Creating a Kafka Instance¶
Kafka instances are tenant-exclusive, and physically isolated in deployment. You can customize the computing capabilities and storage space of a Kafka instance as required.
Preparing Instance Dependencies¶
Before creating a Kafka instance, prepare the resources listed in Table 1.
Resource | Requirement | Operations |
|---|---|---|
VPC and subnet | You need to configure a VPC and subnet for the Kafka instance as required. You can use the current account's existing VPC and subnet, or create new ones. Note when creating a VPC and a subnet:
| For details on how to create a VPC and a subnet, see Creating a VPC. If you need to create and use a new subnet in an existing VPC, see Creating a Subnet for the VPC. |
Security group | Different Kafka instances can use the same or different security groups. Before accessing a Kafka instance, configure security groups based on the access mode. For details, see Table 2. | For details on how to create a security group, see Creating a Security Group. For details on how to add rules to a security group, see Adding a Security Group Rule. |
EIP | To access a Kafka instance on a client over a public network, create EIPs in advance. Note the following when creating EIPs:
| For details about how to create an EIP, see Assigning an EIP. |
KMS key | To encrypt the disk for a Kafka instance, create a KMS key. The KMS key must be created in the same region as the Kafka instance. | For details about how to create a KMS key, see Creating a Key. |
Procedure¶
Log in to the console.
Click
 in the upper left corner to select a region.
in the upper left corner to select a region.Select a region near you to ensure the lowest latency possible.
Click Service List and choose Application > Distributed Message Service. The Kafka instance list is displayed.
Click Create Instance in the upper right corner of the page.
Select a region.
DMS for Kafka instances in different regions cannot communicate with each other over an intranet. Select a nearest location for low latency and fast access.
Select a Project.
Projects isolate compute, storage, and network resources across geographical regions. For each region, a preset project is available.
Select an AZ.
An AZ is a physical region where resources use independent power supply and networks. AZs are physically isolated but interconnected through an internal network.
Select one, three, or more AZs as required. The AZs cannot be changed once the instance is created.
Enter an Instance Name.
You can customize a name that complies with the rules: 4-64 characters; starts with a letter; can contain only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Select an Enterprise Project.
This parameter is for enterprise users. An enterprise project manages cloud resources. The enterprise project management service unifies cloud resources in projects, and resources and members in a project. The default project is default.
Configure the following instance specifications:
Specifications: Select Cluster or Single-node.
If you select Cluster, specify the version, broker flavor and quantity, disk type, and storage space to be supported by the cluster Kafka instance as required.
Version: Cluster instances support Kafka 2.3.0, 2.7, and 3.x. The version cannot be changed once the instance is created.
Broker Flavor: Select a broker flavor that best fit your needs.
Maximum number of partitions per broker x Number of brokers = Maximum number of partitions of an instance. If the total number of partitions of all topics exceeds the upper limit of partitions, topic creation fails.
For Brokers, specify the broker quantity.
Storage space per broker: Disk type and size for storing the instance data. The disk type cannot be changed once the Kafka instance is created.
The storage space is consumed by message replicas, logs, and metadata. Specify the storage space based on the expected service message size, the number of replicas, and the reserved disk space. Each Kafka broker reserves 33 GB disk space for storing logs and metadata.
Disks are formatted when an instance is created. As a result, the actual available disk space is 93% to 95% of the total disk space.
The disk type can be high I/O or ultra-high I/O. For more information, see Disk Types and Performance.
Disk Encryption: Specify whether to enable disk encryption.
Enabling disk encryption improves data security, but slows down disk read/write. Disk encryption depends on Key Management Service (KMS). If you enable disk encryption, select a KMS key. This parameter cannot be modified once the Kafka instance is created.
Capacity Threshold Policy: Policy used when the disk usage reaches the threshold. The capacity threshold is 95%.
Automatically delete: Messages can be created and retrieved, but 10% of the earliest messages will be deleted to ensure sufficient disk space. This policy is suitable for scenarios where no service interruption can be tolerated. Data may be lost.
