What Is WAF?¶
Web Application Firewall (WAF) keeps web services stable and secure. It examines all HTTP and HTTPS requests to detect and block the following attacks: Structured Query Language (SQL) injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), web shells, command and code injections, file inclusion, sensitive file access, third-party vulnerability exploits, Challenge Collapsar (CC) attacks, malicious crawlers, and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
After you enable a WAF instance,you still need to add your website domain to the WAF instance on the WAF console. All public network traffic for your website then goes to WAF first. WAF identifies and filters out the illegitimate traffic, and routes only the legitimate traffic to your origin server to ensure site security.
How WAF Works (Dedicated Mode)¶
After applying for WAF, add the website to WAF on the WAF console. After a website is connected to WAF, all website access requests are forwarded to WAF first. WAF detects and filters out malicious attack traffic, and returns normal traffic to the origin server to ensure that the origin server is secure, stable, and available.
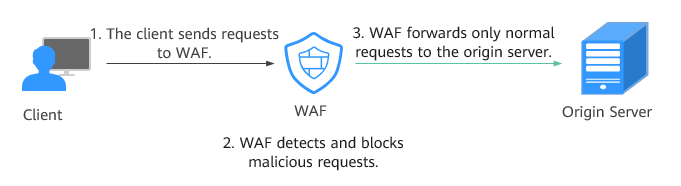
Figure 1 How WAF Works¶
The process of forwarding traffic from WAF to origin servers is called back-to-source. WAF uses back-to-source IP addresses to send client requests to the origin server. When a website is connected to WAF, the destination IP addresses to the client are the IP addresses of WAF, so that the origin server IP address is invisible to the client.
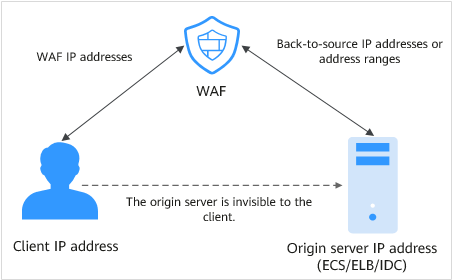
Figure 2 Back-to-source IP address¶
How WAF Works (ELB Access Mode)¶
If you connect a website to WAFELB access mode, WAF works as follows:
In this mode, WAF is integrated into the gateway of an ELB load balancer through an SDK module. WAF extracts traffic through the SDK module embedded in the gateway for inspection.
WAF synchronizes the inspection result to the load balancer, and the load balancer determines whether to forward client requests to the origin server based on the inspection result.
In this method, WAF does not forward traffic. This reduces compatibility and stability problems.
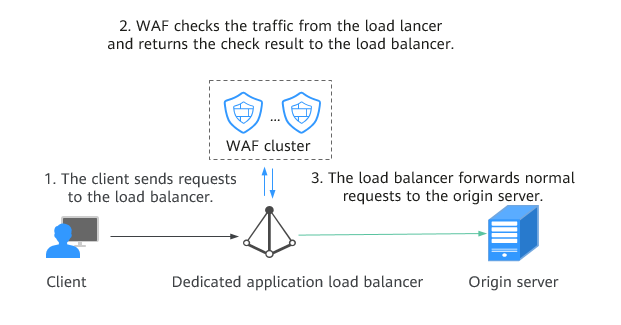
Figure 3 How WAF in ELB load balancer access mode works¶
What WAF Protects¶
Objects WAF can protect: domain names or IP addresses of web applications on the cloud