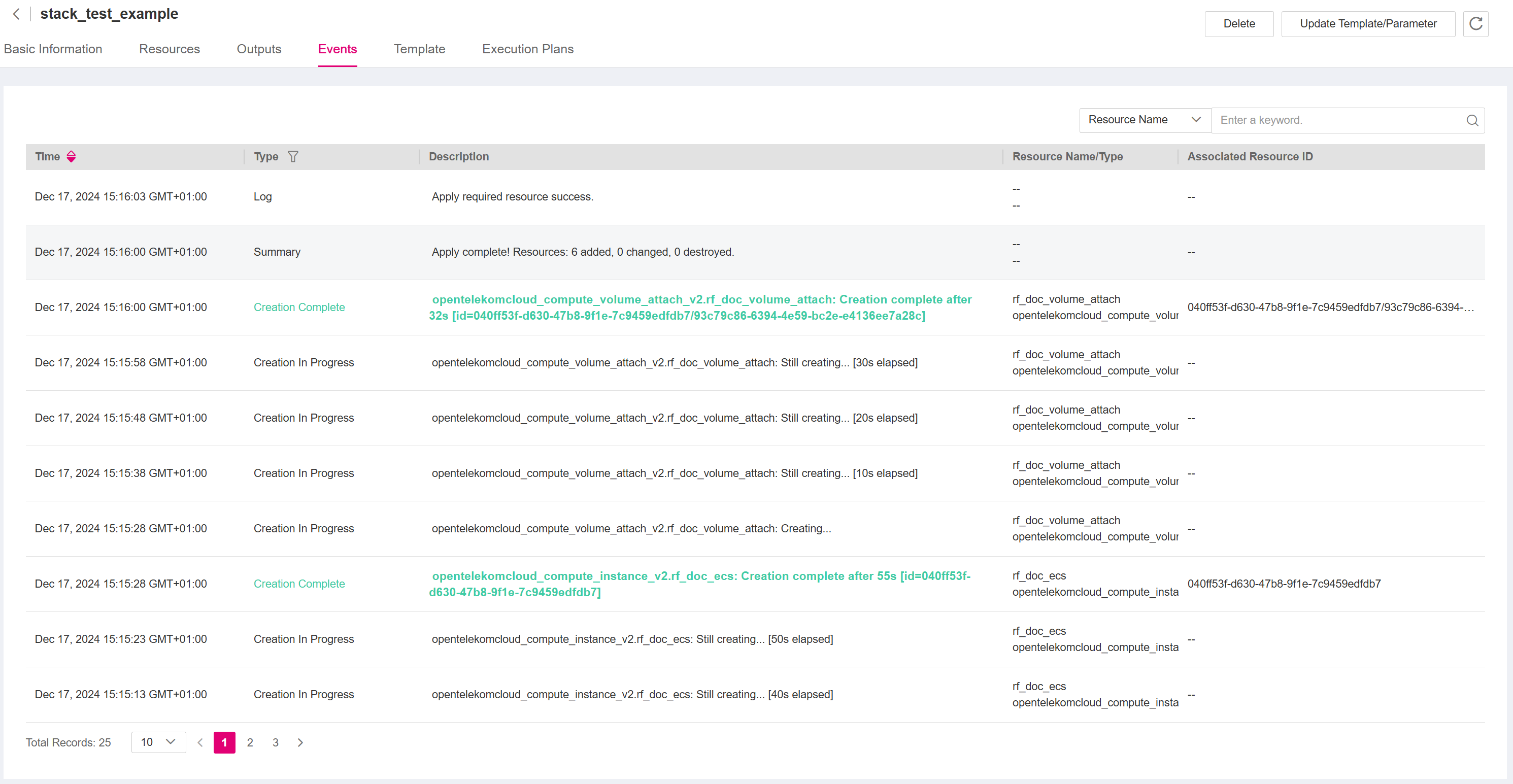
Figure 13 Stack Events¶
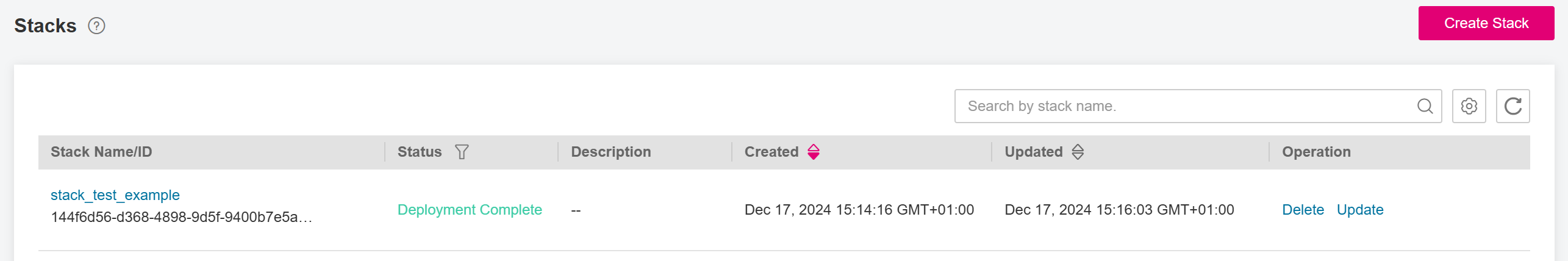
If everything goes well, the status will change to Deployment Complete, as shown in Figure Deployment complete.
