Configuring a Precise Protection Rule¶
WAF allows you to customize protection rules by combining HTTP headers, cookies, URLs, request parameters, and client IP addresses.
You can combine common HTTP fields, such as IP, Path, Referer, User Agent, and Params in a protection rule to let WAF allow, block, or only log the requests that match the combined conditions.
A reference table can be added to a precise protection rule. The reference table takes effect for all protected domain names.
Note
If you have enabled enterprise projects, ensure that you have all operation permissions for the project where your WAF instance locates. Then, you can select the project from the Enterprise Project drop-down list and configure protection policies for the domain names in the project.
Prerequisites¶
A website has been added to WAF.
Constraints¶
It takes several minutes for a new rule to take effect. After the rule takes effect, protection events triggered by the rule will be displayed on the Events page.
If you configure Protective Action to Block for a precise protection rule, you can configure a known attack source rule by referring to Configuring a Known Attack Source Rule. WAF will block requests matching the configured IP address, Cookie, or Params for a length of time configured as part of the rule.
Application Scenarios¶
Precise protection rules are used for anti-leeching and website management background protection.
Procedure¶
Log in to the management console.
Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.Click
 in the upper left corner and choose Web Application Firewall (Dedicated) under Security.
in the upper left corner and choose Web Application Firewall (Dedicated) under Security.In the navigation pane on the left, choose Website Settings.
In the Policy column of the row containing the target website, click the number to go to the policy configuration page.
In the Precise Protection configuration area, change Status as needed and click Customize Rule to go to the Precise Protection page.

Figure 1 Precise Protection configuration area¶
On the Precise Protection page, set Detection Mode.
Two detection modes are available:
Instant Detection: If a request matches a configured precise protection rule, WAF immediately ends threat detection and blocks the request.
Full Detection: If a request matches a configured precise protection rule, WAF finishes its scan first and then blocks all requests that match the configured precise protection rule.
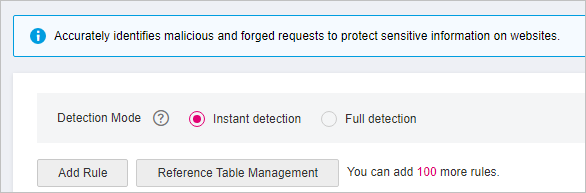
Figure 2 Setting Detection Mode¶
Click Add Rule.
In the displayed dialog box, add a rule by referring to Table 1.
The settings shown in Figure 3 are used as an example. If a visitor tries to access a URL containing /admin, WAF will block the request.
Important
To ensure that WAF blocks only attack requests, configure Protective Action to Log only first and check whether normal requests are blocked on the Events page. If no normal requests are blocked, configure Protective Action to Block.
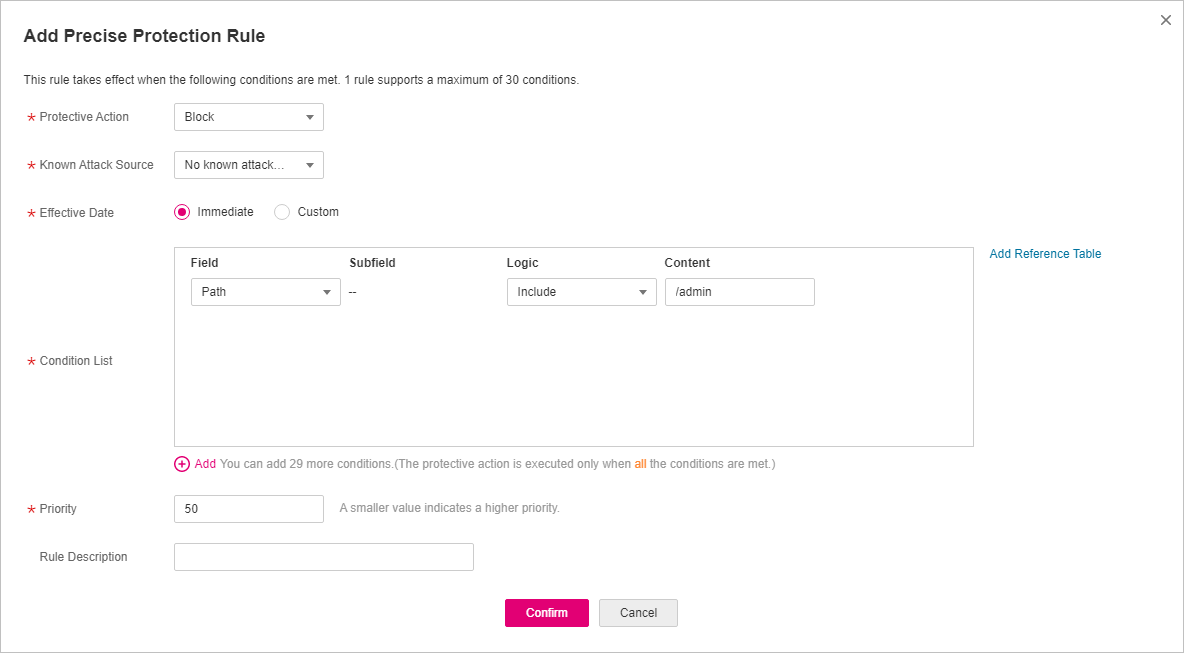
Figure 3 Add Precise Protection Rule¶
Table 1 Rule parameters¶ Parameter
Description
Example Value
Protective Action
