Using Clusters with Kerberos Authentication Enabled¶
This section instructs you to use security clusters and run MapReduce, Spark, and Hive programs.
The Presto component of MRS 3.x does not support Kerberos authentication.
You can get started by reading the following topics:
Creating a Security Cluster and Logging In to Manager¶
Create a security cluster. For details, see Creating a Custom Cluster. Enable Kerberos Authentication, set Password, and confirm the password. This password is used to log in to Manager. Keep it secure.
Log in to the MRS console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Active Clusters and click the target cluster name on the right to access the cluster details page.
Click Access Manager on the right of MRS Manager to log in to Manager.
If you have bound an EIP when creating the cluster, perform the following operations:
Add a security group rule. By default, your public IP address used for accessing port 9022 is filled in the rule. If you want to view, modify, or delete a security group rule, click Manage Security Group Rule.
Note
It is normal that the automatically generated public IP address is different from your local IP address and no action is required.
If port 9022 is a Knox port, you need to enable the permission to access port 9022 of Knox for accessing Manager.
Select I confirm that xx.xx.xx.xx is a trusted public IP address and MRS Manager can be accessed using this IP address.
If you have not bound an EIP when creating the cluster, perform the following operations:
Select an available EIP from the drop-down list or click Manage EIP to create one.
Add a security group rule. By default, your public IP address used for accessing port 9022 is filled in the rule. If you want to view, modify, or delete a security group rule, click Manage Security Group Rule.
Note
It is normal that the automatically generated public IP address is different from the local IP address and no action is required.
If port 9022 is a Knox port, you need to enable the permission of port 9022 to access Knox for accessing MRS Manager.
Select I confirm that xx.xx.xx.xx is a trusted public IP address and MRS Manager can be accessed using this IP address.
Click OK. The Manager login page is displayed. To assign permissions to other users to access Manager, add their public IP addresses as trusted ones by referring to Accessing MRS Manager (MRS 2.x or Earlier).
Enter the default username admin and the password you set when creating the cluster, and click Log In.
If the cluster version is earlier than MRS 1.8.0, perform the following steps:
Create a security cluster. For details, see . Enable Kerberos Authentication and set parameters including Password and Confirm Password. This password is used to log in to Manager. Keep it secure.
Log in to the MRS console and choose Active Clusters.
On the Active Clusters page, click the name of the security cluster you created.
On the cluster details page, take note of the AZ, VPC, Cluster Manager IP Address, and Default Security Group of the master node.
On the ECS console, create an ECS.
The AZ, VPC, and Security Group of the ECS must be the same as those of the cluster to be accessed.
Select a Windows public image.
For details about other configuration parameters, see Elastic Cloud Server > User Guide > Getting Started > Creating and Logging In to a Windows ECS.
Note
If the security group of the ECS is different from Default Security Group of the master node, you can modify the configuration using either of the following methods:
Change the security group of the ECS to the default security group of the master node. For details, see Elastic Cloud Server > User Guide > Security Groups > Changing a Security Group.
Add two security group rules to the security groups of the master and core nodes to enable the ECS to access the cluster. Set Protocol to TCP and ports of the two security group rules to 28443 and 20009, respectively. For details, see Virtual Private Cloud > User Guide > Security > Security Group > Adding a Security Group Rule.
On the VPC console, apply for an EIP and bind it to the ECS.
For details, see Virtual Private Cloud > User Guide > Elastic IP > Assigning an EIP and Binding It to an ECS.
Log in to the ECS.
The Windows system account, password, EIP, and the security group rules are required for logging in to the ECS. For details, see Elastic Cloud Server > User Guide > ECS Logins > Logging In to a Windows ECS.
On the Windows remote desktop, use your browser to access Manager.
For example, you can use Internet Explorer 11 in the Windows 2012 OS.
The Manager access address is in the format of https://Cluster Manager IP address:28443/web. Cluster Manager IP address is the Cluster Manager IP Address obtained in 3. When you access Manager, you need to enter the MRS cluster username, for example, admin, and the password you set when enabling Kerberos Authentication during cluster creation in 1.
