Querying and Accessing a VPC Endpoint¶
Scenarios¶
After a VPC endpoint is created, you can query its details and access it.
Constraints¶
One VPC endpoint supports up to 3,000 concurrent connections.
Querying a VPC Endpoint¶
You can query details of a VPC endpoint, including its ID, VPC, VPC endpoint service name, creation time, private domain name, status, type, IPv4 address, access control, and description.
Log in to the management console.
Click
 in the upper left corner and select the required region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the required region and project.
Click Service List and choose Networking > VPC Endpoint.
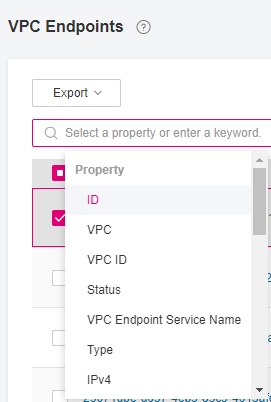
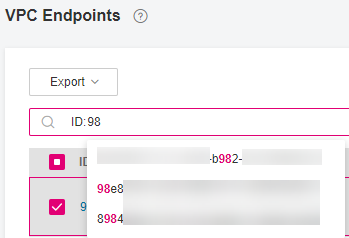
On the displayed page, locate the VPC endpoint by entering a keyword in the upper search box:
Search for a VPC endpoint by parameters including ID, VPC, VPC ID, Status, VPC Endpoint Service Name, Type, IPv4, Created, or Description. Take ID or VPC Endpoint Service Name as an example.
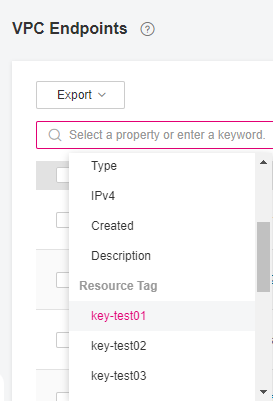
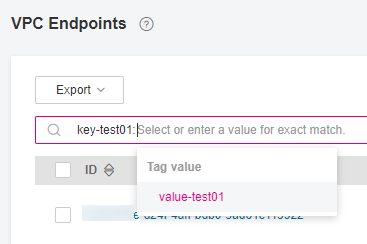
Search by tag.
In the VPC endpoint list, click the ID of the VPC endpoint to view its details.
After an interface VPC endpoint is created, an IPv4 address is assigned together with a private domain name if you select Create a Private Domain Name.
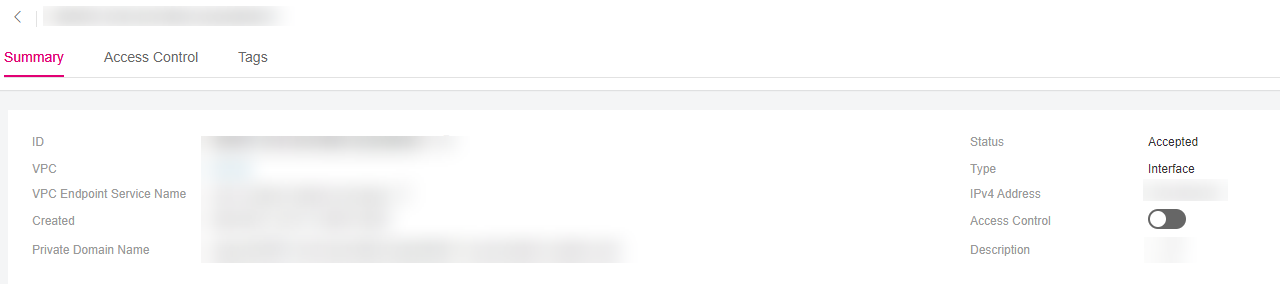
Figure 5 Summary of the VPC endpoint (for accessing an interface VPC endpoint service)¶
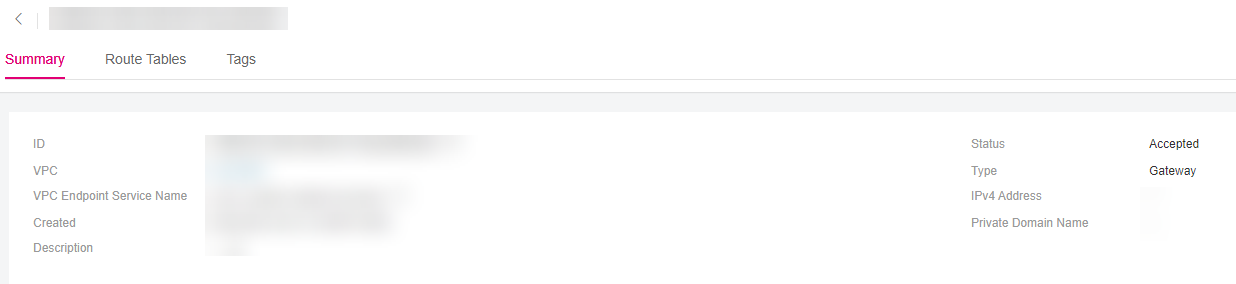
Figure 6 Summary of the VPC endpoint (for accessing a gateway VPC endpoint service)¶
Table 1 Parameters contained in the details of a VPC endpoint¶ Tab
Parameter
Description
Summary
ID
Specifies the ID of the VPC endpoint.
