What Is EVS?¶
Overview¶
Elastic Volume Service (EVS) offers scalable block storage for cloud servers. EVS disks provide high reliability, high performance, and come with a variety of disk types. They can be used for distributed file systems, development and test environments, data warehouses, and high-performance computing (HPC) applications. Cloud servers that EVS supports include Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs) and Bare Metal Servers (BMSs).
Just like the physical disks in local PC need to be installed before they can be used, EVS disks need to be attached to servers before they can be used. They cannot be used alone. You also need to partition and create file systems on them before they can be used for persistent data storage.
In this document, EVS disks are sometimes just referred to as "disks".
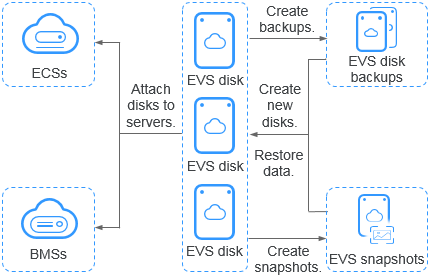
Figure 1 EVS architecture¶
EVS Advantages¶
EVS has the following advantages.
Advantage | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
Various disk types | EVS provides a variety of disk types for you to choose from. They can be used as data disks or system disks for cloud servers. You can select whichever disk type that has the specifications best suited to your budget and service requirements. | |
Elastic scalability | The EVS disk capacity ranges from 10 GiB to 32 TiB. You can start with 10 GiB, and if, later on, that no longer meets your needs, you can expand the disk capacity to up to 32 TiB in increments of 1 GiB, without interrupting your applications. | |
In addition to the disk capacity limit, there is an EVS capacity quota. The additional space you add cannot exceed the remaining quota. However, if this happens, you can apply for a higher quota. | ||
High security and reliability | Both system disks and data disks support data encryption to ensure data security. | |
High security and reliability | Data protection functions, such as backups, safeguard the disk data. If your data is ever damaged by a software exception or online attack, you can restore your data from backups. | |
High security and reliability | Data protection functions, such as snapshots, safeguard the disk data. If your data is ever damaged by a software exception or online attack, you can restore your data from snapshots. | |
Real-time monitoring | On Cloud Eye, you can monitor the disk health and operating status at any time. |
Differences Among EVS, SFS, and OBS¶
There are three types of storage available for you to choose from: EVS, Scalable File Service (SFS), and Object Storage Service (OBS). Their differences are described in the following table.
Service | Overall Introduction | Typical Application Scenarios | Storage Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
EVS | EVS provides scalable block storage that features high reliability, high performance, and a variety of specifications for servers. |
| EVS disks start at 10 GiB and can be expanded as required in 1 GiB increments to up to 32 TiB. |
SFS | SFS provides completely hosted shared file storage for cloud servers. Compatible with the Network File System (NFS) protocol, SFS is expandable to pebibyte and seamlessly handles data-intensive and bandwidth-intensive applications. |
| SFS storage capacity is available on demand and can be expanded to a maximum of 2 PiB. |
OBS | OBS provides cloud storage for unstructured data, such as files, pictures, and videos. With multiple options for migration to the cloud, OBS provides low-cost, reliable storage access for massive data and supports online multimedia processing. |
| OBS has limitless storage capacity, and storage resources are available for linear and nearly infinite expansion. |
Access Methods¶
The public cloud system provides a web-based management console and HTTPS-based APIs that you can use to access the EVS service.
APIs
Use APIs if you need to integrate EVS into a third-party system for secondary development. For details, see Elastic Volume Service API Reference.
Management console
Use the management console if you do not need to integrate EVS with a third-party system. Log in to the management console and choose Elastic Volume Service from the service list.
User Permissions¶
Users with resource management permissions can control the operations performed on cloud service resources. For EVS, a user with the Server Administrator permission can perform operations on EVS resources, including creating disks, deleting disks, and creating snapshots.
For details about user permissions, see Permissions.
Project¶
A project is used to group and isolate OpenStack resources, including compute, storage, and network resources. A project can be a department or a project team. You can access IAM with a security administrator to create projects in a region and perform isolated management of resources. For details about projects, see Managing Projects.