Scaling a Real-Time Service¶
Overview¶
Note
This is a whitelist feature. Contact technical support for a trial as you need.
ModelArts provides manual scaling and auto scaling to meet different user requirements. Only the number of instances of a single model can be changed.
Manual scaling allows you to manually change the number of instances of a single model.
Auto Scaling allows you to configure scaling policies to add instances when the traffic is high, and reduce them when the traffic is low. This helps you use your resources more efficiently.
Table 1 Comparison between manual scaling and auto scaling¶ Scaling Type
Manual Scaling
Auto Scaling
Method
Manual
Auto
Operation
Change the number of instances.
Configure scaling policies.
Execution
Executed after manual configuration
Periodically triggered or triggered by metrics
Result after scaling failed
The number of instances reverts to the previous value.
The number of instances changes to a specific value.
Prerequisites¶
The service status is Running, Abnormal, or Alarm.
Constraints¶
Real-time services deployed in a public resource pool do not support auto scaling.
Scaling is not allowed when a service is stopped, abnormal, being deployed, or being scaled.
At least one policy rule must be configured.
Manual Scaling¶
Manual scaling allows you to manually change the number of instances of a single model.
Log in to the ModelArts console. In the navigation pane, choose Model Deployment > Real-Time Services.
Choose More > Resize Compute Resources in the Operation column of the target service, and click Resize Compute Resources in the Operation column of the target model version.
Set the following parameters. Other parameters cannot be modified.
Auto Stop: This parameter is displayed if auto stop is enabled for the service. The service will automatically stop upon the specified time. You can click Modify to change the auto stop time.
Resize Type: Select Manual.
Instances: Set the number of required instances. The minimum value is 1.
Click Next and then Submit. The real-time service list page is displayed.
Auto Scaling¶
Auto scaling allows you to configure scaling policies to add instances when the traffic is high, and reduce them when the traffic is low. This helps you use your resources more efficiently.
Log in to the ModelArts console. In the navigation pane, choose Model Deployment > Real-Time Services.
Choose More > Resize Compute Resources in the Operation column of the target service, and click Resize Compute Resources in the Operation column of the target model version.
Configure parameters. The service name, current model version, resource pool, model and version, and instance specifications cannot be modified.
Auto Stop: This parameter is displayed if auto stop is enabled for the service. The service will automatically stop upon the specified time. You can click Modify to change the auto stop time.
Configuring a scaling policy
The following table lists the parameters.
Table 2 Policy parameters¶ Parameter
Description
Policy Name
Name of a scaling policy. The value can contain 1 to 64 visible characters, including only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.), and must start or end with a letter or digit.
Trigger Type
Scheduled: Set a scheduled scaling policy to trigger scaling at a specified time.
Scheduling Rule: View, add, delete, enable, or disable scheduling rules. You can add rules only when the service is in the Running, Alarm, Stopped, Deploying, or Abnormal state. A maximum of 10 scheduling rules can be added. A maximum of two unique resource metric rules can be added.
Type of the scaling, which can be scheduled scaling and metric-based scaling.
Scheduled: Set a scheduled scaling policy to trigger scaling at a specified time.
Scheduling Rule: View, add, delete, enable, or disable scheduling rules.
Metric-based: You can set metric policy rules to automatically trigger scaling when metrics are met. Metric parameters:
Min Instances: Minimum number of instances for each automatic capacity reduction. This number defaults to the instance number when the pool is resized.
Max Instances: Maximum number of instances for each automatic capacity reduction.
Cooldown Period: Data cooldown time window. After the scale-out or scale-in, the system enters the cooldown period. During this period, scale-out or scale-in will not be triggered again. The minimum value is 1 minute.
Scheduling Rule: View, add, delete, enable, or disable scheduling rules.
Viewing a rule
In the scheduling rule list, you can view the rule name, status, rule type, triggering condition, number of target instances, whether to enable the rule, and operations.
The rule statuses include Creating, Configured, Configuration failed, Triggered, Trigger failed. If a rule has been configured but not triggered, its status is Configured. After a rule is triggered and the resource pool is resized, the rule status is Triggered. If a rule is created when the service is stopped, the status is Creating. After the service is started, the rule is automatically configured.
Adding a rule
Click Add. In the Add Rule dialog box that appears, configure parameters and click OK.
The following table describes the rule parameters.
Table 3 Rule parameters (scheduled triggering)¶ Parameter
Description
Rule Name
The value can contain only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.), and must start and end with a letter or digit. The rule name must be unique. A maximum of 20 characters are supported.
Target Instances
Set the number of target instances for scaling.
Triggered
Choose when to run the rule. You can set it to run daily, weekly, monthly, or at a custom time using a cron expression. This time indicates the local time of where the node is deployed. For details about how to use a cron expression, see Cron Expression.
Table 4 Rule parameters (metric-based triggering)¶ Parameter
Description
Rule Name
Name of a policy. The value can contain only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.), and must start and end with a letter or digit. The rule name must be unique. A maximum of 20 characters are supported.
Triggered By
You can select the CPU usage and memory usage metrics.
Expected Value
This parameter indicates the expected value of the selected metric. The number of new instances required (rounded up) = Current metric value/Expected value x Number of current instances
Tolerance Range
Scaling will not be triggered when the value is within the range. The expected value must be within the tolerance range.
Note
You can add a maximum of 10 rules.
Deleting a rule
Click Delete in the Operation column of the scheduling rule you want to remove.
Enabling or disabling a rule
Click the button in the Enable column of the scheduling rule you want to enable or disable. After a rule is disabled, it does not take effect.
After you click Next and Submit, the service automatically resizes based on the configured scaling policy.
Cron Expression¶
You can use a cron expression to trigger auto scaling. A cron expression is in the format of "Minute Hour Date Month Week". For example, 30 10 15 * * indicates that the rule is triggered at 10:30 on the 15th day of each month. You must set the cron expression based on the local time zone.
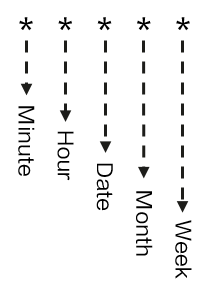
Figure 1 Cron expression syntax¶
Time parameters
Table 5 Time parameters¶ Parameter
Option
Available Special Character
Minute
0 to 59
* , - /
Hour
0 to 23
* , - /
Day
1 to 31
* , - /
Month
1 to 12 or JAN to DEC
* , - /
Day in a week
0 to 6 or SUN to SAT
* , - /
Special characters
Table 6 Special characters¶ Special Character
Description
Wildcard (
*)Can be any value. For example, 0 0 1 * * indicates 00:00 on the first day of each month.
Comma (,)
Separates items in a list. For example, 0 12,16 * * * indicates 12:00 and 16:00 every day.
Hyphen (-)
Indicates a value range. For example, 0 12-16 * * * indicates 12:00 to 16:00 every day.
Slash (/)
Indicates the range increment. For example, */10 * * * * indicates the 0th minute, 10th minute, 20th minute, 30th minute, 40th minute, and 50th minute of each hour. A slash can be used together with a hyphen. For example, 3-59/15 * * * indicates that a value is obtained every 15 minutes from the 3rd minute to the 59th minute in an hour. The valid time points can be 0:03, 0:18, 0:43, and 0:58.