Kafka Specifications¶
This section applies to MRS 3.x or later.
Upper Limit of Topics¶
The maximum number of topics depends on the number of file handles (mainly used by data and index files on site) opened in the process.
Run the ulimit -n command to view the maximum number of file handles that can be opened in the process.
Run the lsof -p <Kafka PID> command to view the file handles (which may keep increasing) that are opened in the Kafka process on the current single node.
Determine whether the maximum number of file handles will be reached and whether the running of Kafka is affected after required topics are created, and estimate the maximum size of data that each partition folder can store and the number of data
*log file, whose default size is 1 GB and can be adjusted by modifying log.segment.bytes) and index*index file, whose default size is 10 MB and can be adjusted by modifying log.index.size.max.bytes) files that will be produced after required topics are created.
Number of Concurrent Consumers¶
In an application, it is recommended that the number of concurrent consumers in a group be the same as the number of partitions in a topic, ensuring that a consumer consumes data in only a specified partition. If the number of concurrent consumers is more than the number of partitions, the redundant consumers have no data to consume.
Relationship Between Topic and Partition¶
If K Kafka nodes are deployed in the cluster, each node is configured with N disks, the size of each disk is M, the cluster contains n topics (named as T1, T2, ..., Tn), the data input traffic per second of the m topic is X (Tm) MB/s, the number of configured replicas is R (Tm), and the configured data retention time is Y (Tm) hour, the following requirement must be met:
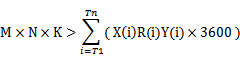
If the size of a disk is M, the disk has n partitions (named as P0, P1, ..., Pn), the data write traffic per second of the m partition is Q (Pm) MB/s (calculation method: data traffic of the topic to which the m partition belongs divided by the number of partitions), and the data retention time is T (Pm) hours, the following requirement must be met for the disk:
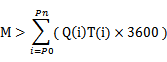
Based on the throughput, if the throughput that can be reached by the producer is P, the throughput that can be reached by the consumer is C, and the expected throughput of Kafka is T, it is recommended that the number of partitions of the topic be set to Max(T/P, T/C).
Note
In a Kafka cluster, more partitions mean higher throughput. However, too many partitions also pose potential impacts, such as a file handle increase, unavailability increase (for example, if a node is faulty, the time window becomes large after the leader is reselected in some partitions), and end-to-end latency increase.
Suggestion: The disk usage of a partition is smaller than or equal to 100 GB; the number of partitions on a node is smaller than or equal to 3,000; the number of partitions in the entire cluster is smaller than or equal to 10,000.