You can select Block, Allow, or Log only. Default value: Block
Block
Known Attack Source
If you set Protective Action to Block, you can select a blocking type for a known attack source rule. Then, WAF blocks requests matching the configured IP, Cookie, or Params for a length of time that depends on the selected blocking type.
Long-term IP address blocking
Effective Date
Select Immediate to enable the rule immediately, or select Custom to configure when you wish the rule to be enabled.
Immediate
Condition List
Click Add to add conditions. At least one condition needs to be added. You can add up to 30 conditions to a protection rule. If more than one condition is added, all of the conditions must be met for the rule to be applied. A condition includes the following parameters:
Parameters for configuring a condition are described as follows:
Field
Subfield: Configure this field only when Params, Cookie, or Header is selected for Field.
Logic: Select a logical relationship from the drop-down list.
Note
If Include any value, Exclude any value, Equal to any value, Not equal to any value, Prefix is any value, Prefix is not any of them, Suffix is any value, or Suffix is not any of them is selected, select an existing reference table in the Content drop-down list. For details, see Adding a Reference Table.
Exclude any value, Not equal to any value, Prefix is not any of them, and Suffix is not any of them indicates, respectively, that WAF performs the protection action (block, allow, or log only) when the field in the access request does not contain, is not equal to, or the prefix or suffix is not any value set in the reference table. For example, assume that Path field is set to Exclude any value and the test reference table is selected. If test1, test2, and test3 are set in the test reference table, WAF performs the protection action when the path of the access request does not contain test1, test2, or test3.
Content: Enter or select the content of condition matching.
Note
For more details about the configurations in general, see Table 2.
Path Include /admin
Priority
Rule priority. If you have added multiple rules, rules are matched by priority. The smaller the value you set, the higher the priority.
5
Rule Description
A brief description of the rule. This parameter is optional.
None
Table 2 Condition list configurations¶ Field
Subfield
Logic
Example Content
Path: Part of a URL that does not include a domain name. This value supports exact matches only. For example, if the path to be protected is /admin, Path must be set to /admin.
None
Select a logical relationship from the drop-down list.
/buy/phone/
Important
NOTICE: If Path is set to /, all paths of the website are protected.
User Agent: A user agent of the scanner to be checked.
None
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1)
IP: An IP address of the visitor for the protection.
--
XXX.XXX.1.1
Params: A request parameter.
All fields
Any subfield
Custom
201901150929
Referer: A user-defined request resource.
For example, if the protected path is /admin/xxx and you do not want visitors to access the page from www.test.com, set Content to http://www.test.com.
--
Cookie: A small piece of data to identify web visitors.
