Installing ICAgent (Extra-Region Hosts)¶
ICAgent is a log collection tool for LTS. To use LTS to collect logs from extra-region hosts, you need to install ICAgent on the hosts. This section describes how to install ICAgent on an extra-region host.
Prerequisites¶
Before installing ICAgent, ensure that the time and time zone of your local browser are consistent with those of the host. If they are inconsistent, errors may occur during log reporting.
Installation Methods¶
There are two methods to install ICAgent.
Method | Scenario |
|---|---|
Initial installation | You can use this method to install ICAgent on a host that has no ICAgent installed. |
Inherited installation (supported only for Linux hosts) | When ICAgent has already been installed on one host but needs to be installed on multiple hosts, you can use this method. |
Initial Installation (Linux)¶
Before installing ICAgent on a host not in this region, apply for an ECS as a jump server on the ECS console. For details, see Using Multiple Jump Servers.
Note
You are advised to use CentOS 6.5 64bit or later images. The minimum flavor for the ECS is 1 vCPU and 1 GB of memory, while the recommended flavor is 2 vCPUs and 4 GB of memory.
Log in to the management console and choose Management & Deployment > Log Tank Service.
Choose Host Management > Hosts in the navigation pane.
Click Install ICAgent in the upper right corner.
Set Host to Extra-region hosts.
Set OS to Linux.
Set Network Connectivity to Private line. When the network is connected via a private line, hosts in other IDCs are disconnected from LTS backend by default and a network connectivity solution is required. You are advised to select VPCEP.
Note
Private line: Extra-region hosts connect to LTS in the current region through a jump server or VPC Endpoint (VPCEP), offering greater security and stability. In this scenario, extra-region hosts cannot communicate with LTS in the current region by default, and ICAgent installed on these hosts cannot directly access the network segment used by LTS in the current region to report logs. Therefore, you need to configure a network connection solution to use a jump server or VPCEP to connect to the LTS backend and forward data to LTS.
Jump server: functions as a data forwarder and forwards the data collected by ICAgent from extra-region hosts to LTS. This solution is suitable for tests or scenarios with low log traffic. VPCEP is recommended for scenarios with high log traffic.
VPCEP: provides private channels to connect your VPC to LTS in the current region, enabling resources in the VPC to access VPC endpoint services without the need for EIPs. This solution reduces the risks of data transmission on public networks and improves the transmission security and efficiency.
If you set LTS Backend Connection to VPCEP, enter the VPCEP domain name and go to 9.
With the assistance of network engineers, configure DNS domain name resolution rules on other clouds to resolve VPCEP domain names to specified IP addresses.
Then, copy the ping command displayed on this page and run it on the target host whose logs are to be collected. A successful ping test indicates that the network configuration is correct.
Enable forwarding ports on the jump server. This step is mandatory when LTS Backend Connection is set to Jump server.
Apply for an ECS in the current region as a jump server.
Add security group rules for the jump server and enable the corresponding inbound ports to ensure data connectivity between the extra-region hosts and the jump server.
On the ECS console, click the ECS name to access the details page, and click the Security Groups tab. The security group list is displayed.
Click a security group name to access the details page.
On the security group details page, click the Inbound Rules tab and then click Add Rule. On the page displayed, add a security group rule based on Table 2.
Table 2 Security group rule¶ Direction
Protocol
Port
Description
Inbound
TCP
8149, 8102, 8923, 30200, 30201, and 80
Ports used by ICAgent to send data to the jump server, ensuring data connectivity between VMs in other regions and the jump server.
Enter the private IP address of the jump server and generate an SSH tunneling command.
Figure 1 Entering the private IP address of the jump server¶
Note
The private IP address of the jump server refers to the internal IP address of the VPC where the jump server is located.
Click Copy Command.
