Conditional Statements¶
Conditional statements are used to decide whether given conditions are met. Operations are executed based on the decisions made.
GaussDB(DWS) supports five usages of IF:
IF_THEN

Figure 1 IF_THEN::=¶
IF_THEN is the simplest form of IF. If the condition is true, statements are executed. If it is false, they are skipped.
Examples
IF v_user_id <> 0 THEN UPDATE users SET email = v_email WHERE user_id = v_user_id; END IF;
IF_THEN_ELSE
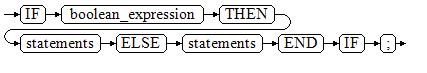
Figure 2 IF_THEN_ELSE::=¶
IF-THEN-ELSE statements add ELSE branches and can be executed if the condition is false.
Examples
IF parentid IS NULL OR parentid = '' THEN RETURN; ELSE hp_true_filename(parentid); -- Call the stored procedure. END IF;
IF_THEN_ELSE IF
IF statements can be nested in the following way:
IF gender = 'm' THEN pretty_gender := 'man'; ELSE IF gender = 'f' THEN pretty_gender := 'woman'; END IF; END IF;
Actually, this is a way of an IF statement nesting in the ELSE part of another IF statement. Therefore, an END IF statement is required for each nesting IF statement and another END IF statement is required to end the parent IF-ELSE statement. To set multiple options, use the following form:
IF_THEN_ELSIF_ELSE
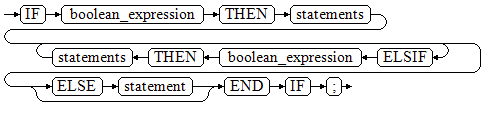
Figure 3 IF_THEN_ELSIF_ELSE::=¶
Examples
IF number_tmp = 0 THEN result := 'zero'; ELSIF number_tmp > 0 THEN result := 'positive'; ELSIF number_tmp < 0 THEN result := 'negative'; ELSE result := 'NULL'; END IF;
IF_THEN_ELSEIF_ELSE
ELSEIF is an alias of ELSIF.
Example
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_control_structure(i in integer) AS BEGIN IF i > 0 THEN raise info 'i:% is greater than 0. ',i; ELSIF i < 0 THEN raise info 'i:% is smaller than 0. ',i; ELSE raise info 'i:% is equal to 0. ',i; END IF; RETURN; END; / CALL proc_control_structure(3); -- Delete the stored procedure. DROP PROCEDURE proc_control_structure;