How to define a ConnectsTo relationship between service catalogs¶
This example shows how to define a relationship for NodeA (a SOURCE node) to connect to NodeB (a TARGET node) as in Figure 1.
We will define
capabilitieson the NodeB containing all information for NodeA to setup a connection.We will define the
relationshipinterfaces to setup the connection.
Steps¶
Step 1. Define an endpoint capability in the TARGET node (NodeB)¶
An endpoint capability contains information of a TARGET node for a SOURCE node to setup the connection.
In NodeB, we define the following capabilities block:
node_types:
otc.nodes.SoftwareComponent.NodeB:
...
capabilities:
db_endpoint:
type: tosca.capabilities.Endpoint.Database
In this example, we defined a new capability db_endpoint from the TOSCA type tosca.capabilities.Endpoint.Database. The capability db_endpoint will inherit all default properties from the TOSCA type (e.g., port, protocol, url_path).
In the designer, users can specifiy values for the capability db_endpoint. For example, they may set the port to 27017.
Tip
The tosca.capabilities.Endpoint also has a runtime attribute ip_address. The orchestrator will automatically set the IP address of the hosted compute node to this attribute. A SOURCE node can use this runtime attribute to setup a connection.
Step 2. Define a requirement in the SOURCE node (NodeA)¶
In the NodeA node, add the following requirements block:
node_types:
otc.nodes.NodeA:
derived_from: tosca.nodes.WebApplication
...
requirements:
- db_endpoint:
# NodeA requires a node that has the capability Endpoint.Database
capability: tosca.capabilities.Endpoint.Database
# NodeA uses this relationship to setup the connection (see step 3)
relationship: otc.relationships.NodeAConnectToNodeB
# (Optional) specifiy relationship instance one-to-one
# it means, one NodeA has one NodeB
occurrences: [1, 1]
Step 3: Define the relationship¶
Define a new relationship otc.relationships.NodeAConnectToNodeB, how NodeA setups the connection with NodeB:
relationship_types:
otc.relationships.NodeAConnectToNodeB:
derived_from: tosca.relationships.ConnectsTo
interfaces:
Configure:
pre_configure_source:
inputs:
# The input NODEA_PORT gets the port property of NodeA
NODEA_PORT: { get_property: [SOURCE, port] }
# The input NODEB_PORT gets the port property of NodeB
NODEB_PORT: { get_property: [TARGET, port] }
# The input NODEB_IP gets the runtime attribute ip_address of NodeB
NODEB_IP: { get_attribute: [TARGET, db_endpoint, ip_address] }
implementation: scripts/setup-connection.sh
In the above example, we defined the interface pre_configure_source by providing a shell script (e.g., setup-connection.sh). The script uses the input parameters NODEA_PORT, NODEB_PORT, and NODEB_IP to configure NodeA to connect to NodeB.
Note
Use the function
get_propertyto get a SOURCE or TARGET node property.Use the function
get_attributeto get a runtime attribute of a SOURCE or TARGET node (e.g., ip_address).
2. Relationship interfaces¶
In addition to the interface pre_configure_source, we have the following interfaces
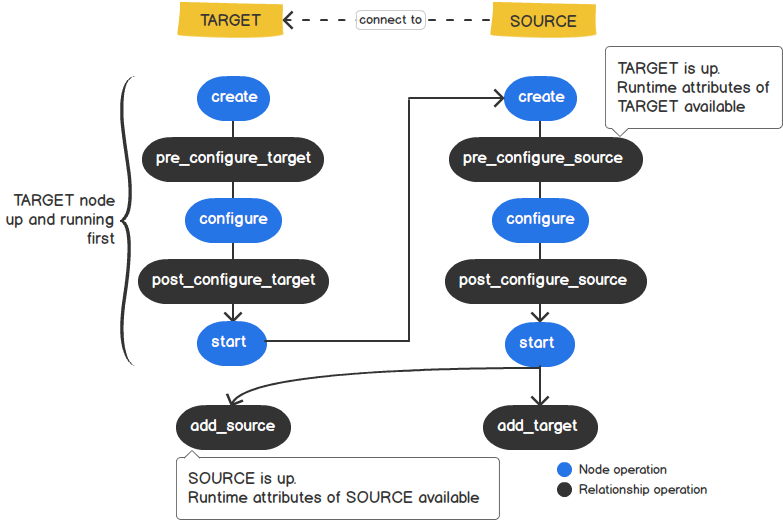
Figure 2. Relationship lifecycle¶
2.1. Interfaces executed on the TARGET node¶
pre_configure_target: executes after theTARGETnode is created.post_configure_target: executes after theTARGETnode is configured.add_source: executes onTARGETnode, notifying that theSOURCEnode is up and running.
2.2. Interfaces executed on the SOURCE node¶
pre_configure_sourceexecutes after theSOURCEnode is created.post_configure_source: executes after theSOURCEnode is configured.add_target: executes after theSOURCEnode is started.remove_target: executes after theTARGETnode is removed.
Note
The
TARGETnode is always up and running first before theSOURCEnode.All runtime attributes of the
SOURCEnode are not available until it is up and running (i.e., they are available in theadd_sourceinterface). Therefore, to configure theTARGETnode with any runtime attributes of theSOURCEnode, you can use theadd_sourceinterface.
3. Links¶
See full example.