Concurrent Operation Consistency¶
If there is a successful response to a write or deletion request sent by a client, the client can obtain the latest data. If a write operation times out, or the server returns HTTP response error code 500 or 503, the follow-up read operations may fail. If such an error occurs, query whether the data has been successfully uploaded to the server. If not, upload the data again.
If multiple clients simultaneously upload, query, or delete the same object or bucket, these operations may reach the system at different times and have different latency periods. The results that return may also be different than those expected. For example, if multiple clients simultaneously upload the same object, a new upload request will replace the prior one. If you want to prevent an object from being simultaneously accessed, you must add a lock mechanism for the object in upper-layer applications.
Concurrent Operation Examples¶
The following provides eight concurrent operation examples.
At the same time as Client 2 is uploading object v1, Client 1 is uploading object v2 with the same name. After the object data is successfully uploaded, both Client1 and Client 2 can access the latest object v2, as shown in Figure 1.
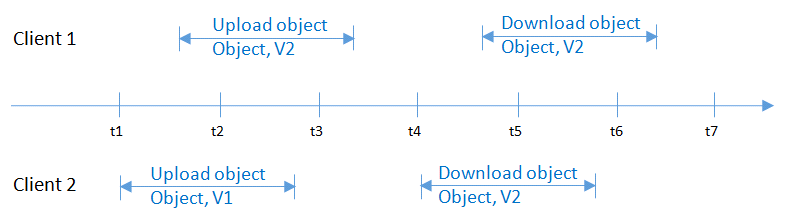
Figure 1 Concurrent uploading of the same object¶
At the same time as Client 2 is uploading object v1 and before metadata is written, Client 1 deletes an object with the same name. The uploading operation of Client 1 is still successful, and both Client 1 and Client 2 can access object v1, as shown in Figure 2.
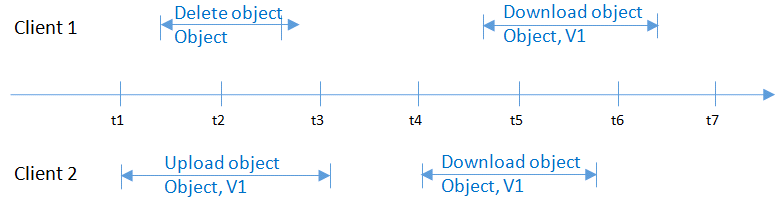
Figure 2 Concurrent uploading and deletion of the same object (1)¶
At the same time as Client 2 has successfully uploaded object v1 and while metadata is still being written, Client 1 deletes an object with the same name. The uploading operation of Client 1 is still successful, but when Client 1 and Client 2 attempt to download the object, an error may display indicating that the object does not exist, as shown in Figure 3.
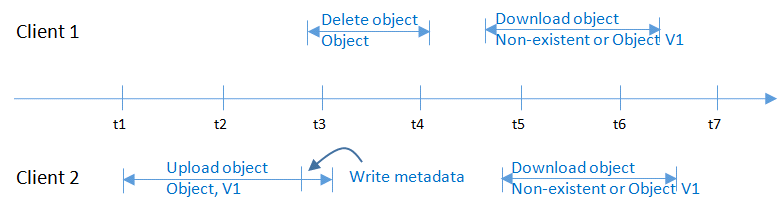
Figure 3 Concurrent uploading and deletion of the same object (2)¶
At the same time as Client 1 is downloading an object, Client 2 is deleting an object with the same name. Client 1 may download complete object data, or may download only a part of data. After Client 2 receives a deletion success message, the attempt to download the object will fail, and an error will return indicating that the object does not exist, as shown in Figure 4.
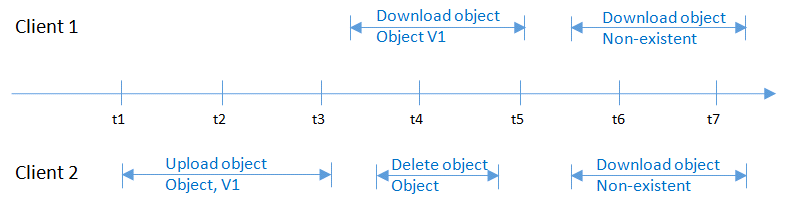
Figure 4 Concurrent downloading and deletion of the same object¶
At the same time as Client 1 is downloading an object, Client 2 is updating an object with the same name. Client 1 may download complete object data, or may download only a part of data. After Client 2 receives an update success message, the attempt to download the object will succeed, and the latest data will return, as shown in Figure 5.
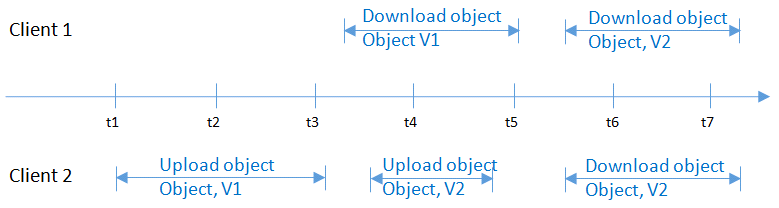
Figure 5 Concurrent downloading and updating of the same object¶
At the same time as Client 1 is uploading part v2 of an object, Client 2 is uploading part v1 of the same object. After part v2 is uploaded successfully, both Client 1 and Client 2 can list the information about the multipart whose entity tag (ETag) is part v2, as shown in Figure 6.
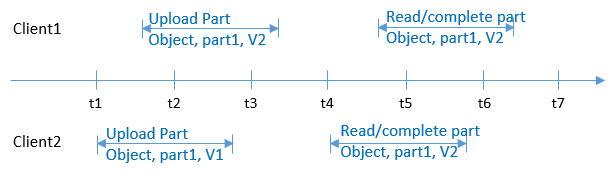
Figure 6 Concurrently uploading the same multipart of the same object¶
If a client uploads an object and a timeout occurs or error code 500 or 503 is returned, one of the following symptoms will occur in a subsequent object downloading and listing operation:
If the object fails to be uploaded, the object cannot be downloaded and is not in the object list.
If the object upload operation times out, there is an extremely low possibility that the head operation on the object is normal, but the 500 error code is reported for an attempt to download this object. In this case, please upload the object again.
If the object is newly created, it is not in the object list but can be downloaded using its name.
If the object is overwritten, its listed information, such as the size, ETag, creation time, and owner, is inconsistent with that obtained when you download it.
If Client 1 uploads object v1 and Client 2 uploads object v2 with the same name concurrently, and status code 200 is returned, one of the following symptoms will occur in a subsequent object downloading and listing operation:
Object v1 is downloaded and listed.
Object v2 is downloaded and listed.
Object v1 is downloaded while object v2 is displayed in the object list.
Object v2 is downloaded while object v1 is displayed in the object list.