All fields
Any subfield
Custom
jsessionid
Header: A user-defined HTTP header.
All fields
Any subfield
Custom
text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
Method: the user-defined request method.
None
GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH
Request Line: Length of a user-defined request line.
None
50
Request: Length of a user-defined request. It includes the request header, request line, and request body.
None
None
Protocol: the protocol of the request.
None
http
Click Confirm. You can then view the added precise protection rule in the protection rule list.
To disable a rule, click Disable in the Operation column of the rule. The default Rule Status is Enabled.
To modify a rule, click Modify in the row containing the rule.
To delete a rule, click Delete in the row containing the rule.
Protection Effect¶
If you have configured a precise protection rule as shown in Figure 3 for your domain name, to verify WAF is protecting your website (www.example.com) against the rule:
Clear the browser cache and enter the domain name in the address bar to check whether the website is accessible.
If the website is inaccessible, connect the website domain name to WAF by following the instructions in Step 1: Add a Website to WAF.
If the website is accessible, go to Step 2.
Clear the browser cache and enter http://www.example.com/admin (or any page containing /admin) in the address bar. Normally, WAF blocks the requests that meet the conditions and returns the block page.
Return to the WAF console. In the navigation pane, click Events. On the displayed page, view or download events data.
Configuration Example - Blocking a Certain Type of Attack Requests¶
Analysis of a specific type of WordPress pingback attack shows that the User Agent field contains WordPress.
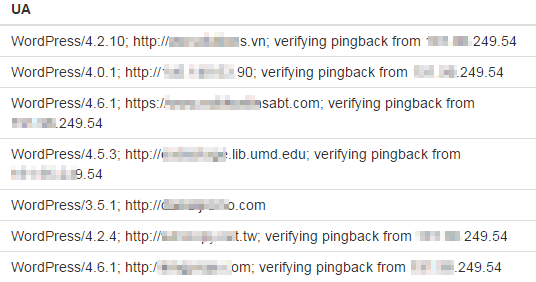
Figure 4 WordPress pingback attack¶
A precise rule as shown in the figure can block this type of attack.
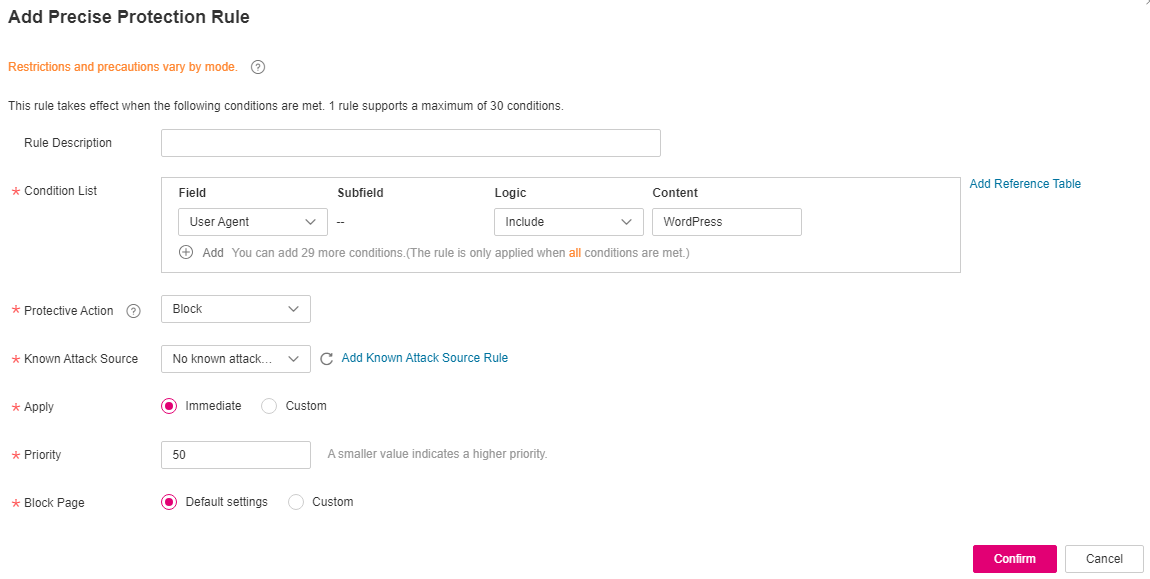
Figure 5 User Agent configuration¶
Configuration Example - Blocking Specified File Types (ZIP, TAR, and DOCX)¶
You can configure file types that match the path field to block specific files of certain types. For example, if you want to block .zip files, you can configure a precise protection rule as shown in Figure 6 to block access requests of .zip files.
