Mounting a File System Times Out¶
Symptom¶
When a file system is mounted to servers using the mount command, message timed out is displayed.
Possible Causes¶
Cause 1: The network status is not stable.
Cause 2: The network connection is abnormal.
Cause 3: The DNS configuration of the server is incorrect. As a result, the domain name of the file system cannot be resolved, and the mounting fails. This issue will not occur on SFS Turbo file systems.
Cause 4: The server that mounts the file system runs Ubuntu18 or later.
Fault Diagnosis¶
After the network fault is excluded, run the mount command again.
Solution¶
Cause 1 and Cause 2: The network status is not stable or the network connection is abnormal.
Re-mount the file system after the network issue is addressed.
If the patch is uninstalled successfully, no further action is required.
If the problem persists, see the solution for cause 3.
Cause 3: The DNS configuration of the server is incorrect. As a result, the domain name of the file system cannot be resolved, and the mounting fails.
Check the DNS configuration of the tenant and run the cat /etc/resolv.conf command.
If the DNS has not been configured, configure it. For details about how to configure the DNS, see Configuring DNS.
If the DNS has been configured, run the following command to check whether the DNS is correct:
nslookup File system domain name
If the resolved IP address is in network segment 100, the DNS configuration is correct. If the IP address is in another network segment, the DNS configuration is incorrect. In this case, go to 2.
Modify the /etc/resolv.conf configuration file, configure the correct tenant DNS, and run vi /etc/resolv.conf to edit the /etc/resolv.conf file. Add the DNS server IP address above the existing nameserver information. The DNS server IP address is 100.125.4.25.
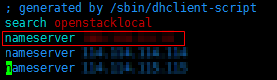
Figure 1 Configuring DNS¶
The format is as follows:
nameserver 100.125.4.25
If the configuration succeeds, go to 3.
If the configuration fails, run the lsattr /etc/resolv.conf command. If the information shown in Figure 2 is displayed, the file is locked.

Figure 2 A locked file¶
Run the chattr -i/etc/resolv.conf command to unlock the file. Then, re-configure the DNS and go to 3.
Press Esc, input :wq, and press Enter to save the changes and exit the vi editor.
The default DNS of the ECS applied by the user is inherited from the VPC to which the ECS belongs. Therefore, when the ECS restarts, the ECS changes synchronously. For this reason, changing configurations of the ECS does not settle the issue completely. You need to modify configurations in the VPC. Set a correct tenant DNS for the subnet of the VPC to which the ECS belongs. See Figure 3 and Figure 4.
Figure 3 VPC details¶
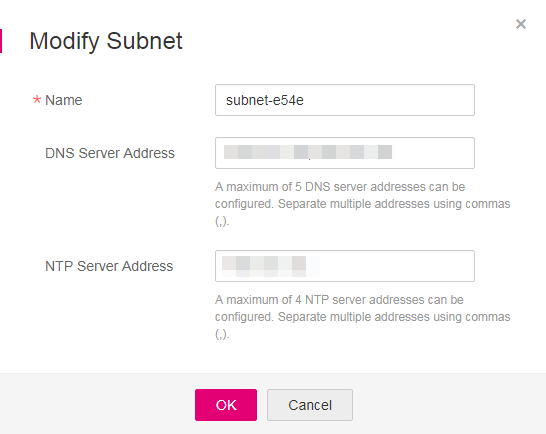
Figure 4 Modifying the DNS¶
(Optional) Restart the server.
Run the mount command again.
If the problem is solved, no further action is required.
If the problem persists, see the solution for cause 4.
Cause 4: The server that mounts the file system runs Ubuntu18 or later.
Reconfigure DNS by referring to Configuring DNS.
Check whether the target server running Ubuntu18 or later uses a private image.
Convert the public image server to a private image server.
To create a private image based on an existing ECS, see section "Creating an Image" in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
Use the private image created in 3.a to create an ECS or change the ECS OS. For details, see section "Changing the OS" in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
Log in to the server and mount the file system again.