Using Flink from Scratch¶
This section describes how to use Flink to run wordcount jobs.
Prerequisites¶
Flink has been installed in an MRS cluster.
The cluster runs properly and the client has been correctly installed, for example, in the /opt/hadoopclient directory. The client directory in the following operations is only an example. Change it to the actual installation directory.
Using the Flink Client (Versions Earlier Than MRS 3.x)¶
Log in to the node where the client is installed as the client installation user.
Run the following command to go to the client installation directory:
cd /opt/hadoopclient
Run the following command to initialize environment variables:
source /opt/hadoopclient/bigdata_env
If Kerberos authentication is enabled for the cluster, perform the following steps. If not, skip this whole step.
Prepare a user for submitting Flink jobs..
Log in to Manager and download the authentication credential.
Log in to Manager of the cluster. For details, see Accessing MRS Manager (Versions Earlier Than MRS 3.x). Choose System Settings > User Management. In the Operation column of the row that contains the added user, choose More > Download Authentication Credential.
Decompress the downloaded authentication credential package and copy the user.keytab file to the client node, for example, to the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf directory on the client node. If the client is installed on a node outside the cluster, copy the krb5.conf file to the /etc/ directory on this node.
Configure security authentication by adding the keytab path and username in the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/flink-conf.yaml configuration file.
security.kerberos.login.keytab: <user.keytab file path>
security.kerberos.login.principal: <Username>
Example:
security.kerberos.login.keytab: /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/user.keytab
security.kerberos.login.principal: test
Generate the generate_keystore.sh script and place it in the bin directory of the Flink client. In the bin directory of the Flink client, run the following command to perform security hardening. For details, see Authentication and Encryption. Set password in the following command to a password for submitting jobs:
sh generate_keystore.sh <password>
The script automatically replaces the SSL value in the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/flink-conf.yaml file. For an MRS 2.x or earlier security cluster, external SSL is disabled by default. To enable external SSL, configure the parameter and run the script again. For details, see Security Hardening.
Note
You do not need to manually generate the generate_keystore.sh script.
After authentication and encryption, the generated flink.keystore, flink.truststore, and security.cookie items are automatically filled in the corresponding configuration items in flink-conf.yaml.
Configure paths for the client to access the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files.
Absolute path: After the script is executed, the file path of flink.keystore and flink.truststore is automatically set to the absolute path /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/ in the flink-conf.yaml file. In this case, you need to move the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files from the conf directory to this absolute path on the Flink client and Yarn nodes.
Relative path: Perform the following steps to set the file path of flink.keystore and flink.truststore to the relative path and ensure that the directory where the Flink client command is executed can directly access the relative paths.
Create a directory, for example, ssl, in /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/.
cd /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/
mkdir ssl
Move the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files to the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/ssl/ directory.
mv flink.keystore ssl/
mv flink.truststore ssl/
Change the values of the following parameters to relative paths in the flink-conf.yaml file:
security.ssl.internal.keystore: ssl/flink.keystore security.ssl.internal.truststore: ssl/flink.truststore
Run a wordcount job.
Important
To submit or run jobs on Flink, the user must have the following permissions:
If Ranger authentication is enabled, the current user must belong to the hadoop group or the user has been granted the /flink read and write permissions in Ranger.
If Ranger authentication is disabled, the current user must belong to the hadoop group.
