Basic Concepts¶
Account
An account refers to the username created during user registration and has complete access to all resources and cloud services. It can reset user passwords and assign user permissions. To ensure account security, it is recommended that you do not use the account for daily management tasks. Instead, create IAM users and use them for such purposes.
User
A user is created in IAM using an account and is a person who uses cloud services with identity credentials such as a password and access key. Typically, when authorizing API calls, you will need to provide information such as the account name, username, and password.
Region
A region is a physical location where a cloud service is deployed. Availability zones (AZs) in the same region can communicate with each other over an intranet but AZs in different regions cannot communicate with each other. By creating cloud resources in different regions, you can design applications to better meet customer requirements and comply with local laws and regulations.
Availability zone
An AZ contains one or more physical data centers. It has independent cooling, fire extinguishing, moisture-proof, and electricity facilities. Within an AZ, compute network, storage, and other resources are logically divided into multiple clusters. AZs within a region are interconnected using high-speed optical fibers to allow you to build cross-AZ high-availability systems.
Project
Projects group and isolate resources (including compute, storage, and network resources) across physical regions. A default project is provided for each region, and subprojects can be created under each default project. Users can be granted permissions to access all resources in a specific project. If you need more refined access control, create subprojects under a default project and purchase resources in subprojects. Then you can assign users the permissions required to access only the resources in the specific subprojects.
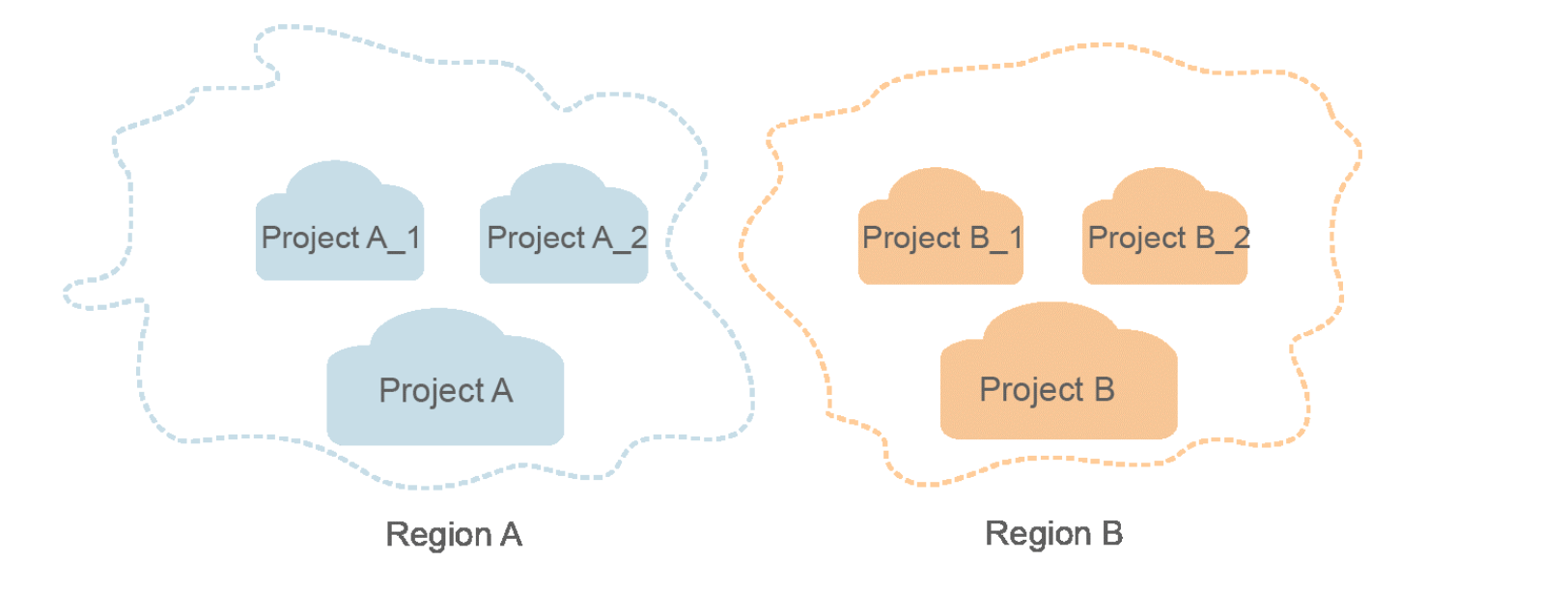
Figure 1 Example project isolation model¶
Checkpoint
Consumption checkpoint. When an application consumes data, the latest SN of the consumed data is recorded as a checkpoint. When the data is consumed again, the consumption can be continued based on this checkpoint.
App
Application identifier. Multiple applications can access data in the same stream. Checkpoints generated for each application are used to record the consumed data in the stream by each application.