Stop production: New messages cannot be created, but existing messages can still be retrieved. This policy is suitable for scenarios where no data loss can be tolerated.
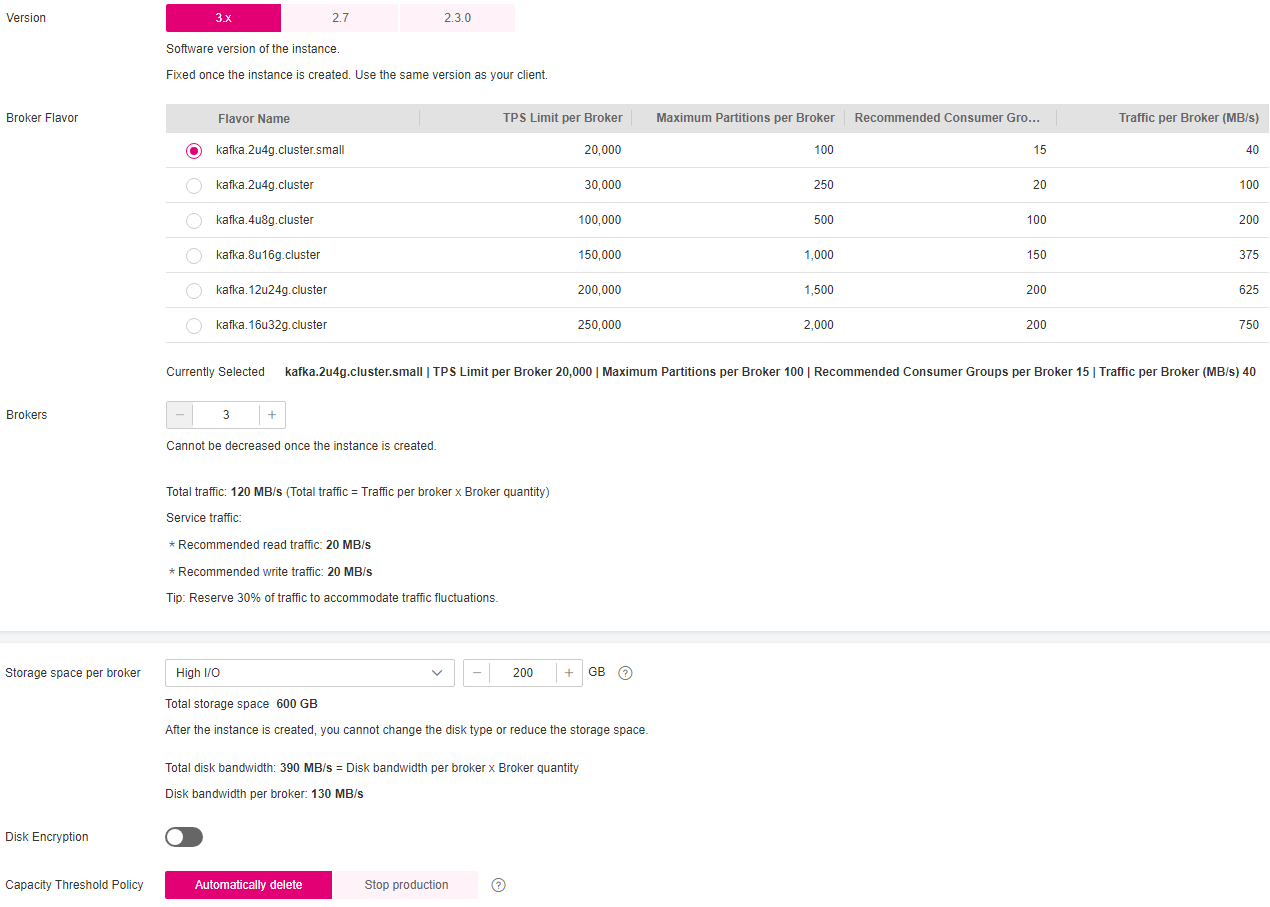
Figure 1 Cluster instance specifications¶
Single-node: Create a Kafka 2.7 instance with one broker. For details about single-node instances, see Comparing Single-node and Cluster Kafka Instances.