Normal cluster (Kerberos authentication disabled)
Run the following commands to start a session and submit a job in the session:
yarn-session.sh -nm "session-name"
flink run /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Run the following command to submit a single job on Yarn:
flink run -m yarn-cluster /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Security cluster (Kerberos authentication enabled)
If the flink.keystore and flink.truststore file are stored in the absolute path:
Run the following commands to start a session and submit a job in the session:
yarn-session.sh -nm "session-name"
flink run /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Run the following command to submit a single job on Yarn:
flink run -m yarn-cluster /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
If the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files are stored in the relative path:
In the same directory of SSL, run the following commands to start a session and submit jobs in the session. The SSL directory is a relative path. For example, if the SSL directory is opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/, then run the following commands in this directory:
yarn-session.sh -t ssl/ -nm "session-name"
flink run /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Run the following command to submit a single job on Yarn:
flink run -m yarn-cluster -yt ssl/ /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
After the job has been successfully submitted, the following information is displayed on the client:
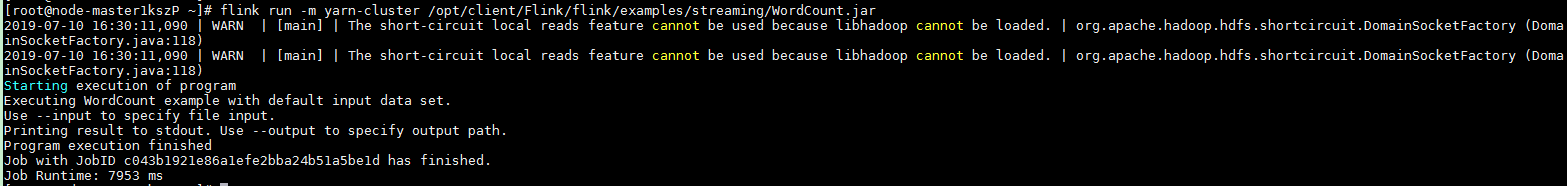
Figure 1 Job submitted successfully on Yarn¶

Figure 2 Session started successfully¶
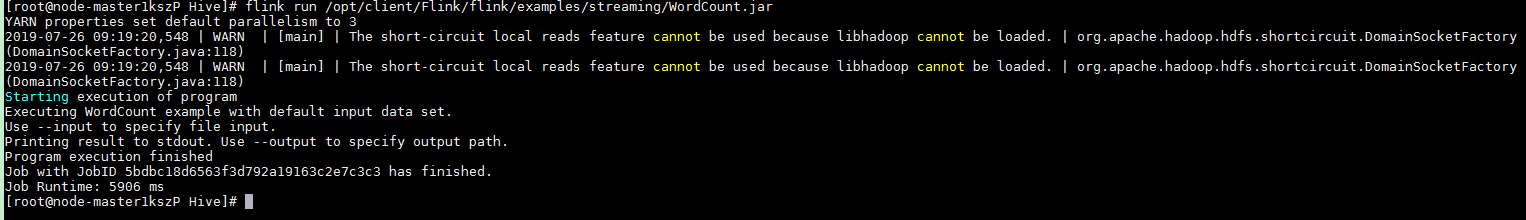
Figure 3 Job submitted successfully in the session¶
Go to the native YARN service page, find the application of the job, and click the application name to go to the job details page. For details, see Viewing Flink Job Information.
If the job is not completed, click Tracking URL to go to the native Flink page and view the job running information.
If the job submitted in a session has been completed, you can click Tracking URL to log in to the native Flink service page to view job information.
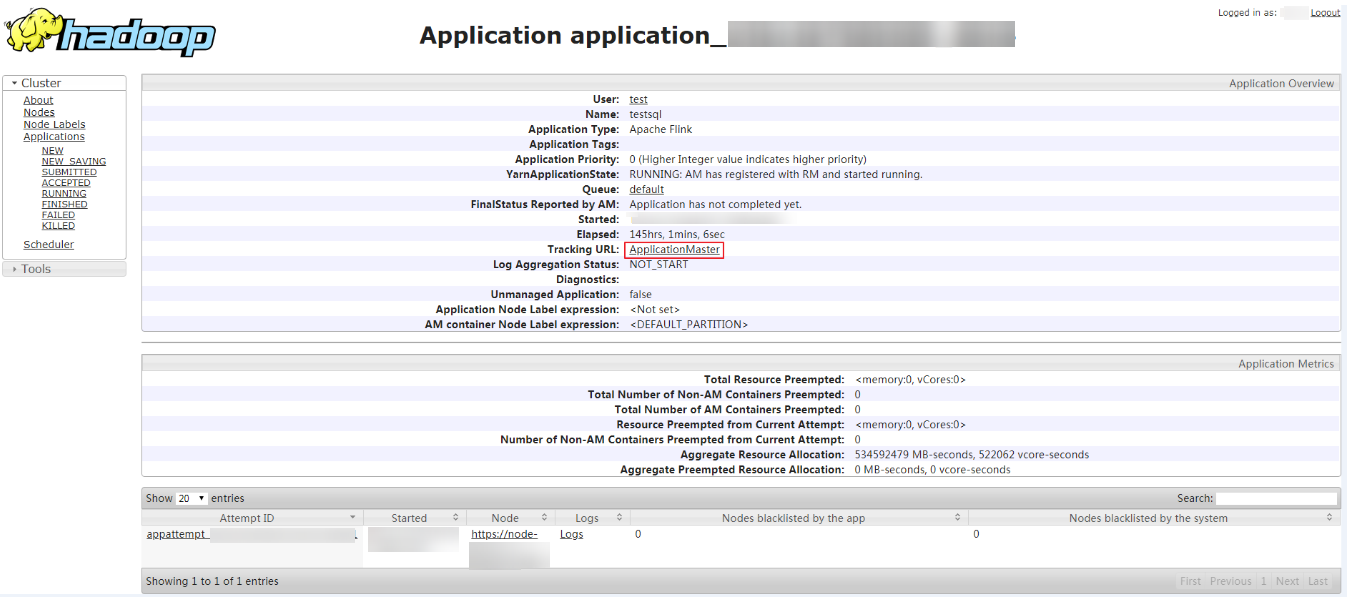
Figure 4 Application¶
Using the Flink Client (MRS 3.x or Later)¶
Log in to the node where the client is installed as the client installation user.
