Creating a Public NAT Gateway¶
Scenarios¶
Create a public NAT gateway to enable your servers to access the Internet or provide services accessible from the Internet.
Notes and Constraints¶
Rules on one public NAT gateway can use the same EIP, but rules on different NAT gateways must use different EIPs.
Each VPC can be associated with multiple public NAT gateways.
SNAT and DNAT rules can use the same EIP to save resources. However, when Port Type of a DNAT rule is set to All ports, the resource in the DNAT rule will preferentially use all ports of the EIP. So an SNAT rule cannot share an EIP with such a DNAT rule.
If both an EIP and a public NAT gateway are configured for a server, data will be forwarded through the EIP.
Prerequisites¶
The VPC and subnet where your public NAT gateway will be deployed are available.
To allow traffic to pass through the public NAT gateway, a route to the public NAT gateway in the VPC is required. When you create a public NAT gateway, a default route 0.0.0.0/0 to the public NAT gateway is automatically added to the default route table of the VPC. If the default route 0.0.0.0/0 already exists in the default route table of the VPC before you create the public NAT gateway, the default route that points to the public NAT gateway will fail to be added automatically. In this case, perform the following operations after the public NAT gateway is successfully created: Manually add a different route that points to the gateway or create a default route 0.0.0.0/0 pointing to the gateway in the new routing table.
Procedure¶
Log in to the management console.
Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.In the upper left corner of the page, click
 to expand the service list and choose Network > NAT Gateway.
to expand the service list and choose Network > NAT Gateway.The Public NAT Gateways page is displayed.
On the Public NAT Gateways page, click Create Public NAT Gateway.
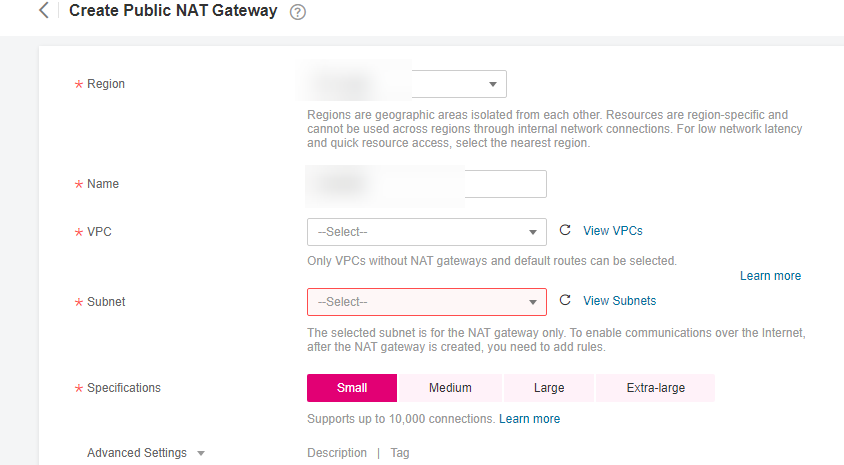
Figure 1 Create Public NAT Gateway¶
Configure required parameters. For details, see Table 1.
Table 1 Descriptions of public NAT gateway parameters¶ Parameter
Description
Region
The region where the public NAT gateway is located.
Specifications
The specifications of the public NAT gateway.
The value can be Micro, Small, Medium, Large, or Extra-large. You can click Learn more on the page to view details of each specification.
Name
The name of the public NAT gateway. Enter up to 64 characters. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.) are allowed.
VPC
The VPC that the public NAT gateway belongs to.
The selected VPC cannot be changed after the public NAT gateway is created.
Note
To allow traffic to pass through the public NAT gateway, a route to the public NAT gateway in the VPC is required. When you create a public NAT gateway, a default route 0.0.0.0/0 to the public NAT gateway is automatically added to the default route table of the VPC. If the default route 0.0.0.0/0 already exists in the default route table of the VPC before you create the public NAT gateway, the default route that points to the public NAT gateway will fail to be added automatically. In this case, perform the following operations after the public NAT gateway is successfully create: Manually add a different route that points to the gateway or create a default route 0.0.0.0/0 pointing to the gateway in the new routing table.
Subnet
The subnet that the public NAT gateway belongs to.
The subnet must have at least one available IP address.
The selected subnet cannot be changed after the public NAT gateway is created.
The NAT gateway will be deployed in the selected subnet. The NAT gateway works for the entire VPC where it is deployed. To enable communications over the Internet, add SNAT or DNAT rules.
Enterprise Project
The enterprise project that the public NAT gateway belongs to. If an enterprise project has been configured, select the enterprise project. If you have not configured any enterprise project, select the default enterprise project.
Advanced Settings (Optional)
Click the drop-down arrow to configure advanced parameters of the public NAT gateway, such as Description.
Description
Supplementary information about the public NAT gateway. Enter up to 255 characters. Angle brackets (<>) are not allowed.
Tag
The identifier of the public NAT gateway. A tag is a key-value pair. You can add up to 20 tags to each public NAT gateway.
The tag key and value must meet the requirements listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Tag requirements¶ Parameter
Requirement
Key
Cannot be left blank.
Must be unique for each NAT gateway.
Can contain a maximum of 36 characters.
Contains only letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and at signs (@).
Value
Can contain a maximum of 43 characters.
Contains only letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and at signs (@).
Click Create Now. On the page displayed, confirm the public NAT gateway specifications.
Click Submit.
It takes 1 to 5 minutes to create a public NAT gateway.
In the public NAT gateway list, you can see the gateway status. For details about the NAT gateway status, see Table 3.
Table 3 NAT gateway statuses¶ Status
Description
Running
The NAT gateway is normal.
Creating
The NAT gateway is being created.
Updating
The NAT gateway is being updated.
Deleting
The NAT gateway is being deleted.
Frozen
The NAT gateway has been frozen.
Abnormal
The NAT gateway is abnormal.
Note
After the public NAT gateway is created, check whether a default route (0.0.0.0/0) that points to the public NAT gateway exists in the default route table of the VPC where the public NAT gateway is. If no, add a route pointing to the public NAT gateway to the default route table, alternatively, create a custom route table and add the default route 0.0.0.0/0 pointing to the public NAT gateway to the table.
What Should I Do If the Number of NAT Gateway Connections Exceeds the Upper Limit?¶
If the number of requests exceeds the maximum allowed connections of a public NAT gateway, services will be adversely affected. To avoid this situation, create alarm rules on the Cloud Eye console to monitor the number of SNAT connections.
If the number of requests exceeds the maximum allowed connections of a NAT gateway, you are advised to update the NAT gateway by referring to Managing Public NAT Gateways.
Does Changing NAT Gateway Specifications Interrupt Services?¶
Using a public NAT gateway of more robust specifications does not affect services, but if you switch to a public NAT gateway of less robust specifications, ensure that its capacity can still be enough to meet your service requirements.