Configuring HBase Replication¶
Scenario¶
As a key feature to ensure high availability of the HBase cluster system, HBase cluster replication provides HBase with remote data replication in real time. It provides basic O&M tools, including tools for maintaining and re-establishing active/standby relationships, verifying data, and querying data synchronization progress. To achieve real-time data replication, you can replicate data from the HBase cluster to another one.
Prerequisites¶
The active and standby clusters have been successfully installed and started (the cluster status is Running on the Active Clusters page), and you have the administrator rights of the clusters.
The network between the active and standby clusters is normal and ports can be used properly.
Cross-cluster mutual trust has been configured. For details, see Configuring Cross-Cluster Mutual Trust Relationships.
If historical data exists in the active cluster and needs to be synchronized to the standby cluster, cross-cluster replication must be configured for the active and standby clusters. For details, see Enabling Cross-Cluster Copy.
Time is consistent between the active and standby clusters and the Network Time Protocol (NTP) service on the active and standby clusters uses the same time source.
Mapping relationships between the names of all hosts in the active and standby clusters and service IP addresses have been configured in the /etc/hosts file by appending 192.*.***.*** host1** to the hosts file.
The network bandwidth between the active and standby clusters is determined based on service volume, which cannot be less than the possible maximum service volume.
Constraints¶
Despite that HBase cluster replication provides the real-time data replication function, the data synchronization progress is determined by several factors, such as the service loads in the active cluster and the health status of processes in the standby cluster. In normal cases, the standby cluster should not take over services. In extreme cases, system maintenance personnel and other decision makers determine whether the standby cluster takes over services according to the current data synchronization indicators.
Currently, the replication function supports only one active cluster and one standby cluster in HBase.
Typically, do not perform operations on data synchronization tables in the standby cluster, such as modifying table properties or deleting tables. If any misoperation on the standby cluster occurs, data synchronization between the active and standby clusters will fail and data of the corresponding table in the standby cluster will be lost.
If the replication function of HBase tables in the active cluster is enabled for data synchronization, after modifying the structure of a table in the active cluster, you need to manually modify the structure of the corresponding table in the standby cluster to ensure table structure consistency.
Procedure¶
Enable the replication function for the active cluster to synchronize data written by Put.
Log in to the MRS console, click a cluster name and choose Components.
Go to the All Configurations page of the HBase service. For details, see Modifying Cluster Service Configuration Parameters.
Note
If the Components tab is not displayed on the cluster details page, synchronize the IAM user first. (In the Dashboard area of the cluster details page, click Click to synchronize on the right of IAM User Sync to synchronize IAM users.)
Choose RegionServer > Replication and check whether the value of hbase.replication is true. If the value is false, set hbase.replication to true.
(Optional) Set configuration items listed in Table 1. You can set the parameters based on the description or use the default values.
Table 1 Optional configuration items¶ Navigation Path
Parameter
Default Value
Description
HMaster > Performance
hbase.master.logcleaner.ttl
600000
Time to live (TTL) of HLog files. If the value is set to 604800000 (unit: millisecond), the retention period of HLog is 7 days.
hbase.master.cleaner.interval
60000
Interval for the HMaster to delete historical HLog files. The HLog that exceeds the configured period will be automatically deleted. You are advised to set it to the maximum value to save more HLogs.
RegionServer > Replication
replication.source.size.capacity
16777216
Maximum size of edits, in bytes. If the edit size exceeds the value, HLog edits will be sent to the standby cluster.
replication.source.nb.capacity
25000
Maximum number of edits, which is another condition for triggering HLog edits to be sent to the standby cluster. After data in the active cluster is synchronized to the standby cluster, the active cluster reads and sends data in HLog according to this parameter value. This parameter is used together with replication.source.size.capacity.
replication.source.maxretriesmultiplier
10
Maximum number of retries when an exception occurs during replication.
replication.source.sleepforretries
1000
Retry interval (unit: ms)
hbase.regionserver.replication.handler.count
6
Number of replication RPC server instances on RegionServer
Enable the replication function for the active cluster to synchronize data written by bulkload.
Determine whether to enable bulkload replication.
Note
If bulkload import is used and data needs to be synchronized, you need to enable Bulkload replication.
If yes, go to 6.
If no, go to 10.
Go to the All Configurations page of the HBase service parameters by referring to Modifying Cluster Service Configuration Parameters.
On the HBase configuration interface of the active and standby clusters, search for hbase.replication.cluster.id and modify it. It specifies the HBase ID of the active and standby clusters. For example, the HBase ID of the active cluster is set to replication1 and the HBase ID of the standby cluster is set to replication2 for connecting the active cluster to the standby cluster. To save data overhead, the parameter value length is not recommended to exceed 30.