Log in to the jump server as user root and run the SSH tunneling command:
ssh -f -N -L {Jump server IP address}:8149:{ELB IP address}:8149 -L {Jump server IP address}:8102:{ELB IP address}:8102 -L {Jump server IP address}:8923:{ELB IP address}:8923 -L {Jump server IP address}:30200:{ELB IP address}:30200 -L {Jump server IP address}:30201:{ELB IP address}:30201 -L {Jump server IP address}:80:icagent-{Region}.{OBS domain name}:80 {Jump server IP address}
Enter the password of user root as prompted.
Run the netstat -lnp | grep ssh command to check whether the corresponding TCP ports are being listened to. If the command output similar to Figure 2 is returned, the ports are open.
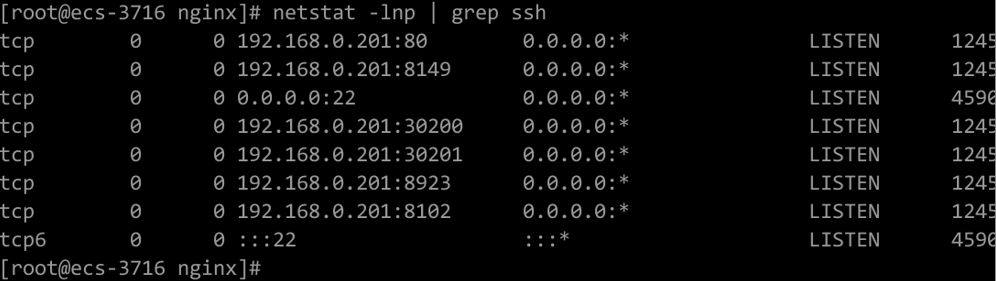
Figure 2 Open TCP ports¶
Note
If the jump server powers off and restarts, run the preceding command again.
Obtain an AK/SK and specify DC and Connection IP.
Note
DC: Specify a name for the data center of the host so it is easier to find the host.
Connection IP: For EIP connection, use the EIP of the jump server. For VPC peering connection, use the internal IP address of the VPC where the jump server locates.
Copy the ICAgent installation command.
Log in as user root to the host which is deployed in the region same as that you are logged in to (by using a remote login tool such as PuTTY) and run the copied command.
Note
When message "ICAgent install success" is displayed, ICAgent has been installed in the /opt/oss/servicemgr/ directory of the host. You can then choose Host Management > Hosts in the navigation pane of the LTS console to check the ICAgent status.
If the installation fails, uninstall ICAgent and reinstall it. If the reinstallation fails, contact technical support.
Initial Installation (Windows)¶
Before installing ICAgent on a host not in this region, apply for a Linux ECS as a jump server on the ECS console. For details, see Using Multiple Jump Servers.
Note
You are advised to use CentOS 6.5 64bit or later images. The minimum flavor for the ECS is 1 vCPU and 1 GB of memory, while the recommended flavor is 2 vCPUs and 4 GB of memory.
Click Install ICAgent in the upper right corner.
Set Host to Extra-region hosts.
Set OS to Windows.
Set Network Connectivity to Private line. When the network is connected via a private line, hosts in other IDCs are disconnected from LTS backend by default and a network connectivity solution is required. You are advised to select VPCEP.
Note
Private line: Extra-region hosts connect to LTS in the current region through a jump server or VPC Endpoint (VPCEP), offering greater security and stability. In this scenario, extra-region hosts cannot communicate with LTS in the current region by default, and ICAgent installed on these hosts cannot directly access the network segment used by LTS in the current region to report logs. Therefore, you need to configure a network connection solution to use a jump server or VPCEP to connect to the LTS backend and forward data to LTS.
Jump server: functions as a data forwarder and forwards the data collected by ICAgent from extra-region hosts to LTS. This solution is suitable for tests or scenarios with low log traffic. VPCEP is recommended for scenarios with high log traffic.
VPCEP: provides private channels to connect your VPC to LTS in the current region, enabling resources in the VPC to access VPC endpoint services without the need for EIPs. This solution reduces the risks of data transmission on public networks and improves the transmission security and efficiency.
If you set LTS Backend Connection to VPCEP, enter the VPCEP domain name and go to 7.