Figure 14 Deployment complete
If you click Create Execution Plan, a dialog box of creating execution plan will be displayed. In this dialog box, you can set the name and description of the execution plan.
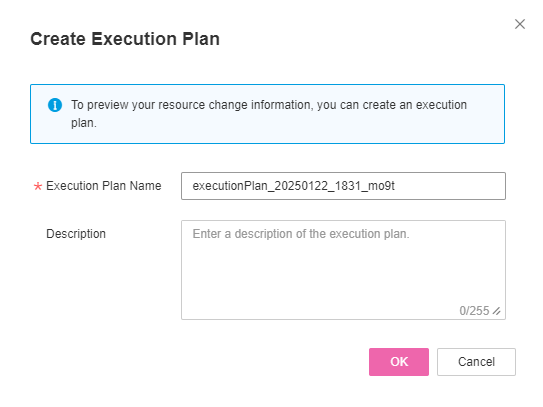
Figure 15 Create Execution Plan dialog box¶
Caution
The execution plan name must start with a letter and can contain a maximum of 128 characters, including only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
Click OK. The Execution Plans tab page is displayed.
Wait until the execution plan is created and refresh the page. The execution plan status will change to Available, as shown in Figure Execution Plan Available.
Figure 16 Execution Plan Available
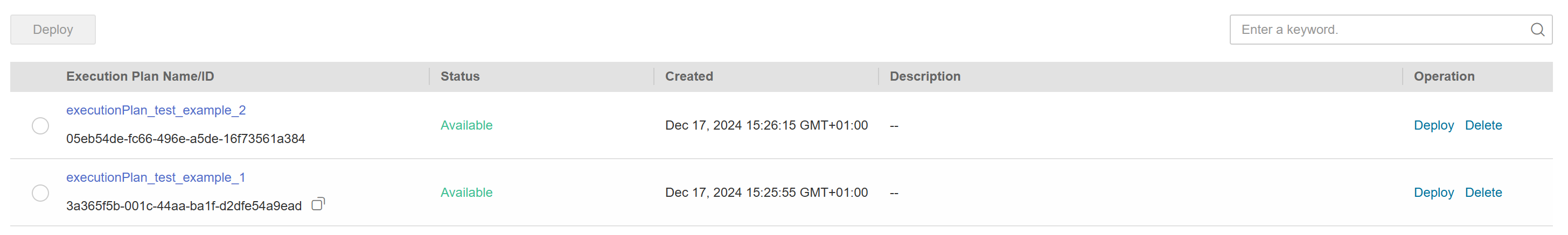
Return to the stack list page. A stack is generated and its stack status is Creation Complete, as shown in Figure 17.
Figure 17 Stack list

Caution
Creating an execution plan can preview the resource attribute changes of the entire stack and evaluate the impact. If the execution plan meets your expectations, you can execute the plan. Creating an execution plan does not incur fees. The system changes your stack only when you execute the plan.
Go back to the Execution Plans tab page of the stack and click Deploy in the Operation column of the execution plan to deploy it, as shown in Figure 18.