On the HBase configuration interface of the standby cluster, search for hbase.replication.conf.dir and modify it. It specifies the HBase configurations of the active cluster client used by the standby cluster and is used for data replication when the bulkload data replication function is enabled. The parameter value is a path name, for example, /home.
Note
When bulkload replication is enabled, you need to manually place the HBase client configuration files (core-site.xml, hdfs-site.xml, and hbase-site.xml) in the active cluster on all RegionServer nodes in the standby cluster. The actual path for placing the configuration file is ${hbase.replication.conf.dir}/${hbase.replication.cluster.id}. For example, if hbase.replication.conf.dir of the standby cluster is set to /home and hbase.replication.cluster.id of the active cluster is set to replication1, the actual path for placing the configuration files in the standby cluster is /home/replication1. You also need to change the corresponding directory and file permissions by running the chown -R omm:wheel /home/replication1 command.
You can obtain the client configuration files from the client in the active cluster, for example, the /opt/client/HBase/hbase/conf path. For details about how to update the configuration file, see Updating a Client.
On the HBase configuration page of the active cluster, search for and change the value of hbase.replication.bulkload.enabled to true to enable bulkload replication.
Restarting the HBase service and install the client
Save the configurations and restart HBase.
In the active and standby clusters choose Cluster > Dashboard > More > Download Client. For details about how to update the client configuration file, see Updating a Client.
Synchronize table data of the active cluster. (Skip this step if the active cluster has no data.)
Access the HBase shell of the active cluster as user hbase.
On the active management node where the client has been updated, run the following command to go to the client directory:
cd /opt/client
Run the following command to configure environment variables:
source bigdata_env
If Kerberos authentication is enabled for the current cluster, run the following command to authenticate the current user. If Kerberos authentication is disabled for the current cluster, skip this step.
kinit hbase
Run the following HBase client command:
hbase shell
Check whether historical data exists in the standby cluster. If historical data exists and data in the active and standby clusters must be consistent, delete data from the standby cluster first.
On the HBase shell of the standby cluster, run the list command to view the existing tables in the standby cluster.
Delete data tables from the standby cluster based on the output list.
disable 'tableName'
drop 'tableName'
After HBase replication is configured and data synchronization is enabled, check whether tables and data exist in the active cluster and whether the historical data needs to be synchronized to the standby cluster.
Run the list command to check the existing tables in the active cluster and run the scan 'tableName' command to check whether the tables contain historical data.
If tables exist and data needs to be synchronized, go to 15.
If no, no further action is required.
The HBase replication configuration does not support automatic synchronization of historical data in tables. You need to back up the historical data of the active cluster and then manually synchronize the historical data to the standby cluster.
Manual synchronization refers to the synchronization of a single table that is implemented by Export, distcp, and Import.
The process for manually synchronizing data of a single table is as follows:
Export table data from the active cluster.
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.Export -Dhbase.mapreduce.include.deleted.rows=true Table name Directory where the source data is stored
Example: hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.Export -Dhbase.mapreduce.include.deleted.rows=true t1 /user/hbase/t1
Copy the data that has been exported to the standby cluster.
hadoop distcp Directory for storing source data in the active cluster hdfs://ActiveNameNodeIP:9820/ Directory for storing source data in the standby cluster
ActiveNameNodeIP indicates the IP address of the active NameNode in the standby cluster.
Example: hadoop distcp /user/hbase/t1 hdfs://192.168.40.2:9820/user/hbase/t1
Import data to the standby cluster as the HBase table user of the standby cluster.
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.Import -Dimport.bulk.output=Directory where the output data is stored in the standby cluster Table name Directory where the source data is stored in the standby cluster
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.LoadIncrementalHFiles Directory where the output data is stored in the standby cluster Table name
For example, hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.Import -Dimport.bulk.output=/user/hbase/output_t1 t1 /user/hbase/t1 and
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.LoadIncrementalHFiles /user/hbase/output_t1 t1
Add the replication relationship between the active and standby clusters.
Run the following command on the HBase Shell to create the replication synchronization relationship between the active cluster and the standby cluster:
add_peer 'Standby cluster ID', CLUSTER_KEY => 'ZooKeeper address of the standby cluster',{HDFS_CONFS => true}
Standby cluster ID indicates an ID for the active cluster to recognize the standby cluster. It is recommended that the ID contain letters and digits.
The ZooKeeper address of the standby cluster includes the service IP address of ZooKeeper, the port for listening to client connections, and the HBase root directory of the standby cluster on ZooKeeper.
{HDFS_CONFS => true} indicates that the default HDFS configuration of the active cluster will be synchronized to the standby cluster. This parameter is used for HBase of the standby cluster to access HDFS of the active cluster. If bulkload replication is disabled, you do not need to use this parameter.
