JupyterLab Overview and Common Operations¶
JupyterLab is the next-generation web-based interactive development environment of Jupyter Notebook, enabling you to compile notebooks, operate terminals, edit Markdown text, enable interaction, and view CSV files and images.
JupyterLab is the future mainstream development environment for developers. It has the same components as Jupyter Notebook, but offering more flexibility and powerful functions.
Accessing JupyterLab¶
To access JupyterLab from a running notebook instance, perform the following operations:
Log in to the ModelArts management console. Choose DevEnviron > Notebook in the navigation pane on the left. The notebook list of the new version is displayed.
Click Open in the Operation column of a running notebook instance to access JupyterLab.

Figure 1 Accessing a notebook instance¶
The Launcher page is automatically displayed. Perform required operations. For details, see JupyterLab Documentation.
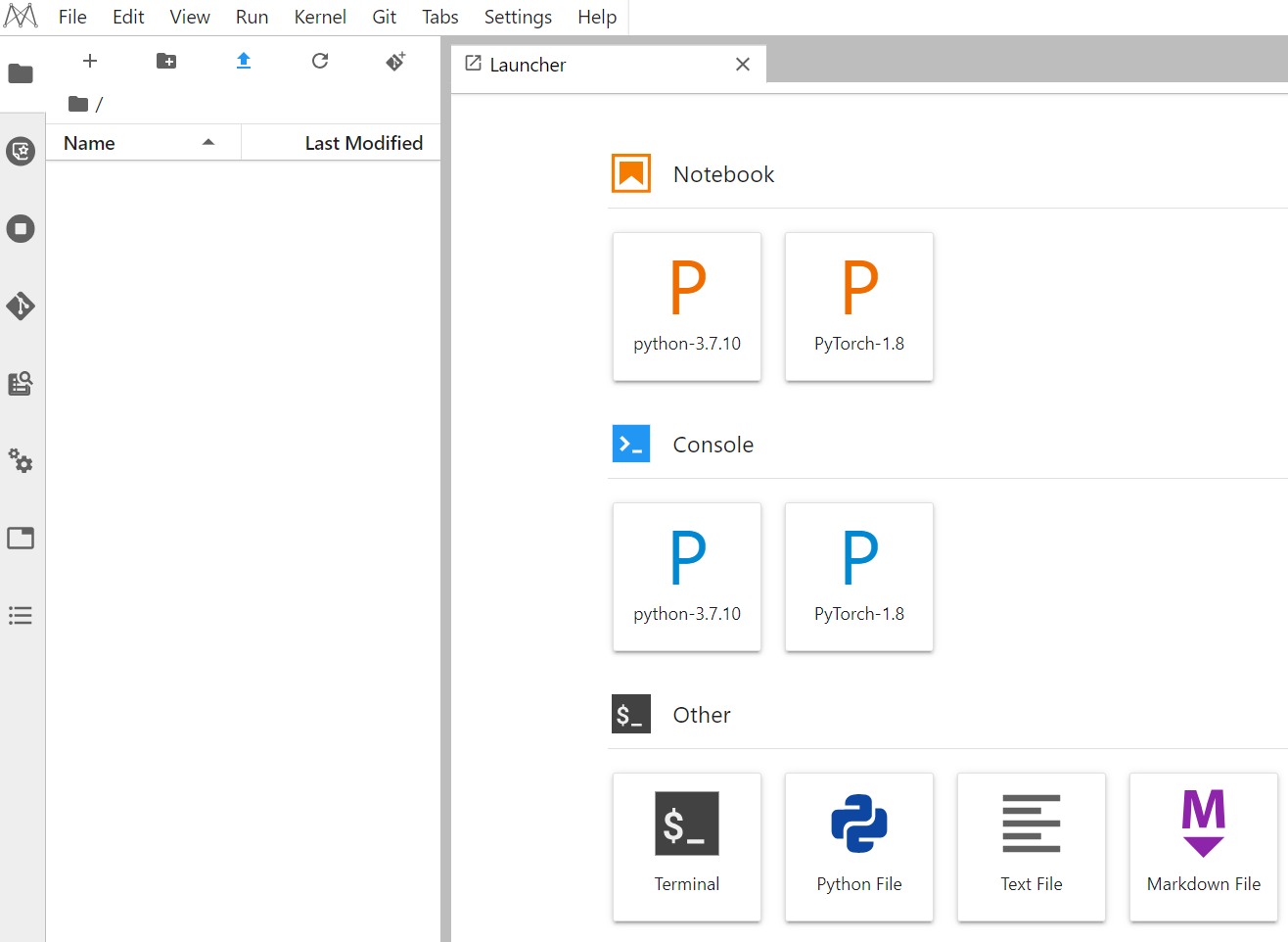
Figure 2 JupyterLab homepage¶
Notebook: Select a kernel for running notebook, for example, TensorFlow or Python.