Version: Kafka version, which can only be 2.7.
Broker Flavor: Select a broker flavor that best fit your needs.
Brokers: The instance can have only one broker.
Storage space per broker: Disk type and size for storing the instance data. The disk type cannot be changed once the Kafka instance is created.
The storage space is consumed by message replicas, logs, and metadata. Specify the storage space based on the expected service message size, the number of replicas, and the reserved disk space. Each Kafka broker reserves 33 GB disk space for storing logs and metadata.
Disks are formatted when an instance is created. As a result, the actual available disk space is 93% to 95% of the total disk space.
The disk type can be high I/O or ultra-high I/O. For more information, see Disk Types and Performance.
Disk Encryption: Specify whether to enable disk encryption.
Enabling disk encryption improves data security, but slows down disk read/write. Disk encryption depends on Key Management Service (KMS). If you enable disk encryption, select a KMS key. This parameter cannot be modified once the Kafka instance is created.
Capacity Threshold Policy: Policy used when the disk usage reaches the threshold. The capacity threshold is 95%.
Automatically delete: Messages can be created and retrieved, but 10% of the earliest messages will be deleted to ensure sufficient disk space. This policy is suitable for scenarios where no service interruption can be tolerated. Data may be lost.
Stop production: New messages cannot be created, but existing messages can still be retrieved. This policy is suitable for scenarios where no data loss can be tolerated.
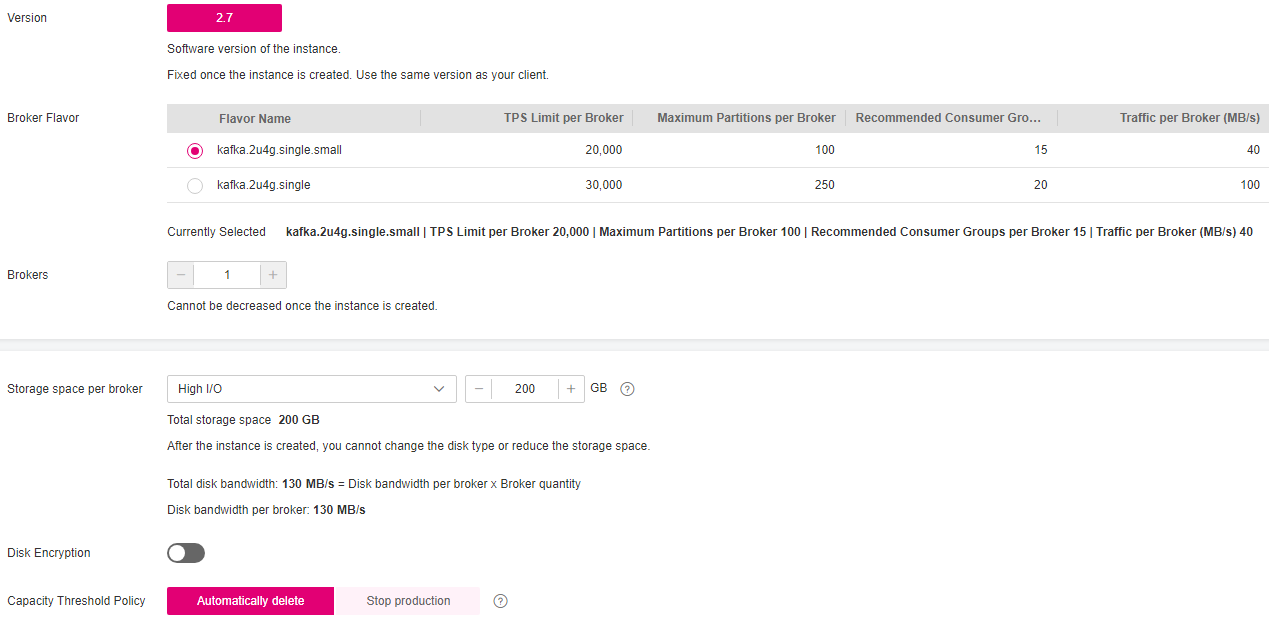
Figure 2 Single-node instance specifications¶
Configure the instance network parameters.
