GaussDB(DWS) Stored Procedure Declaration Syntax¶
Basic Structure¶
A PL/SQL block can contain a sub-block which can be placed in any section. The following describes the architecture of a PL/SQL block:
DECLARE: declares variables, types, cursors, and regional stored procedures and functions used in the PL/SQL block.
DECLARENote
This part is optional if no variable needs to be declared.
An anonymous block may omit the DECLARE keyword if no variable needs to be declared.
For a stored procedure, AS is used, which is equivalent to DECLARE. The AS keyword must be reserved even if there is no variable declaration part.
EXECUTION: specifies procedure and SQL statements. It is the main part of a program. It is mandatory.
BEGINEXCEPTION: processes errors. It is optional.
EXCEPTIONEND
END; /
Important
You are not allowed to use consecutive tabs in the PL/SQL block, because they may result in an exception when the parameter -r is executed using the gsql tool.
PL/SQL Block Classification¶
PL/SQL blocks are classified into the following types:
Anonymous block: a dynamic block that can be executed only for once. For details about the syntax, see Anonymous Block.
Subprogram: a stored procedure, function, operator, or packages stored in a database. A subprogram created in a database can be called by other programs.
Anonymous Block¶
An anonymous block applies to a script infrequently executed or a one-off activity. An anonymous block is executed in a session and is not stored.
Syntax
Figure 1 shows the syntax diagrams for an anonymous block.
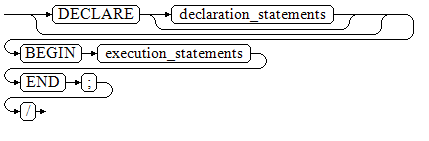
Figure 1 anonymous_block::=¶
Details about the syntax diagram are as follows:
The execute part of an anonymous block starts with a BEGIN statement, has a break with an END statement, and ends with a semicolon (;). Type a slash (/) and press Enter to execute the statement.
Important
The terminator "/" must be written in an independent row.
The declaration section includes the variable definition, type, and cursor definition.
A simplest anonymous block does not execute any commands. At least one statement, even a null statement, must be presented in any implementation blocks.
Examples
The following lists basic anonymous block programs:
-- Null statement block:
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
-- Print information to the console:
BEGIN
dbms_output.put_line('hello world!');
END;
/
-- Print variable contents to the console:
DECLARE
my_var VARCHAR2(30);
BEGIN
my_var :='world';
dbms_output.put_line('hello'||my_var);
END;
/
Subprogram¶
A subprogram stores stored procedures, functions, operators, and advanced packages. A subprogram created in a database can be called by other programs.