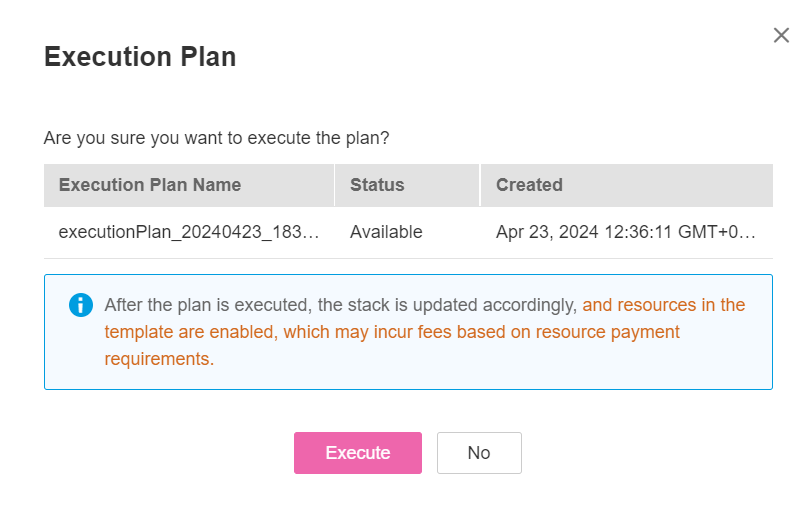
Figure 18 Execution plan dialog box¶
In the Execution Plan dialog box, click Execute. A message indicating that the execution plan is being deployed is displayed in the upper right corner. Return to the stack list page. The stack status is Deployment In Progress, as shown in Figure Deployment in progress.
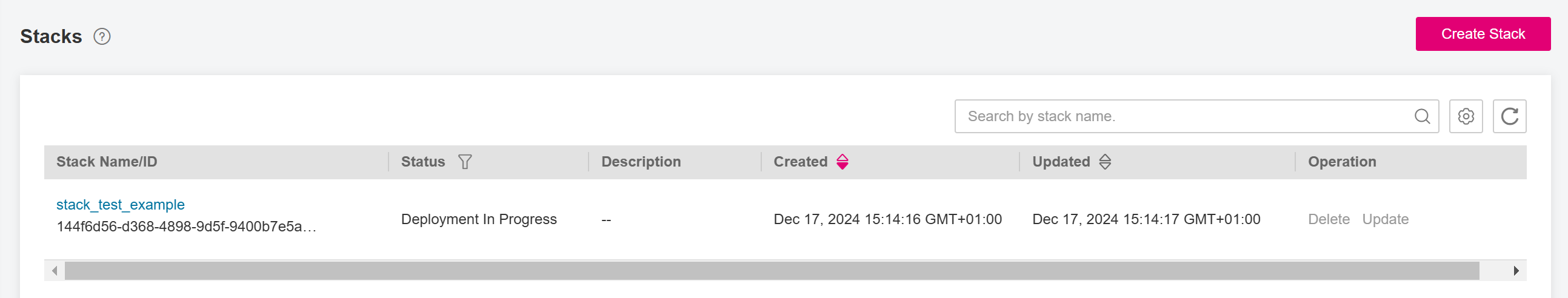
Figure 19 Deployment in progress¶
Then, the stack status changes to Deployment Complete, as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20 Deployment complete
On the Execution Plans tab page of the stack details page, the execution plan status is Applied, as shown in Figure 21.

