Application Scenarios¶
Big data is ubiquitous in people's lives. MRS is suitable to process big data in the industries such as the Internet of things (IoT), e-commerce, finance, manufacturing, healthcare, energy, and government departments.
Large-scale data analysis¶
Large-scale data analysis is a major scenario in modern big data systems. Generally, an enterprise has multiple data sources. After data is accessed,extract, transform, and load (ETL) processing is required to generate modelized data for each service module to analyze and sort out data. This type of service has the following characteristics:
The requirements for real-time execution are not high, and job execution time ranges from dozens of minutes to hours.
The data volume is large.
There are various data sources and diversified formats.
Data processing usually consists of multiple tasks, and resources need to be planned in detail.
In the environmental protection industry, climate data is stored on OBS and periodically dumped into HDFS for batch analysis. 10 TB of climate data can be analyzed in 1 hour.
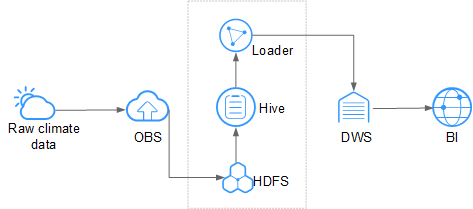
Figure 1 Large-scale data analysis in the environmental protection industry¶
MRS has the following advantages in this scenario.
Low cost: OBS offers cost-effective storage.
Massive data analysis: TB/PB-level data is analyzed by Hive.
Visualized data import and export tool: Loader exports data to Data Warehouse Service (DWS) for business intelligence (BI) analysis.
Large-scale data storage¶
A user who has a large amount of structured data usually requires index-based quasi-real-time query capabilities. For example, in an Internet of Vehicles (IoV) scenario, vehicle maintenance information is queried by vehicle number. Therefore, vehicle information is indexed based on vehicle numbers when it is being stored, to implement second-level response in this scenario. Generally, the data volume is large. The user may store data for one to three years.
For example, in the IoV industry, an automobile company stores data on HBase, which supports PB-level storage and CDR queries in milliseconds.
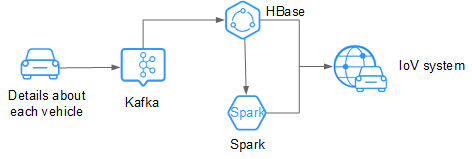
Figure 2 Large-scale data storage in the IoV industry¶
MRS has the following advantages in this scenario.
Real time: Kafka accesses massive amounts of vehicle messages in real time.
Massive data storage: HBase stores massive volumes of data and supports data queries in milliseconds.
Distributed data query: Spark analyzes and queries massive volumes of data.
Real-time data processing¶
Real-time data processing is usually used in scenarios such as anomaly detection, fraud detection, rule-based alarming, and service process monitoring. Data is processed while it is being inputted to the system.
For example, in the Internet of elevators & escalators (IoEE) industry, data of smart elevators and escalators is imported to MRS streaming clusters in real time for real-time alarming.
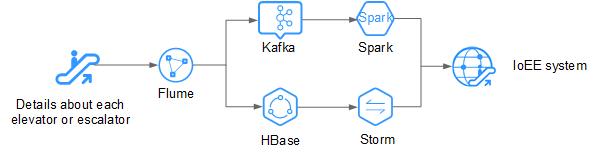
Figure 3 Low-latency streaming processing in the IoEE industry¶
MRS has the following advantages in this scenario.
Real-time data ingestion: Flume implements real-time data ingestion and provides various data collection and storage access methods.
Data source access: Kafka accesses data of tens of thousands of elevators and escalators in real time.