Select a VPC and a subnet.
A VPC provides an isolated virtual network for your Kafka instances. You can configure and manage the network as required.
Note
After the Kafka instance is created, its VPC and subnet cannot be changed.
The Kafka instance supports IPv6 after it is enabled for the subnet.
IPv6: This parameter is displayed after IPv6 is enabled for the subnet. The instance with IPv6 enabled can be accessed on a client using IPv6 addresses.
Note
SASL_SSL cannot be manually configured for instances with IPv6 enabled.
The IPv6 setting is fixed once the instance is created.
Select a security group.
A security group is a set of rules for accessing a Kafka instance. You can click Manage Security Group to view or create security groups on the network console.
Before accessing a Kafka instance on the client, configure security group rules based on the access mode. For details about security group rules, see Table 2.
Configure the instance access mode.
Table 2 Instance access modes¶ Public or Private Network
Plaintext or Ciphertext
Description
Private Network Access
Plaintext Access
Clients connect to the Kafka instance without SASL authentication.
Once enabled, private network access cannot be disabled. Enable plaintext or ciphertext access, or both.
Ciphertext Access
Clients connect to the Kafka instance with SASL authentication.
Once enabled, private network access cannot be disabled. Enable plaintext or ciphertext access, or both. To disable ciphertext access, contact customer service.
If you enable Ciphertext Access, specify a security protocol, SASL/PLAIN, username, and password.
After an instance is created, disabling and re-enabling Ciphertext Access do not affect users.
Public Network Access
Plaintext Access
Clients connect to the Kafka instance without SASL authentication.
Enable or disable plaintext access, and configure addresses for public network access.
Ciphertext Access
Clients connect to the Kafka instance with SASL authentication.
Enable or disable ciphertext access, and configure addresses for public network access.
If you enable Ciphertext Access, specify a security protocol, SASL/PLAIN, username, and password.
After an instance is created, disabling and re-enabling Ciphertext Access do not affect users.
Public IP Addresses
Select the number of public IP addresses as required.
If EIPs are insufficient, click Create Elastic IP to create EIPs. Then, return to the Kafka console and click
 next to Public IP Address to refresh the public IP address list.
next to Public IP Address to refresh the public IP address list.Kafka instances only support IPv4 EIPs.
Note
Ciphertext access is unavailable for single-node instances.
The security protocol, SASL/PLAIN mechanism, username, and password are described as follows.
Table 3 Ciphertext access parameters¶ Parameter
Value
Description
Security Protocol
SASL_SSL
SASL is used for authentication. Data is encrypted with SSL certificates for high-security transmission.
SCRAM-SHA-512 is enabled by default. To use PLAIN, enable SASL/PLAIN.
What are SCRAM-SHA-512 and PLAIN mechanisms?
SCRAM-SHA-512: uses the hash algorithm to generate credentials for usernames and passwords to verify identities. SCRAM-SHA-512 is more secure than PLAIN.
PLAIN: a simple username and password verification mechanism.
SASL_PLAINTEXT
SASL is used for authentication. Data is transmitted in plaintext for high performance.
SCRAM-SHA-512 is enabled by default. To use PLAIN, enable SASL/PLAIN. SCRAM-SHA-512 authentication is recommended for plaintext transmission.
Cross-VPC Access Protocol
-When Plaintext Access is enabled and Ciphertext Access is disabled, PLAINTEXT is used for Cross-VPC Access Protocol.
When Ciphertext Access is enabled and Security Protocol is SASL_SSL, SASL_SSL is used for Cross-VPC Access Protocol.
When Ciphertext Access is enabled and Security Protocol is SASL_PLAINTEXT, SASL_PLAINTEXT is used for Cross-VPC Access Protocol.
Fixed once the instance is created.
SASL/PLAIN
-If SASL/PLAIN is disabled, the SCRAM-SHA-512 mechanism is used for username and password authentication.
If SASL/PLAIN is enabled, both the SCRAM-SHA-512 and PLAIN mechanisms are supported. You can select either of them as required.