Run the following command to go to the client installation directory:
cd /opt/hadoopclient
Run the following command to initialize environment variables:
source /opt/hadoopclient/bigdata_env
If Kerberos authentication is enabled for the cluster, perform the following steps. If not, skip this whole step.
Prepare a user for submitting Flink jobs.
Log in to Manager and download the authentication credential.
Log in to Manager. For details, see Accessing FusionInsight Manager (MRS 3.x or Later). Choose System > Permission > Manage User. On the displayed page, locate the row that contains the added user, click More in the Operation column, and select Download authentication credential.
Decompress the downloaded authentication credential package and copy the user.keytab file to the client node, for example, to the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf directory on the client node. If the client is installed on a node outside the cluster, copy the krb5.conf file to the /etc/ directory on this node.
Append the service IP address of the node where the client is installed, floating IP address of Manager, and IP address of the master node to the jobmanager.web.access-control-allow-origin and jobmanager.web.allow-access-address configuration item in the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/flink-conf.yaml file. Use commas (,) to separate IP addresses.
jobmanager.web.access-control-allow-origin: xx.xx.xxx.xxx,xx.xx.xxx.xxx,xx.xx.xxx.xxx jobmanager.web.allow-access-address: xx.xx.xxx.xxx,xx.xx.xxx.xxx,xx.xx.xxx.xxx
Note
To obtain the service IP address of the node where the client is installed, perform the following operations:
Node inside the cluster:
In the navigation tree of the MRS management console, choose Clusters > Active Clusters, select a cluster, and click its name to switch to the cluster details page.
On the Nodes tab page, view the IP address of the node where the client is installed.
Node outside the cluster: IP address of the ECS where the client is installed.
To obtain the floating IP address of Manager, perform the following operations:
In the navigation tree of the MRS management console, choose Clusters > Active Clusters, select a cluster, and click its name to switch to the cluster details page.
On the Nodes tab page, view the Name. The node that contains master1 in its name is the Master1 node. The node that contains master2 in its name is the Master2 node.
Log in to the Master2 node remotely, and run the ifconfig command. In the command output, eth0:wsom indicates the floating IP address of MRS Manager. Record the value of inet. If the floating IP address of MRS Manager cannot be queried on the Master2 node, switch to the Master1 node to query and record the floating IP address. If there is only one Master node, query and record the cluster manager IP address of the Master node.
Configure security authentication by adding the keytab path and username in the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/flink-conf.yaml configuration file.
security.kerberos.login.keytab: <user.keytab file path>
security.kerberos.login.principal: <Username>
Example:
security.kerberos.login.keytab: /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/user.keytab
security.kerberos.login.principal: test
Generate the generate_keystore.sh script and place it in the bin directory of the Flink client. In the bin directory of the Flink client, run the following command to perform security hardening. For details, see Authentication and Encryption. Set password in the following command to a password for submitting jobs:
sh generate_keystore.sh <password>
The script automatically replaces the SSL value in the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/flink-conf.yaml file.
sh generate_keystore.sh <password>
Note
After authentication and encryption, the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files are generated in the conf directory on the Flink client and the following configuration items are set to the default values in the flink-conf.yaml file:
Set security.ssl.keystore to the absolute path of the flink.keystore file.