Note
If you access Manager with another MRS cluster username, change the password upon your first login. The new password must meet the requirements of the current password complexity policies.
By default, an account is locked after five consecutive incorrect password attempts. It is automatically unlocked after 5 minutes.
Creating a Role and a User¶
For clusters with Kerberos authentication enabled, perform the following steps to create a user and assign permissions to the user to run programs.
On Manager, choose System > Permission > Role.
Click Create Role. For details, see Creating a Role.
Specify the following information:
Enter a role name, for example, mrrole.
In Configure Resource Permission, select the cluster to be operated, choose Yarn > Scheduler Queue > root, and select Submit and Admin in the Permission column. After you finish configuration, do not click OK but click the name of the target cluster shown in the following figure and then configure other permissions.
Choose HBase > HBase Scope. Locate the row that contains global, and select create, read, write, and execute in the Permission column. After you finish configuration, do not click OK but click the name of the target cluster shown in the following figure and then configure other permissions.
Choose HDFS > File System > hdfs://hacluster/ and select Read, Write, and Execute in the Permission column. After you finish configuration, do not click OK but click the name of the target cluster shown in the following figure and then configure other permissions.
Choose Hive > Hive Read Write Privileges, select Select, Delete, Insert, and Create in the Permission column, and click OK.
Choose System. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Permission > User Group > Create User Group to create a user group for the sample project, for example, mrgroup. For details, see Creating a User Group.
Choose System. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Permission > User > Create to create a user for the sample project. For details, see Creating a User.
Enter a username, for example, test. If you want to run a Hive program, enter hiveuser in Username.
Set User Type to Human-Machine.
Enter a password. This password will be used when you run the program.
In User Group, add mrgroup and supergroup.
Set Primary Group to supergroup and bind the mrrole role to obtain the permission.
Click OK.
Choose System. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Permission > User, locate the row where user test locates, and select Download Authentication Credential from the More drop-down list. Save the downloaded package and decompress it to obtain the keytab and krb5.conf files.
Running a MapReduce Program¶
This section describes how to run a MapReduce program in security cluster mode.
Prerequisites
You have compiled the program and prepared data files, for example, mapreduce-examples-1.0.jar, input_data1.txt, and input_data2.txt..
Procedure
Use a remote login software (for example, MobaXterm) to log in to the master node of the security cluster using SSH (using the EIP).
After the login is successful, run the following commands to create the test folder in the /opt/Bigdata/client directory and create the conf folder in the test directory:
cd /opt/Bigdata/client mkdir test cd test mkdir conf
Use an upload tool (for example, WinSCP) to copy mapreduce-examples-1.0.jar, input_data1.txt, and input_data2.txt to the test directory, and copy the keytab and krb5.conf files obtained in 5 in Creating Roles and Users to the conf directory.
Run the following commands to configure environment variables and authenticate the created user, for example, test:
cd /opt/Bigdata/client source bigdata_env export YARN_USER_CLASSPATH=/opt/Bigdata/client/test/conf/ kinit test
Enter the password as prompted. If no error message is displayed (you need to change the password as prompted upon the first login), Kerberos authentication is complete.
Run the following commands to import data to the HDFS:
cd test hdfs dfs -mkdir /tmp/input hdfs dfs -put input_data* /tmp/input
Run the following commands to run the program:
yarn jar mapreduce-examples-1.0.jar xxx /tmp/input /tmp/mapreduce_output
In the preceding commands:
/tmp/input indicates the input path in the HDFS.
/tmp/mapreduce_output indicates the output path in the HDFS. This directory must not exist. Otherwise, an error will be reported.
After the program is executed successfully, run the hdfs dfs -ls /tmp/mapreduce_output command. The following command output is displayed.
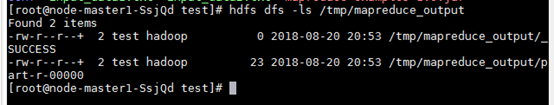
Figure 1 Program running result¶