EVS Disk Encryption¶
What Is EVS Disk Encryption?¶
In case your services require encryption for the data stored on EVS disks, EVS provides you with the encryption function. You can encrypt newly created EVS disks.
EVS uses the industry-standard XTS-AES-256 encryption algorithm and keys to encrypt EVS disks. Keys used by encrypted EVS disks are provided by the Key Management Service (KMS), which is secure and convenient. Therefore, you do not need to establish and maintain the key management infrastructure. KMS uses the Hardware Security Module (HSM) that complies with FIPS 140-2 level 3 requirements to protect keys. All user keys are protected by the root key in HSM to prevent key exposure.
Keys Used for EVS Disk Encryption¶
The keys provided by KMS include a Default Master Key and Customer Master Keys (CMKs).
Default Master Key: A key that is automatically created by EVS through KMS and named evs/default.
The Default Master Key cannot be disabled and does not support scheduled deletion.
CMKs: Keys created by users. You may use existing CMKs or create new CMKs to encrypt disks. For details, see Management > Creating a CMK in the Key Management Service User Guide.
If disks are encrypted using CMKs and a CMK is then disabled or scheduled for deletion, the disks encrypted by this CMK can no longer be read from or written to and data on these disks may never be restored. See Table 1 for more information.
CMK Status |
Impact |
How to Restore |
|---|---|---|
Disabled |
|
Enable the CMK. For details, see Managing CMKs > Enabling One or More CMKs in the Key Management Service User Guide. |
Scheduled deletion |
Cancel the scheduled deletion for the CMK. For details, see Managing CMKs > Canceling the Scheduled Deletion of One or More CMKs in the Key Management Service User Guide. |
|
Deleted |
Data on the disks can never be restored. |
Who Can Use the Disk Encryption Function?¶
The security administrator (having the Security Administrator rights) can grant the KMS access rights to EVS for using the disk encryption function.
When a common user who does not have the Security Administrator rights needs to use the disk encryption function, the condition varies depending on whether the user is the first one ever in the current region or project to use this feature.
If the common user is the first one ever in the current region or project to use the feature, the user must contact a user having the Security Administrator rights to grant the KMS access rights to EVS. Then, the common user can use the disk encryption function.
If the common user is not the first one ever in the current region or project to use the feature, the common user can use the disk encryption function directly.
From the perspective of a tenant, as long as the KMS access rights have been granted to EVS in a region, all the users in the same region can directly use the disk encryption function.
If there are multiple projects in the current region, the KMS access rights need to be granted to each project in this region.
Application Scenarios of EVS Disk Encryption¶
Figure 1 shows the user relationships under regions and projects from the perspective of a tenant. The following example uses region B to describe the two application scenarios of the disk encryption function.
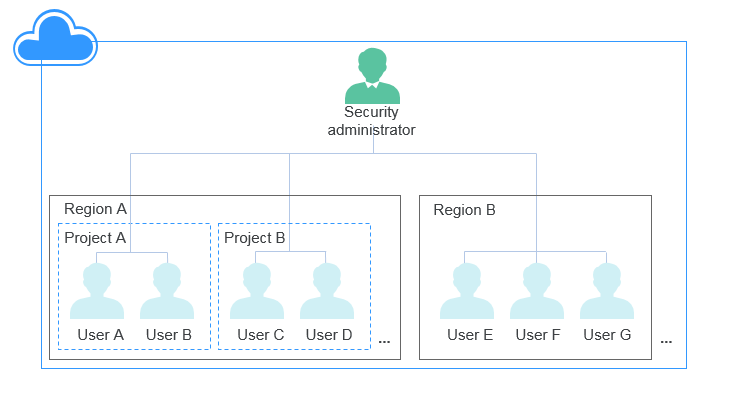
Figure 1 User relationships¶
If the security administrator uses the encryption function for the first time ever, the operation process is as follows:
Grant the KMS access rights to EVS.
After the KMS access rights have been granted, the system automatically creates a Default Master Key and names it evs/default. DMK can be used for disk encryption.
Note
The EVS disk encryption relies on KMS. When the encryption function is used for the first time ever, the KMS access rights need to be granted to EVS. After the KMS access rights have been granted, all users in this region can use the encryption function, without requiring the KMS access rights to be granted again.
Select a key.
You can select one of the following keys:
DMK: evs/default
CMKs: Existing or newly created CMKs. For details, see Creating a CMK in the Key Management Service User Guide.
After the security administrator has used the disk encryption function, all users in Region B can directly use the encryption function.
If User E (common user) uses the encryption function for the first time ever, the operation process is as follows:
When user E uses the encryption function, and the system prompts a message indicating that the KMS access rights have not been granted to EVS.
Contact the security administrator to grant the KMS access rights to EVS.
After the KMS access rights have been granted to EVS, User E as well as all users in Region B can directly use the disk encryption function and do not need to contact the security administrator to grant the KMS access rights to EVS again.