Figure 21 Applied¶
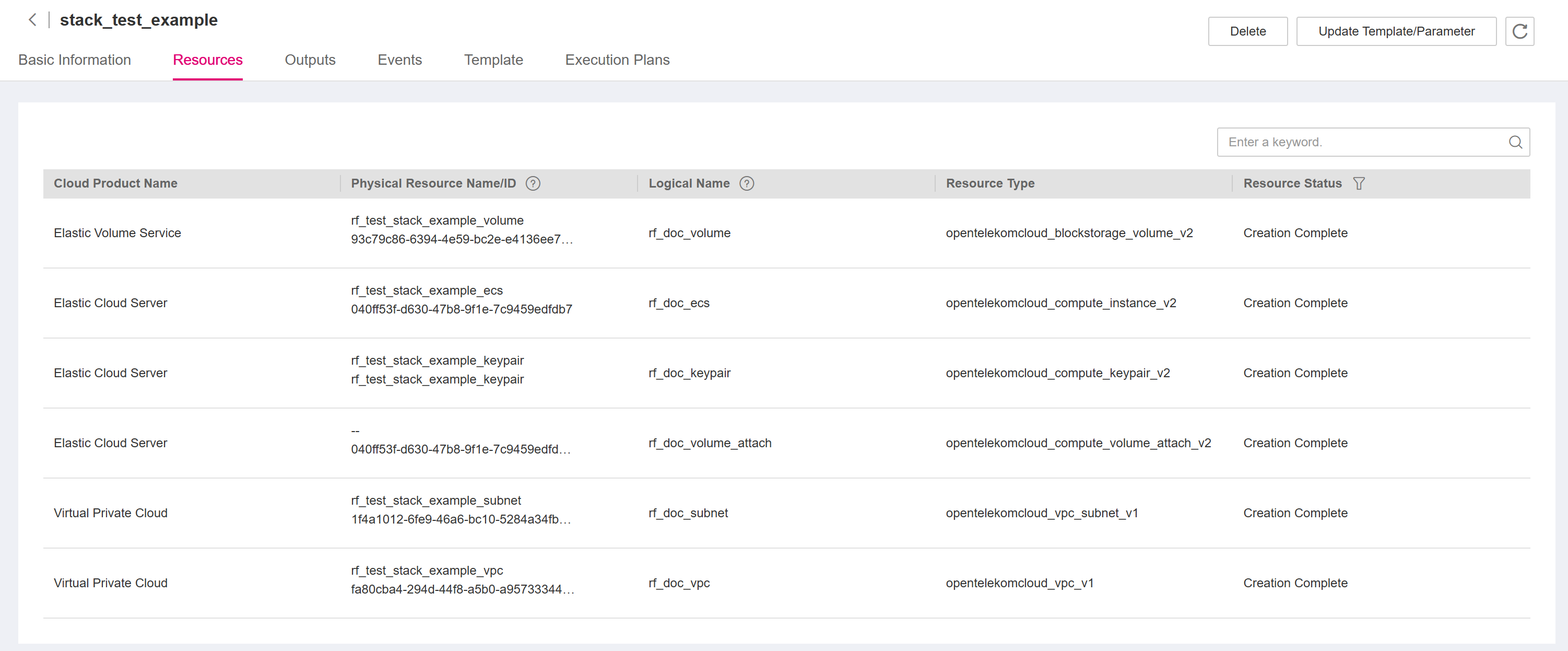
Click the Resources tab. The resource list shows that resources of the stack are deployed, as shown in Figure 22.
Figure 22 Resources deployed
You can view additional details on the console of the corresponding cloud service. (Figure ECS shows the deployed resources on the ECS console for the above example).
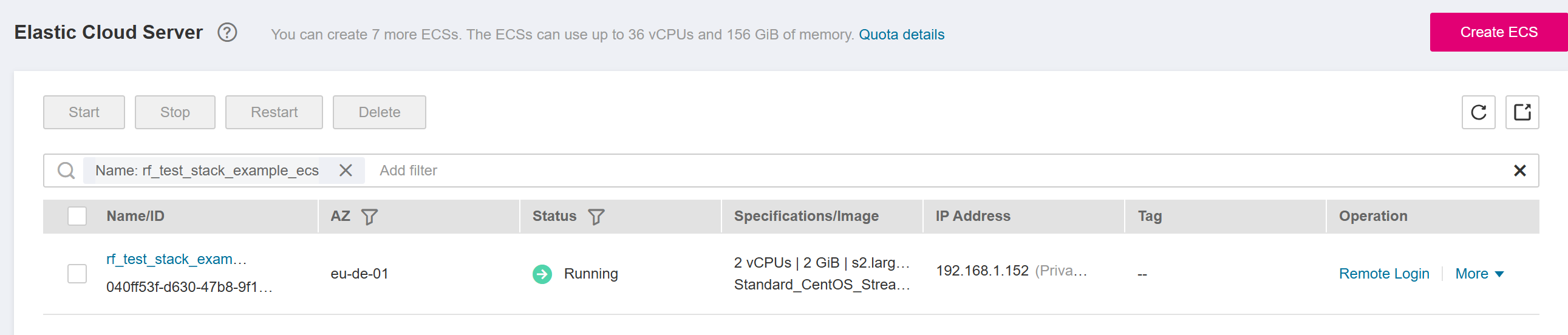
Figure 23 ECS¶