Set security.ssl.truststore to the absolute path of the flink.truststore file.
Set security.cookie to a random password automatically generated by the generate_keystore.sh script.
By default, security.ssl.encrypt.enabled is set to false in the flink-conf.yaml file by default. The generate_keystore.sh script sets security.ssl.key-password, security.ssl.keystore-password, and security.ssl.truststore-password to the password entered when the generate_keystore.sh script is called.
For MRS 3.x or later, if ciphertext is required and security.ssl.encrypt.enabled is set to true in the flink-conf.yaml file, the generate_keystore.sh script does not set security.ssl.key-password, security.ssl.keystore-password, and security.ssl.truststore-password. To obtain the values, use the Manager plaintext encryption API by running curl -k -i -u Username:Password -X POST -HContent-type:application/json -d '{"plainText":"Password"}' 'https://x.x.x.x:28443/web/api/v2/tools/encrypt'.
In the preceding command, Username:Password indicates the user name and password for logging in to the system. The password of "plainText" indicates the one used to call the generate_keystore.sh script. x.x.x.x indicates the floating IP address of Manager.
Configure paths for the client to access the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files.
Absolute path: After the script is executed, the file path of flink.keystore and flink.truststore is automatically set to the absolute path /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/ in the flink-conf.yaml file. In this case, you need to move the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files from the conf directory to this absolute path on the Flink client and Yarn nodes.
Relative path: Perform the following steps to set the file path of flink.keystore and flink.truststore to the relative path and ensure that the directory where the Flink client command is executed can directly access the relative paths.
Create a directory, for example, ssl, in /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/.
cd /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/
mkdir ssl
Move the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files to the /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/ssl/ directory.
mv flink.keystore ssl/
mv flink.truststore ssl/
Change the values of the following parameters to relative paths in the flink-conf.yaml file:
security.ssl.keystore: ssl/flink.keystore security.ssl.truststore: ssl/flink.truststore
Run a wordcount job.
Important
To submit or run jobs on Flink, the user must have the following permissions:
If Ranger authentication is enabled, the current user must belong to the hadoop group or the user has been granted the /flink read and write permissions in Ranger.
If Ranger authentication is disabled, the current user must belong to the hadoop group.
Normal cluster (Kerberos authentication disabled)
Run the following commands to start a session and submit a job in the session:
yarn-session.sh -nm "session-name"
flink run /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Run the following command to submit a single job on Yarn:
flink run -m yarn-cluster /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Security cluster (Kerberos authentication enabled)
If the flink.keystore and flink.truststore files are stored in the absolute path:
Run the following commands to start a session and submit a job in the session:
yarn-session.sh -nm "session-name"
flink run /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Run the following command to submit a single job on Yarn:
flink run -m yarn-cluster /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
If the flink.keystore and flink.truststore file are stored in the relative path:
In the same directory of SSL, run the following commands to start a session and submit jobs in the session. The SSL directory is a relative path. For example, if the SSL directory is opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/conf/, then run the following commands in this directory:
yarn-session.sh -t ssl/ -nm "session-name"
flink run /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
Run the following command to submit a single job on Yarn:
flink run -m yarn-cluster -yt ssl/ /opt/hadoopclient/Flink/flink/examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
After the job has been successfully submitted, the following information is displayed on the client:
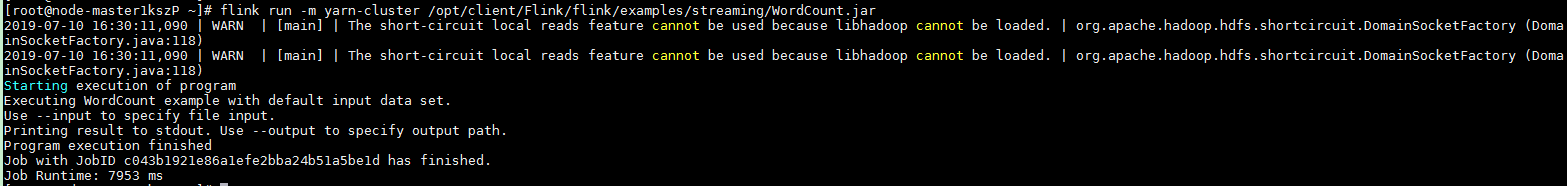
Figure 5 Job submitted successfully on Yarn¶

Figure 6 Session started successfully¶
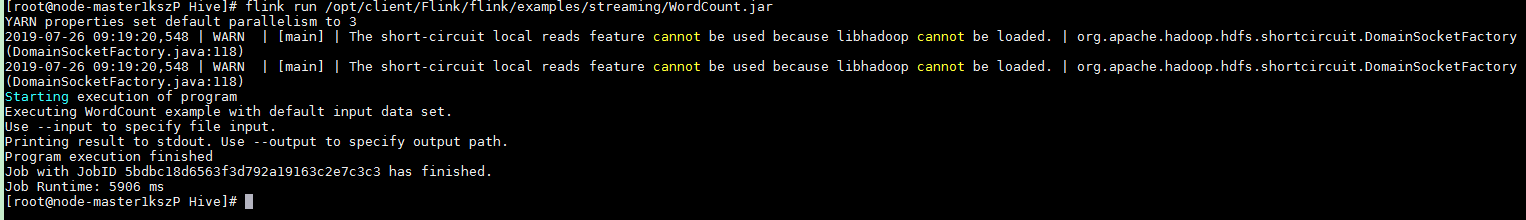
Figure 7 Job submitted successfully in the session¶
Go to the native YARN service page, find the application of the job, and click the application name to go to the job details page. For details, see Viewing Flink Job Information.
If the job is not completed, click Tracking URL to go to the native Flink page and view the job running information.
If the job submitted in a session has been completed, you can click Tracking URL to log in to the native Flink service page to view job information.
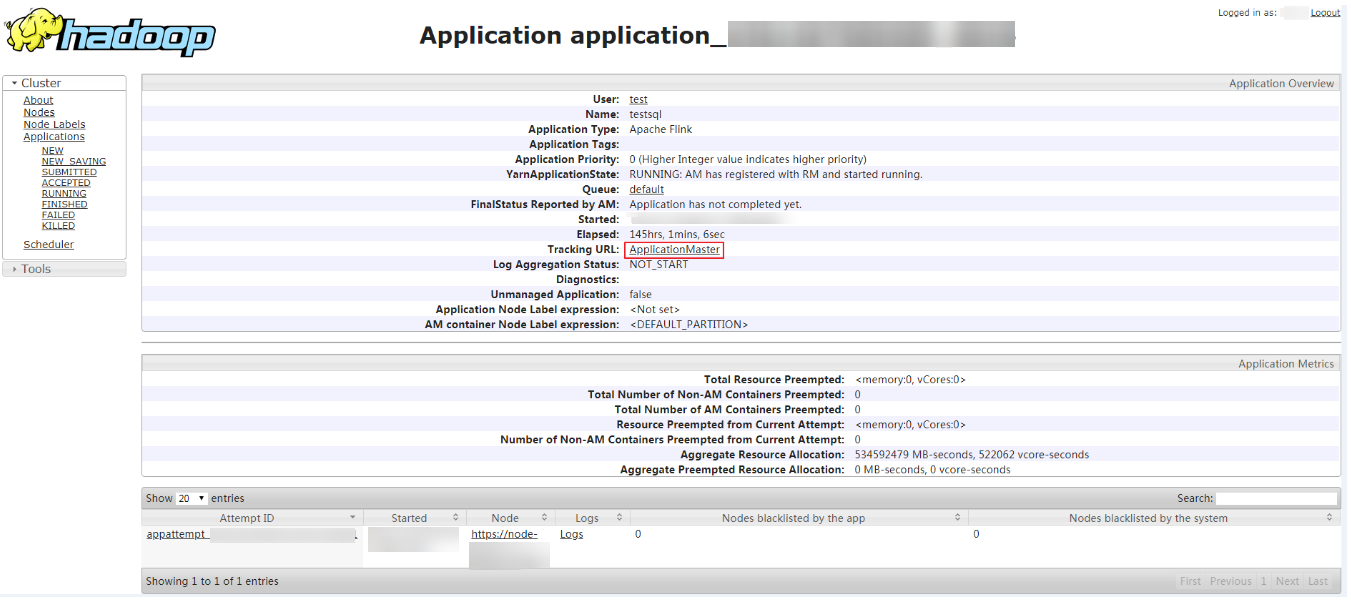
Figure 8 Application¶