The SASL/PLAIN setting cannot be changed once ciphertext access is enabled.
Username and Password
-Username and password used by the client to connect to the Kafka instance.
A username should contain 4 to 64 characters, start with a letter, and contain only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
A password must meet the following requirements:
Contains 8 to 32 characters.
Cannot start with a hyphen (-) and must contain at least three of the following character types: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, spaces, and special characters `~! @#$
%^&*()-_=+\|[{}];:'",<.>?Cannot be the username spelled forwards or backwards.
The username cannot be changed once ciphertext access is enabled.
Note
Private Network Access or Public Network Access is not displayed for instances with IPv6 enabled.
Configure Kafka SASL_SSL.
This parameter indicates whether to enable SASL authentication when a client connects to the instance. If you enable Kafka SASL_SSL, data will be encrypted for transmission to enhance security.
This setting is enabled by default. It cannot be changed after the instance is created. If you want to use a different setting, you must create a new instance.
After Kafka SASL_SSL is enabled, you can determine whether to enable SASL/PLAIN. If SASL/PLAIN is disabled, the SCRAM-SHA-512 mechanism is used to transmit data. If SASL/PLAIN is enabled, both the SCRAM-SHA-512 and PLAIN mechanisms are supported. You can select either of them as required. The SASL/PLAIN setting cannot be changed once the instance is created.
What are SCRAM-SHA-512 and PLAIN mechanisms?
SCRAM-SHA-512: uses the hash algorithm to generate credentials for usernames and passwords to verify identities. SCRAM-SHA-512 is more secure than PLAIN.
PLAIN: a simple username and password verification mechanism.
If you enable Kafka SASL_SSL, you must also set the username and password for accessing the instance.
Note
This parameter is displayed for instances with IPv6 enabled.
Click Advanced Settings to configure more parameters.
Configure public access.
Public access is disabled by default. You can enable or disable it as required.
After public access is enabled, configure an IPv4 EIP for each broker.
Note
This parameter is displayed for instances with IPv6 enabled.
Configure Smart Connect.
Smart Connect is used for data synchronization between heterogeneous systems. You can configure Smart Connect tasks to synchronize data between Kafka and another cloud service or between two Kafka instances.
Enabling Smart Connect creates two brokers.
Note
Single-node instances do not have this parameter.
Configure Automatic Topic Creation.
This setting is disabled by default. You can enable or disable it as required.
If this option is enabled, a topic will be automatically created when a message is produced in or consumed from a topic that does not exist. The default topic parameters are listed in Table 4.
After you change the value of the log.retention.hours (retention period), default.replication.factor (replica quantity), or num.partitions (partition quantity) parameter, the value will be used in later topics that are automatically created. For example, assume that num.partitions is changed to 5, an automatically created topic has parameters listed in Table 4.
Table 4 Topic parameters¶ Parameter
Default Value
Modified Value
Partitions
3
5
Replicas
3
3
Aging Time (h)
72
72
Synchronous Replication
Disabled
Disabled
Synchronous Flushing
Disabled
Disabled
Message Timestamp
CreateTime
CreateTime
Max. Message Size (bytes)
10,485,760
10,485,760
Specify Tags.
Tags are used to identify cloud resources. When you have multiple cloud resources of the same type, you can use tags to classify them based on usage, owner, or environment.
If you have predefined tags, select a predefined pair of tag key and value. You can click View predefined tags to go to the Tag Management Service (TMS) console and view or create tags.
You can also create new tags by specifying Tag key and Tag value.
Up to 20 tags can be added to each Kafka instance. For details about the requirements on tags, see Configuring Kafka Instance Tags.
Enter a Description of the instance for 0-1024 characters.
Click Create.
Confirm the instance information, and click Submit.
Return to the instance list and check whether the Kafka instance has been created.
It takes 3 to 15 minutes to create an instance. During this period, the instance status is Creating.
If the instance is created successfully, its status changes to Running.
If the instance is in the Failed state, delete it by referring to Deleting Kafka Instances and try creating another one. If the instance creation fails again, contact customer service.
Note
Instances that fail to be created do not occupy other resources.