Suppose the standby cluster ID is replication2 and the ZooKeeper address of the standby cluster is 192.168.40.2,192.168.40.3,192.168.40.4:2181:/hbase.
Run the add_peer 'replication2',CLUSTER_KEY => '192.168.40.2,192.168.40.3,192.168.40.4:2181:/hbase',CONFIG => { "hbase.regionserver.kerberos.principal" => "<val>", "hbase.master.kerberos.principal" => "<val2>" } command for a security cluster and the add_peer 'replication2',CLUSTER_KEY => '192.168.40.2,192.168.40.3,192.168.40.4:2181:/hbase' command for a common cluster.
The hbase.master.kerberos.principal and hbase.regionserver.kerberos.principal parameters are the Kerberos users of HBase in the security cluster. You can search the hbase-site.xml file on the client for the parameter values. For example, if the client is installed in the /opt/client directory of the Master node, you can run the grep "kerberos.principal" /opt/client/HBase/hbase/conf/hbase-site.xml -A1 command to obtain the principal of HBase. See the following figure.
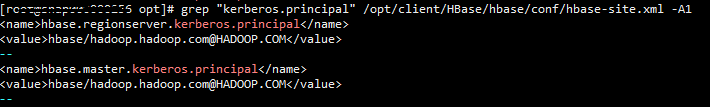
Figure 1 Obtaining the principal of HBase¶
Note
Obtain the ZooKeeper service IP address.
Log in to the MRS console, click the cluster name, and choose Components > ZooKeeper > Instances to obtain the ZooKeeper service IP address.
On the ZooKeeper service parameter configuration page, search for clientPort, which is the port for the client to connect to the server.
Run the list_peers command to check whether the replication relationship between the active and standby clusters is added. If the following information is displayed, the relationship is successfully added.
hbase(main):003:0> list_peers PEER_ID CLUSTER_KEY ENDPOINT_CLASSNAME STATE REPLICATE_ALL NAMESPACES TABLE_CFS BANDWIDTH SERIAL replication2 192.168.0.13,192.168.0.177,192.168.0.25:2181:/hbase ENABLED true 0 false
Specify the data writing status for the active and standby clusters.
On the HBase shell of the active cluster, run the following command to retain the data writing status:
set_clusterState_active
The command is run successfully if the following information is displayed:
hbase(main):001:0> set_clusterState_active => true
On the HBase shell of the standby cluster, run the following command to retain the data read-only status:
set_clusterState_standby
The command is run successfully if the following information is displayed:
hbase(main):001:0> set_clusterState_standby => true
Enable the HBase replication function to synchronize data.
Check whether a namespace exists in the HBase service instance of the standby cluster and the namespace has the same name as the namespace of the HBase table for which the replication function is to be enabled.
On the HBase shell of the standby cluster, run the list_namespace command to query the namespace.
On the HBase shell of the active cluster, run the following command to enable real-time replication for tables in the active cluster. This ensures that modified data in the active cluster can be synchronized to the standby cluster in real time.
You can only synchronize data of one HTable at one time.
enable_table_replication 'Table name'
Note
If the standby cluster does not contain a table with the same name as the table for which real-time synchronization is to be enabled, the table is automatically created.
If a table with the same name as the table for which real-time synchronization is to be enabled exists in the standby cluster, the structures of the two tables must be the same.
If the encryption algorithm SMS4 or AES is configured for 'Table name', the function for synchronizing data from the active cluster to the standby cluster cannot be enabled for the HBase table.
If the standby cluster is offline or has tables with the same name but different structures, the replication function cannot be enabled.
If the standby cluster is offline, start it.
If the standby cluster has a table with the same name but different structure, modify the table structure to make it as the same as the table structure of the active cluster. On the HBase shell of the standby cluster, run the alter command to change the password by referring to the example.
On the HBase shell of the active cluster, run the following command to enable the real-time replication function for the active cluster to synchronize the HBase permission table:
enable_table_replication 'hbase:acl'
Note
After the permission of the active HBase source data table is modified, to ensure that the standby cluster can properly read data, modify the role permission for the standby cluster.
Check the data synchronization status for the active and standby clusters.
Run the following command on the HBase client to check the synchronized data of the active and standby clusters. After the replication function is enabled, you can run this command to check whether the newly synchronized data is consistent.
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.replication.VerifyReplication --starttime=Start time --endtime=End time Column family name ID of the standby cluster Table name
Note
The start time must be earlier than the end time.
The value of starttime and endtime must be in the timestamp format. You need to run date -d "2015-09-30 00:00:00" +%s to change a common time format to a timestamp format. The command output is a 10-digit number (accurate to second), but HBase identifies a 13-digit number (accurate to millisecond). Therefore, you need to add three zeros (000) to the end of the command output.
Switch over active and standby clusters.