Virtual IP Address Overview¶
What Is a Virtual IP Address?¶
A virtual IP address can be shared among multiple ECSs. An ECS can have both private and virtual IP addresses, and you can access the ECS through either IP address. A virtual IP address has the same network access capabilities as a private IP address. You can use either of them to enable layer 2 and layer 3 communications in a VPC, access a different VPC using a peering connection, enable Internet access through EIPs, and connect the cloud to the on-premises servers using VPN connections or Direct Connect connections.
You can bind a virtual IP address to active and standby ECSs, bind an EIP to the virtual IP address, and use Keepalived to set up a high-availability active/standby cluster. If the active ECS goes down, the standby ECS becomes the active server and continues to provide services.
Networking¶
Virtual IP addresses are used for high availability and can work together with Keepalived to make active/standby ECS switchover possible. In this way, If the active ECS goes down, the standby ECS becomes the active server and continues to provide services. ECSs can be configured for HA or as load balancing clusters.
Networking mode 1: HA
If you want to improve service availability and avoid single points of failure, you can deploy ECSs in the active/standby mode or deploy one active ECS and multiple standby ECSs. In this arrangement, the ECSs all use the same virtual IP address. If the active ECS becomes faulty, a standby ECS takes over services from the active ECS and services continue uninterrupted.
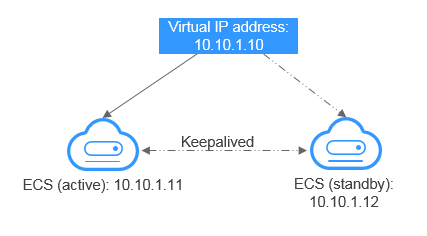
Figure 1 Networking diagram of the HA mode¶
In this configuration, a virtual IP address is bound to two ECSs in the same subnet.
Keepalived is then used to configure the two ECSs to work in the active/standby mode. Follow industry standards for configuring Keepalived. The details are not included here.
Networking mode 2: HA load balancing cluster
If you want to build a high-availability load balancing cluster, use Keepalived and configure LVS nodes as direct routers.
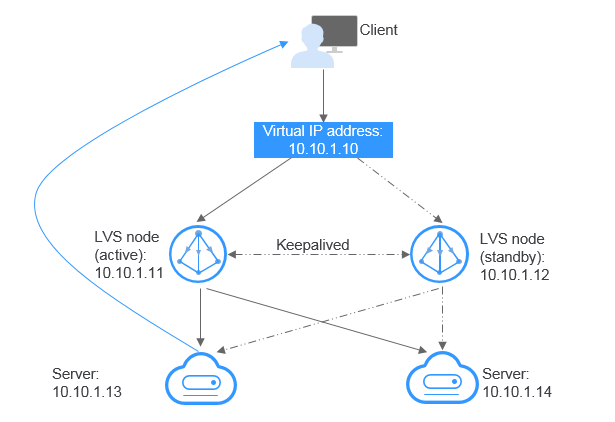
Figure 2 HA load balancing cluster¶
Bind a virtual IP address to two ECSs.
Configure the two ECSs as LVS nodes working as direct routers and use Keepalived to configure the nodes in the active/standby mode. The two ECSs will evenly forward requests to different backend servers.
Configure two more ECSs as backend servers.
Disable the source/destination check for the two backend servers.
Follow industry standards for configuring Keepalived and LVS load balancing. The details are not included here.
Application Scenarios¶
Accessing the virtual IP address through an EIP
If your application has high availability requirements and needs to provide services through the Internet, it is recommended that you bind an EIP to a virtual IP address.
Using a VPN, Direct Connect, or VPC peering connection to access a virtual IP address
To ensure high availability and access to the Internet, use VPN for security and Direct Connect for a stable connection. A VPC peering connection is needed so that two VPCs in the same region can communicate with each other.
Notes and Constraints¶
Virtual IP addresses are not recommended when multiple network interfaces in the same subnet are configured on an ECS. There may be route conflicts on the ECS, which would cause communication failure using the virtual IP address.
If a virtual IP address is used in an active/standby scenario, disable IP forwarding on the standby ECS. For details, see Disabling IP Forwarding on the Standby ECS.