Summary
VPC
Specifies the VPC where the VPC endpoint is deployed.
Summary
VPC Endpoint Service Name
Specifies the name of the VPC endpoint service that the VPC endpoint is used to access.
Summary
IPv4 Address
Specifies the IPv4 address of the VPC endpoint.
Summary
Private Domain Name
Specifies the private domain name for accessing the VPC endpoint.
Summary
Status
Specifies the status of the VPC endpoint.
Summary
Type
Specifies the type of the VPC endpoint service that the VPC endpoint is used to access.
Summary
Created
Specifies the creation time of the VPC endpoint.
Summary
Access Control
Specifies whether the whitelist is enabled for IP addresses to access this VPC endpoint.
If Access Control is enabled, only IP addresses or CIDR blocks in the whitelist are allowed to access the VPC endpoint.
If Access Control is disabled, any IP address or CIDR block can access the VPC endpoint.
Note
Access control can be enabled only for VPC endpoints for connecting to an interface VPC endpoint service.
Summary
Description
Provides supplementary information about the VPC endpoint.
Access Control
IP Address or CIDR Block
Specifies the IP addresses and CIDR blocks that are allowed to access the VPC endpoint.
Access Control
Operation
Specifies the operation to be performed on whitelist records of the VPC endpoint. Only deletion is supported.
Route Tables
Name/ID
Specifies the name or ID of the route table.
Route Tables
VPC
Specifies the VPC that the route table belongs to.
Route Tables
Type
Specifies the type of the route table, which can be Default and Custom.
Route Tables
Associated Subnets
Specifies the number of subnets associated with the route table.
Route Tables
Operation
Specifies the operation to be performed on the route table. The operation can be Disassociate or Associate.
Tags
Key
Specifies the tag key of the VPC endpoint.
Tags
Value
Specifies the tag value of the VPC endpoint.
Tags
Operation
Specifies the operation to be performed on the VPC endpoint tag. You can click Edit or Delete.
Note
The Access Control tab is displayed only for VPC endpoints for connecting to interface VPC endpoint services.
The Route Tables tab is displayed only for VPC endpoints for connecting to gateway VPC endpoint services.
Accessing a VPC Endpoint via Its Private IP Address¶
Perform the following operations to access a VPC endpoint via its private IP address:
In the VPC where the VPC endpoint is deployed, log in to the backend resource, for example, an ECS.
Select a command based on the backend resource type and run the command to access the VPC endpoint. The command format is as follows:
Command Private IP address:Port number
The following is a command example:
curl Private IP address:Port number
Accessing a VPC Endpoint (via Its Private Domain Name)¶
You can access a VPC endpoint via its private domain name if you select Create a Private Domain Name when creating the VPC endpoint.
The system automatically creates a private zone for the generated domain name and adds an A record set for the private zone to resolve the domain name into the private IP address of the VPC endpoint.
You can view the corresponding private zone and its resolution records on the DNS console. For more information, see Configuring a Private Zone.
Viewing the record set of the private domain name
Log in to the management console.
In the service list, choose Network > Domain Name Service.
The DNS console is displayed.
In the navigation pane, choose Private Zones.
The Private Zones page is displayed.
In the private zone list, click the name of the private zone.
The Record Sets page is displayed.
In the record set list, locate the A record set and view its information.
When Status changes to Normal, the resolution takes effect.

Figure 7 Record set of the private domain name¶
Accessing a VPC endpoint via its private domain name
In the VPC where the VPC endpoint is deployed, log in to the backend resource, for example, an ECS.
Select a command based on the backend resource type and run the command to access the VPC endpoint. The command format is as follows:
Command Private domain name:Port number
The following is a command example:
curl Private domain name:Port number