Console: Call the terminal for command control.
Other: Edit other files.
Creating an IPYNB File in JupyterLab¶
On the JupyterLab homepage, click a proper AI engine in the Notebook area to create an IPYNB file.
The AI engines supported by each notebook instance vary depending on the runtime environment. The following figure is only an example. Select an AI engine based on site requirements.
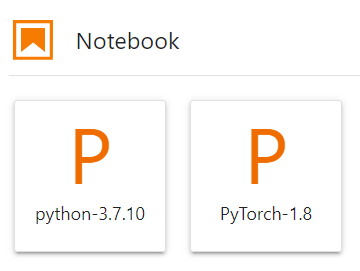
Figure 3 Selecting an AI engine and creating IPYNB file¶
The created IPYNB file is displayed in the navigation pane on the left.
Figure 4 Created IPYNB file¶
Creating a Notebook File and Accessing the Console¶
A console is a Python terminal, which is similar to the native IDE of Python, displaying the output after a statement is entered.
On the JupyterLab homepage, click a proper AI engine in the Console area to create a notebook file.
The AI engines supported by each notebook instance vary depending on the runtime environment. The following figure is only an example. Select an AI engine based on site requirements.
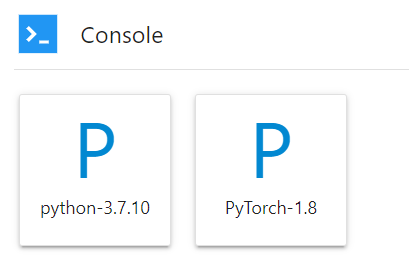
Figure 5 Selecting an AI engine and creating a console¶
After the file is created, the console page is displayed.
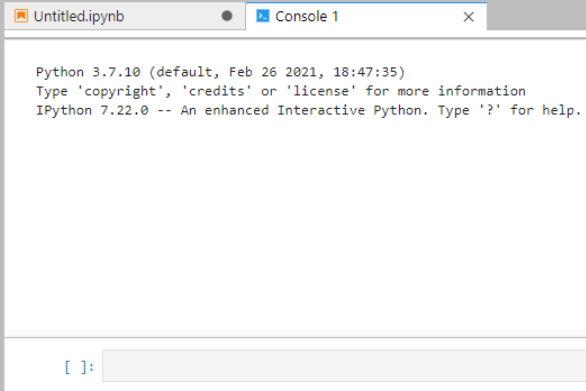
Figure 6 Creating a notebook file (console)¶
Editing a File in JupyterLab¶
JupyterLab allows you to open multiple notebook instances or files (such as HTML, TXT, and Markdown files) in one window and displays them in different tabs.
In JupyterLab, you can customize the display of multiple files. In the file display area on the right, you can drag a file to adjust its position. Multiple files can be concurrently displayed.