With the assistance of network engineers, configure DNS domain name resolution rules on other clouds to resolve VPCEP domain names to specified IP addresses.
Then, copy the ping command displayed on this page and run it on the target host whose logs are to be collected. A successful ping test indicates that the network configuration is correct.
Enable forwarding ports on the jump server. This step is mandatory when LTS Backend Connection is set to Jump server.
Apply for a Linux ECS in the current region as a jump server.
Modify the security group rule used by the jump server.
On the ECS details page, click the Security Groups tab.
Click a security group name to access the details page.
On the security group details page, click the Inbound Rules tab and then click Add Rule. On the page displayed, add a security group rule based on Table 3.
Table 3 Security group rule¶ Direction
Protocol
Port
Description
Inbound
TCP
8149, 8102, 8923, 30200, 30201, and 80
ICAgent will send data to the jump server through the listed ports.
Enter the private IP address of the jump server and generate an SSH tunneling command.
Note
The private IP address of the jump server refers to the internal IP address of the VPC where the jump server is located.
Click Copy Command.
Log in to the jump server as user root and run the SSH tunneling command:
ssh -f -N -L {Jump server IP address}:8149:{ELB IP address}:8149 -L {Jump server IP address}:8102:{ELB IP address}:8102 -L {Jump server IP address}:8923:{ELB IP address}:8923 -L {Jump server IP address}:30200:{ELB IP address}:30200 -L {Jump server IP address}:30201:{ELB IP address}:30201 -L {Jump server IP address}:80:icagent-{Region}.{OBS domain name}:80 {Jump server IP address}
Enter the password of user root as prompted.
Run the netstat -lnp | grep ssh command to check whether the corresponding TCP ports are being listened to. If the command output similar to Figure 3 is returned, the ports are open.
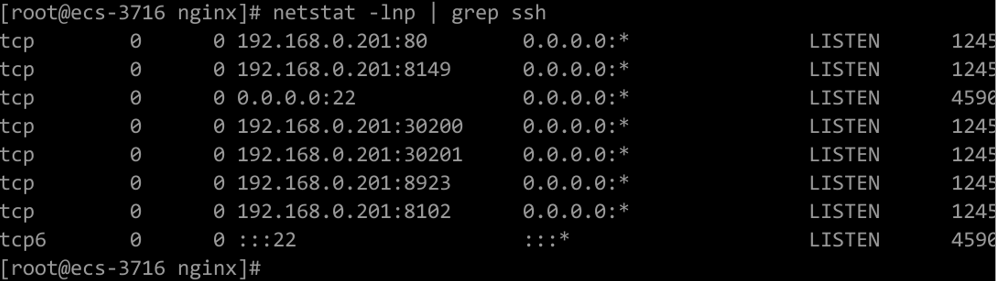
Figure 3 Open TCP ports¶
Note
If the jump server powers off and restarts, run the preceding command again.
Download the ICAgent installation package to the local PC as prompted.
Save the ICAgent installation package to a directory on the Windows host, for example, C:\ICAgent, and decompress the package.
Obtain an AK/SK.
Generate and copy the installation command.
Enter the connection IP in the text box and replace the AK/SK to generate the installation command.
Note
Connection IP: For EIP connection, use the EIP of the jump server. For VPC peering connection, use the internal IP address of the VPC where the jump server locates.
Click Copy Command to copy the ICAgent installation command.
Open the Command Prompt, go to the directory where the ICAgent installation package is decompressed, and run the copied command.
Note
If the message "Service icagent installed successfully" is displayed, the installation is successful. You can then choose Host Management > Hosts in the navigation pane of the LTS console to check the ICAgent status.
If the installation fails, uninstall ICAgent and reinstall it. If the reinstallation fails, contact technical support.
Using Multiple Jump Servers¶
Note
You can use multiple jump servers to prevent the risk of single point of failures and improve access reliability.
Create a Linux ECS that as a jump server.
Note
Configure the CPU and memory based on the service requirements. The recommended specifications are 2 vCPUs and 4 GB of memory, or above.