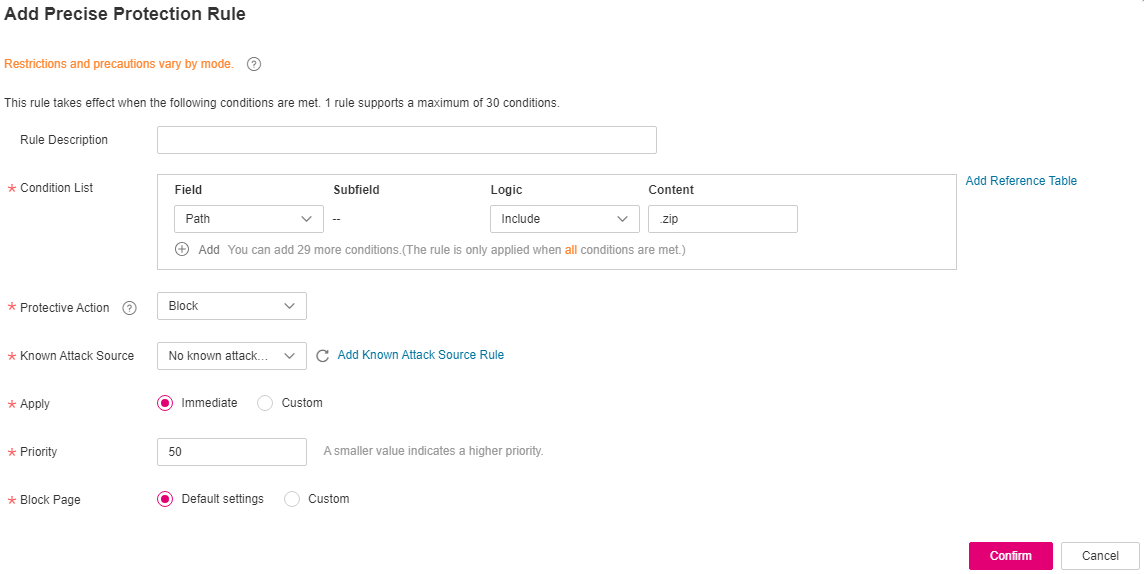
Figure 6 Blocking requests of specific file types¶
Configuration Example - Allowing a Specific IP Address to Access a Certain URL¶
You can configure multiple conditions in the Condition List field. If an access request meets the conditions in the list, WAF will allow the request from a specific IP address to access a specified URL.
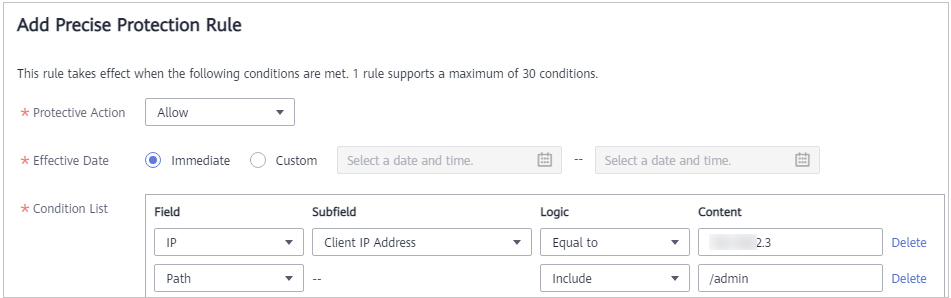
Figure 7 Allowing specific IP addresses to access specified URLs¶