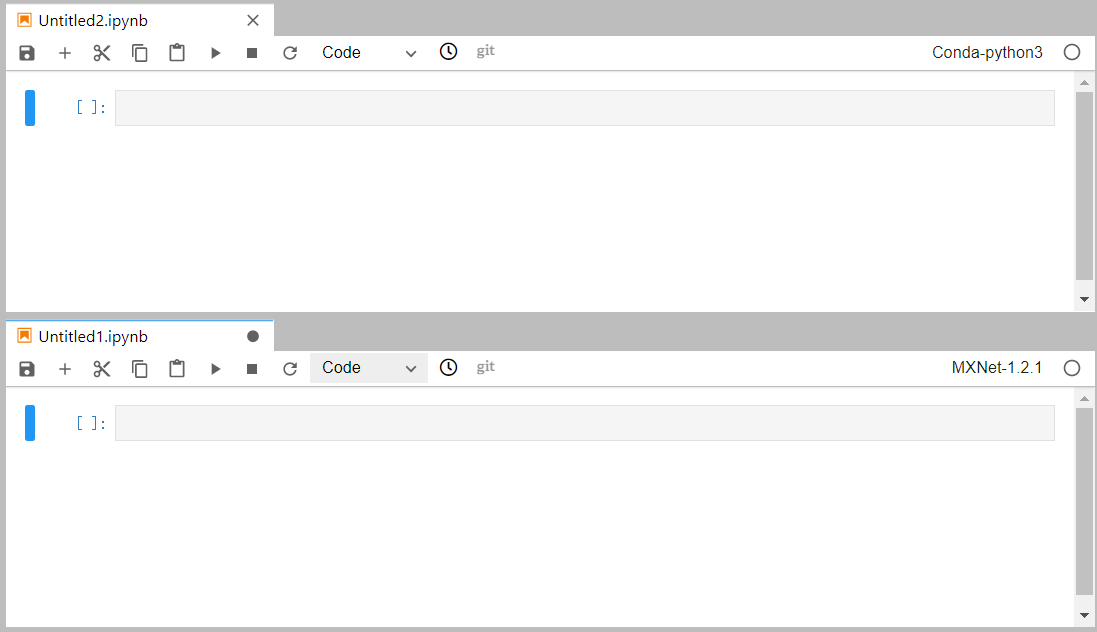
Figure 7 Customized display of multiple files¶
When writing code in a notebook instance, you can create multiple views of a file to synchronously edit the file and view execution results in real time.
To open multiple views, open an IPYNB file and choose File > New View for Notebook.
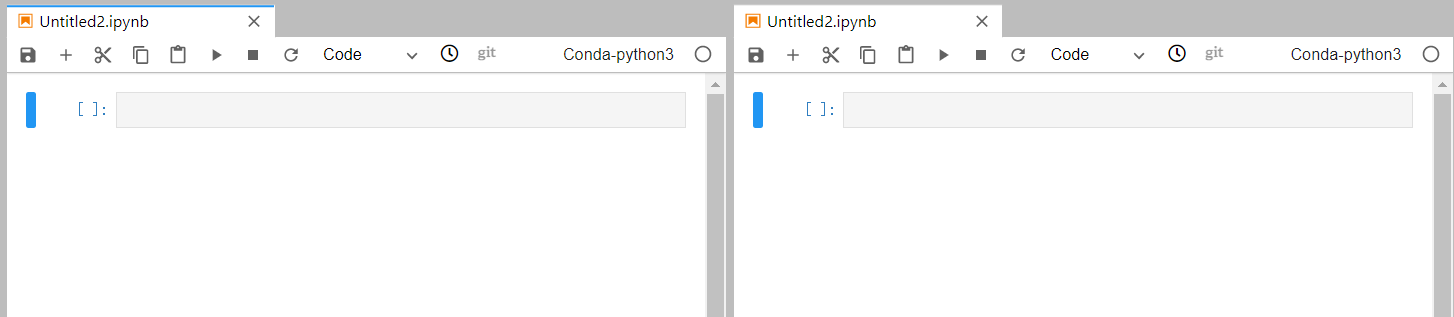
Figure 8 Multiple views of a file¶
Before coding in the code area of an IPYNB file in JupyterLab, add an exclamation mark (!) before the code.
