Parameters¶
Parameters¶
Parameters are specified in the parameters field. Using parameters improves template flexibility and reusability. Some parameters in the template can be replaced as needed during stack creation.
You can use defined parameters in resources and outputs fields by invoking internal function get_param.
The following provides an example:
parameters:
name:
type: string
label:
description:
default: Parameter default value
Description:
type: indicates the value type of a parameter, including string and number.
label: indicates the name of the parameter label displayed on the console.
description: indicates an explanation of this parameter.
default: indicates the default value of the parameter.
Parameter Groups¶
A parameter group is specified in the parameter_groups field. This field is used to group entered parameters and specify their sequence. This field is optional.
The following provides an example:
heat_template_version: 2014-10-16
description: Create a serious of random strings
parameters:
name:
type: string
default: random1
length:
type: number
default: 4
length1:
type: number
default: 5
length2:
type: number
default: 4
parameter_groups:
- label: length
parameters:
- length
- length2
- length1
resources:
random1:
type: OS::Heat::RandomString
properties:
length: 5
random2:
type: OS::Heat::RandomString
properties:
length: 5
The parameter group includes three parameters: length, length1, and length2. Set label to length and define these parameters in the Parameters area. After a template is uploaded, parameters are classified into two types: length Parameters and Other Parameters on the Specify Details page.
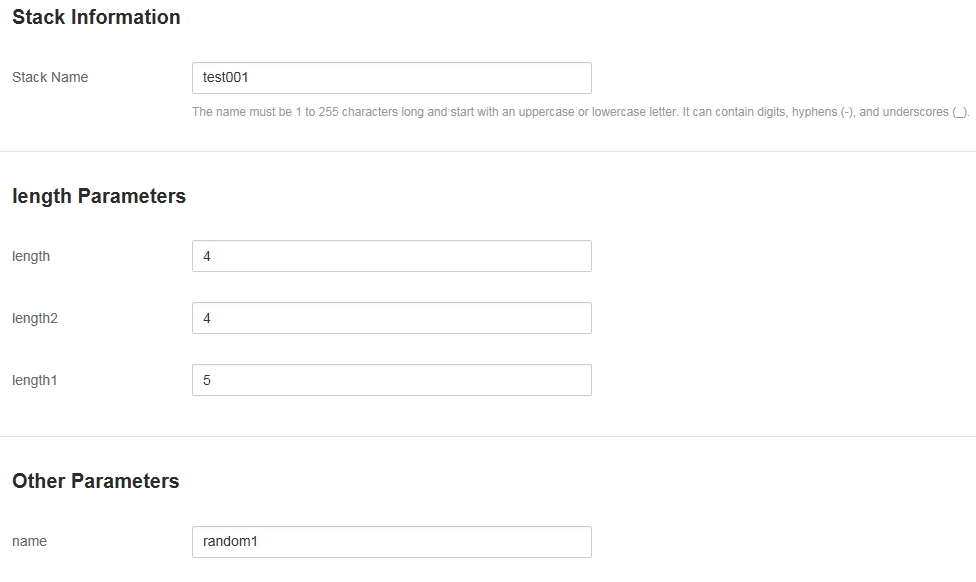
Figure 1 Parameter information¶
Parameter Constraints¶
When compiling a template, you can configure custom_constraint to obtain the list of values on the Specify Details page. You only need to select a value from the drop-downlist, reducing configuration time.
The custom_constraint attribute currently supports the following types:
glance.image
cinder.volume
neutron.network
neutron.router
neutron.subnet
nova.flavor
nova.keypair
For example, custom_constraint is configured for parameters image, key_name, flavor, and networks in the template for creating an ECS. The list of values of four parameters on the Specify Details page. For details, see Creating Resources Using a Template (Using the Console).
Valid Parameter Values¶
Valid-value constraints can be applied to numeric or string-type parameters, which specify a set of parameter values that a parameter may have. During the deployment, user-supplied values must match an element in the list of valid values.
The syntax is as follows:
allowed_values: [<value 1>, <value 2>, ...]
Or the following format:
allowed_values:
- <value 1>
- <value 2>
- ...