Features¶
Private Image Lifecycle¶
After you create a private image, you can use it to create cloud servers or EVS disks. You can also share the image with other tenants. Figure 1 shows the lifecycle of a private image.
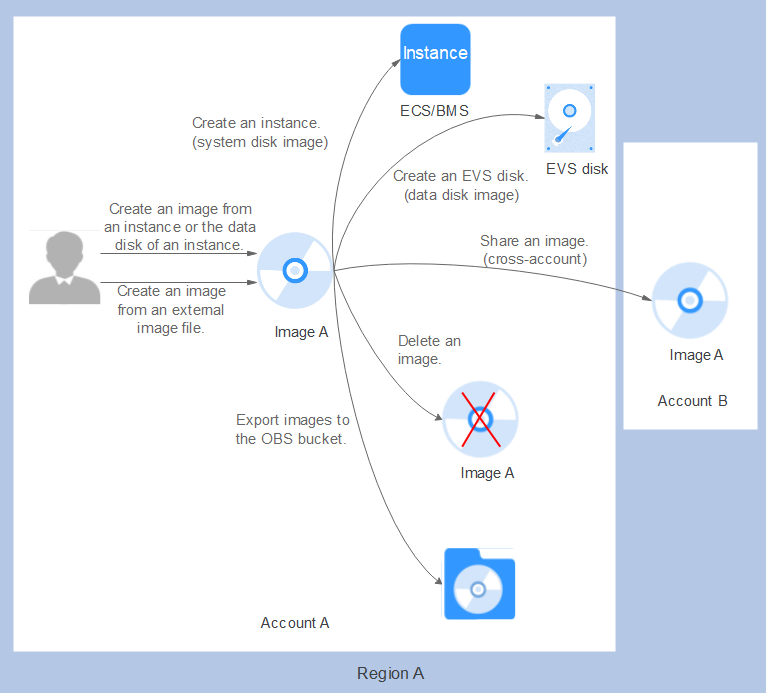
Figure 1 Private Image Lifecycle¶
Features¶
Feature | Description | Helpful Link |
|---|---|---|
Creating a system disk image from an ECS or BMS | After creating a cloud server, you can set it up, installing whatever software or application environment you need, and then use the preconfigured server to create a system disk image. You can create new cloud servers with the custom configurations from the image, which frees you from a lot of repetitive work. | |
Creating a system disk image from an external image file | You can import a system disk from your local PC or other cloud platforms, and use the imported image to create new cloud servers or reinstall or change the OSs of existing cloud servers. | |
Creating a system disk image from an ISO file | In contrast with other image formats, an ISO file can be used only after it is decompressed using a tool, such as UltraISO or VirtualBox. For details about the image creation process, see the Helpful Link column in the table. | |
Creating a data disk image from an ECS | A data disk image only contains user data. You can create a data disk image from an ECS and then use the image to create new EVS disks. This is a convenient way to migrate data from an ECS to EVS disks. | |
Creating a data disk image from an external image file | You can import the data disk image of a local server or a server on another cloud platform to and then the image can be used to create EVS disks. | |
Creating a full-ECS image from an ECS, a CSBS backup, or a CBR backup | You can use an ECS with data disks to create a full-ECS image, complete with an OS, various applications, and your service data. The full-ECS image then can be used to quickly provision identical ECSs for data migration. A full-ECS image can be created from an ECS, a CSBS backup, or a CBR backup. | |
Creating an ECS from a private image | After a system disk image or full-ECS image is created, you can click Apply for Server in the row that contains the image to create an ECS. |
Feature | Description | Helpful Link |
|---|---|---|
Modifying an image | You can modify the following attributes of an image: name, description, minimum memory, maximum memory, and advanced functions such as NIC multi-queue and SR-IOV driver. | |
Sharing images | You can share an image with other accounts. These accounts can use your shared private image to quickly create ECSs or EVS disks. | |
Exporting images | You can export private images to your OBS bucket and download them to your local PC for backup. | |
Encrypting images | You can create encrypted images to improve data security. KMS envelope encryption is used. Encrypted images can be created from external image files or encrypted ECSs. | |
Replicating images | By replicating images, you can convert encrypted and unencrypted images into each other or enable some advanced features, for example, fast instance provisioning. | |
Tagging an image | You can tag your private images for easy management and search. | |
Exporting image list | You can export the public or private image list in a given region as a CSV file for local maintenance and query. | |
Deleting images | You can delete images that will be no longer used. Deleting an image does not affect the ECSs created from that image. |