For example, install an external library Shapely.
!pip install Shapely
For example, obtain PythonPath.
!echo $PYTHONPATH
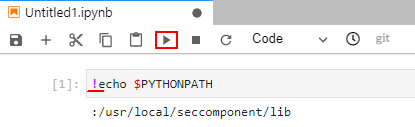
Figure 9 Running code¶
Renewing or Automatically Stopping a Notebook Instance¶
If you enable auto stop when you created or started a notebook instance, the remaining duration for stopping the instance is displayed in the upper right corner of JupyterLab. You can click the time for renewal.
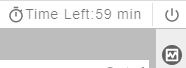
Figure 10 Remaining duration¶
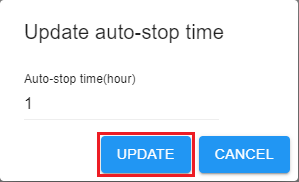
Figure 11 Renewing an instance¶
Setting a Font¶
After accessing a ModelArts notebook instance from iOS, set the font to prevent abnormal display.
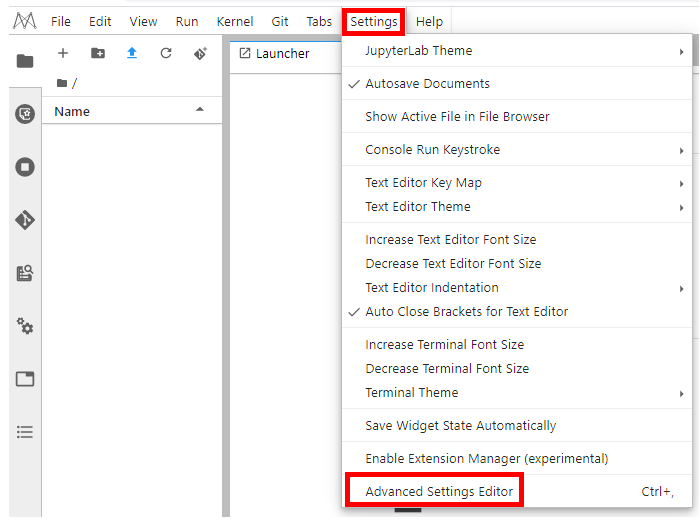
Figure 12 Advanced Settings Editor¶
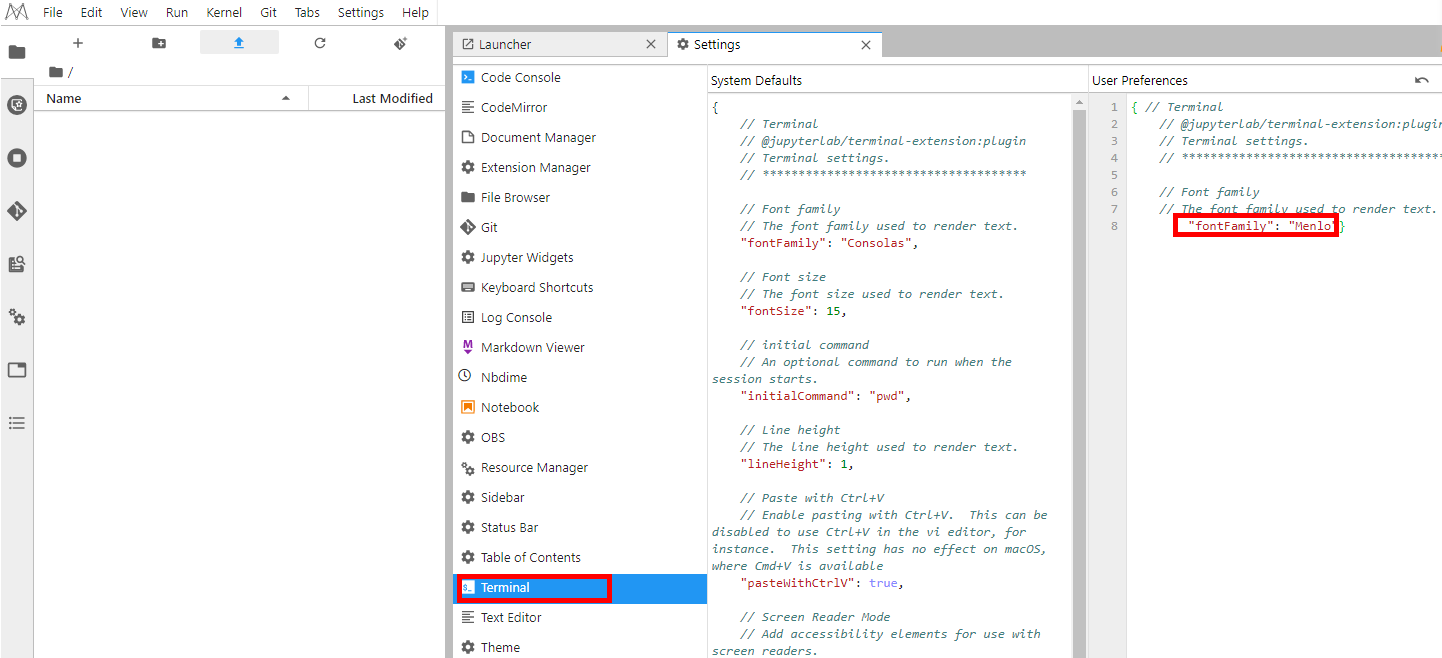
Figure 13 Set fontFamily to Menlo.¶
Monitoring Resources¶
To obtain resource usage, select Resource Monitor in the right pane. The CPU usage and memory usage can be viewed.
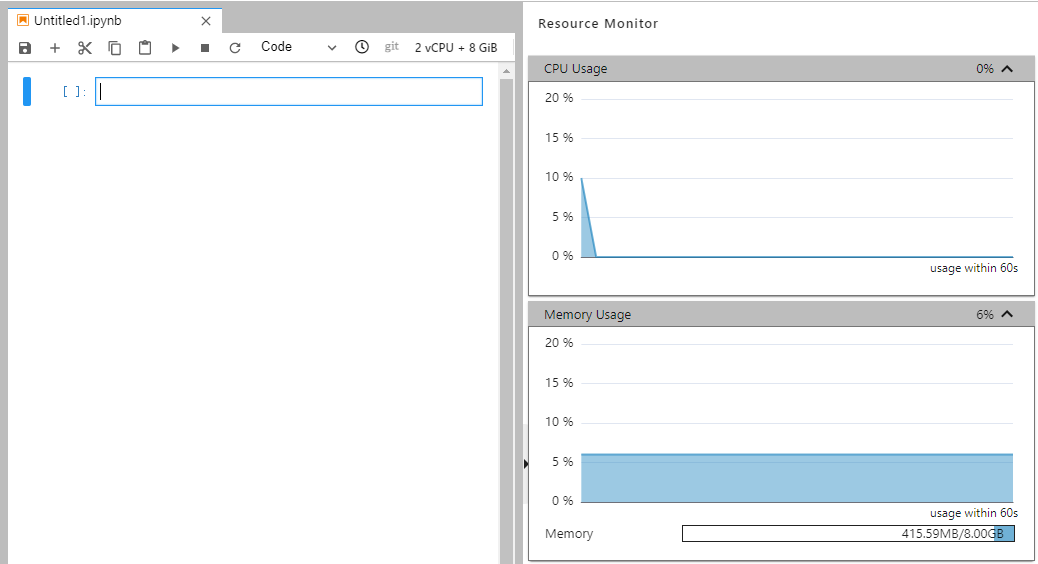
Figure 17 Resource usage¶


























 indicates the code is being executed.
indicates the code is being executed.