Log in to the jump server as use root and use the internal IP address of the jump server to create an SSH tunnel.
On the ECS console, locate the jump server and obtain its private IP address.
On the LTS console, choose Host Management in the navigation pane, and click Install ICAgent in the upper right corner. In the dialog box displayed, select Linux for OS, select Extra-region hosts for Host, and enter the private IP address to generate the SSH tunneling command. Log in to the jump server and run the command to create an SSH tunnel.
If there are multiple jump servers, repeat 2 and add them to the same VPC. When creating an ECS, select the same VPC for Network.
Create a load balancer. When creating the load balancer, you should:
Select the same VPC as that of the jump servers.
Create an EIP for connecting to the jump servers.
Apply for the bandwidth based on the service requirements.
Add listeners for TCP ports 30200, 30201, 8149, 8923, and 8102.
Add all jump servers to the backend server group.
Inherited Installation (Linux)¶
Assume that you need to install ICAgent on multiple hosts, and one of the hosts already has ICAgent installed. The ICAgent installation package, ICProbeAgent.tar.gz, is in the /opt/ICAgent/ directory. To install ICAgent on other hosts one by one:
Run the following command on the host where ICAgent has been installed, where x.x.x.x is the IP address of the host you want to install ICAgent on.
bash /opt/oss/servicemgr/ICAgent/bin/remoteInstall/remote_install.sh -ip x.x.x.x
Enter the password for user root of the host when prompted.
Note
If the Expect tool is installed on the host that has ICAgent installed, the ICAgent installation should be able to complete without prompting you for a password. Otherwise, enter the password as prompted.
Ensure that user root can run SSH or SCP commands on the host where ICAgent has been installed to remotely communicate with the remote host to install ICAgent.
When message "ICAgent install success" is displayed, ICAgent has been installed in the /opt/oss/servicemgr/ directory of the host. You can then choose Host Management > Hosts in the navigation pane of the LTS console to check the ICAgent status.
If the installation fails, uninstall ICAgent and reinstall it. If the reinstallation fails, contact technical support.
Batch Inherited Installation (Linux)¶
Assume that you need to install ICAgent on multiple hosts, and one of the hosts already has ICAgent installed. The ICAgent installation package, ICProbeAgent.tar.gz, is in the /opt/ICAgent/ directory. In this case, you can follow the directions below to install ICAgent on other hosts in batches.
Important
The hosts must all belong to the same VPC and be on the same subnet.
Prerequisites
The IP addresses and passwords of all hosts to install ICAgent have been collected, sorted in the iplist.cfg file, and uploaded to the /opt/ICAgent/ directory on the host that has ICAgent installed. Each IP address and password in the iplist.cfg file must be separated by a space. Examples:
192.168.0.109 Password (Replace the IP address and password with the actual ones)
192.168.0.39 Password (Replace the IP address and password with the actual ones)
Note
The iplist.cfg file contains sensitive information. You are advised to clear it after using it.
If all hosts share a password, list only IP addresses in the iplist.cfg file and enter the password manually during execution. If one of the hosts uses a different password, type the password behind its IP address.
Procedure
Run the following command on the host that has ICAgent installed:
bash /opt/oss/servicemgr/ICAgent/bin/remoteInstall/remote_install.sh -batchModeConfig /opt/ICAgent/iplist.cfg
Enter the default password for user root of the hosts to install ICAgent. If the passwords of all hosts have been configured in the iplist.cfg file, press Enter to skip this step.
batch install begin Please input default passwd: send cmd to 192.168.0.109 send cmd to 192.168.0.39 2 tasks running, please wait... 2 tasks running, please wait... 2 tasks running, please wait... End of install agent: 192.168.0.39 End of install agent: 192.168.0.109 All hosts install icagent finish.
If the message "All hosts install icagent finish." is displayed, ICAgent has been installed on all the hosts listed in the configuration file.
Choose Host Management > Hosts in the navigation pane of the LTS console to check the ICAgent status.