How Can I View My Disk Usage?¶
You can view your disk usages in either of the following ways:
View disk usages manually.
The details depend on the OS. This FAQ uses Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2016, and Linux as samples to describe how to view the disk usage.
Viewing Disk Usage in Linux¶
In this section, CentOS 7.4 64bit is used as an example. The details depend on if you need to view the available space or not.
To query the total capacity only, run lsblk.
Information similar to the following is displayed:
[root@ecs-test-0001 ~]# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT vda 253:0 0 40G 0 disk └─vda1 253:1 0 40G 0 part / vdb 253:16 0 40G 0 disk └─vdb1 253:17 0 40G 0 part
In the command output, the server has two disks, /dev/vda and /dev/vdb. System disk /dev/vda has 40 GiB of capacity, as does data disk /dev/vdb.
To query the total capacity and display the space available as well, run df -TH. Ensure that the disk has been attached and initialized before running this command.
Information similar to the following is displayed:
[root@ecs-0001 ~]# df -TH Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/vda1 ext4 43G 2.0G 39G 5% / devtmpfs devtmpfs 509M 0 509M 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 520M 0 520M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 520M 7.2M 513M 2% /run tmpfs tmpfs 520M 0 520M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs tmpfs 104M 0 104M 0% /run/user/0 /dev/vdb1 ext4 43G 51M 40G 1% /mnt/sdc
In the command output, the server has two partitions, /dev/vda1 and /dev/vdb1. Partition /dev/vda1 is used to deploy the OS, and its total capacity, used capacity, and available capacity are 43 GiB, 2 GiB, and 39 GiB, respectively. Partition /dev/vdb1's total capacity, used capacity, and available capacity are 43 GiB, 51 MiB, and 40 GiB, respectively.
Viewing Disk Usage in Windows Server 2008¶
In this section, Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise 64bit is used as an example.
On the desktop of the server, right-click Computer and choose Manage from the shortcut menu.
The Server Manager window is displayed.
In the navigation tree, choose Storage > Disk Management.
The sizes and available spaces of the volumes on the current disk are displayed in the middle pane.
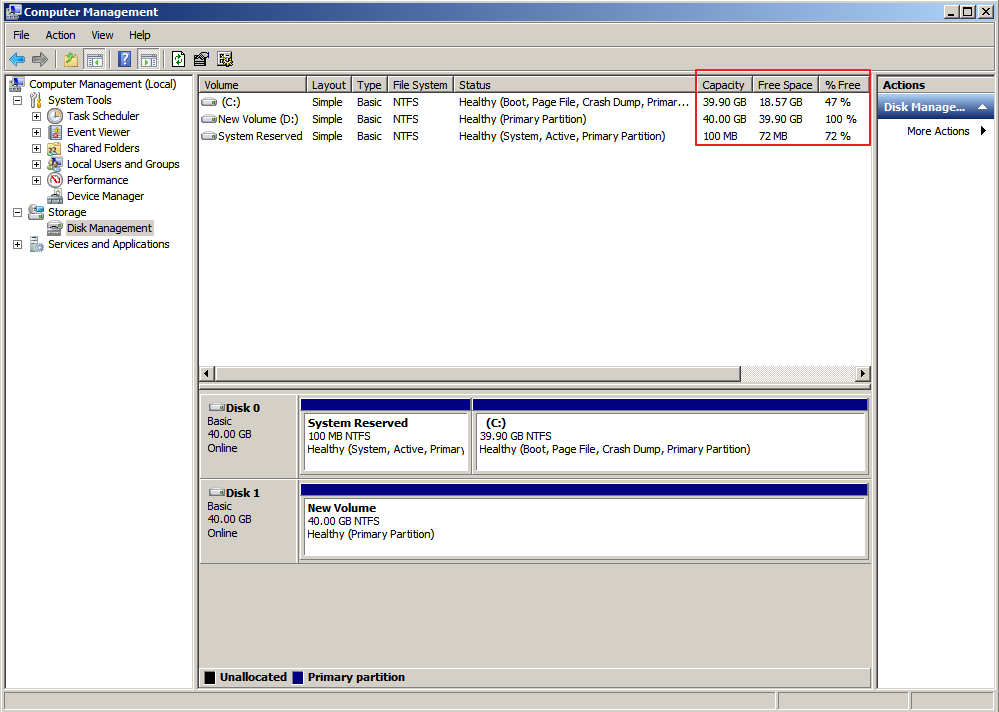
Figure 1 Disk Management page¶
Viewing Disk Usage in Windows Server 2016¶
In this section, Windows Server 2016 Standard 64bit is used as an example.
On the desktop of the server, click the start icon in the lower left corner.
The Windows Server window is displayed.
Click Server Manager.
The Server Manager window is displayed.
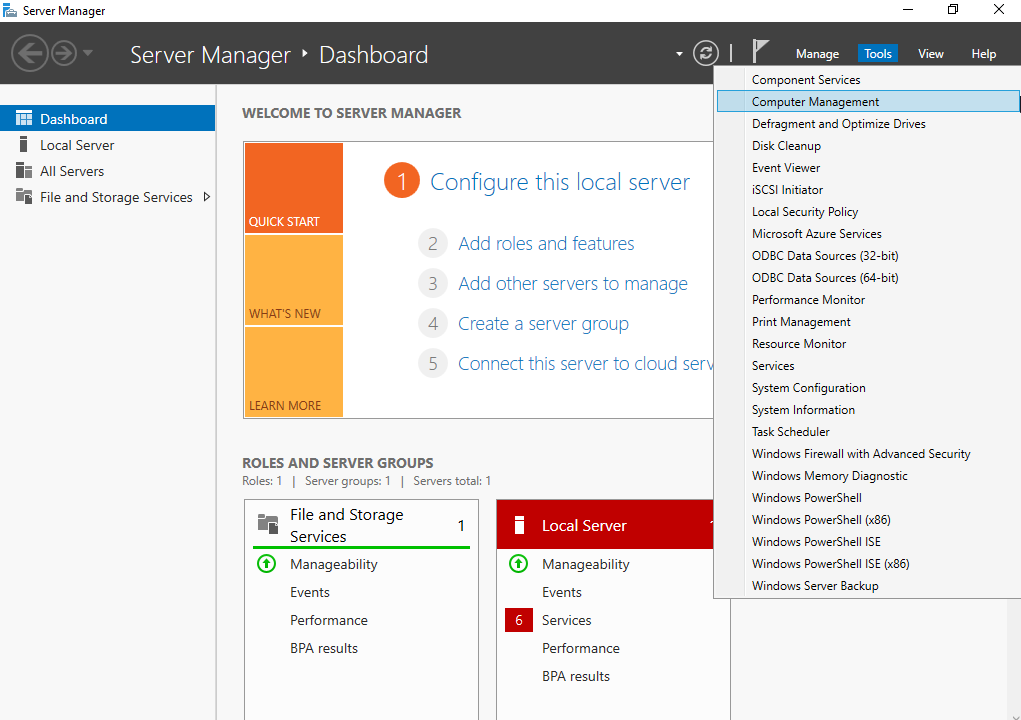
Figure 2 Server Manager page¶
In the upper right corner, choose Tools > Computer Management.
Choose Storage > Disk Management.
In the middle pane, you can view the sizes and available spaces of the volumes on the disk.
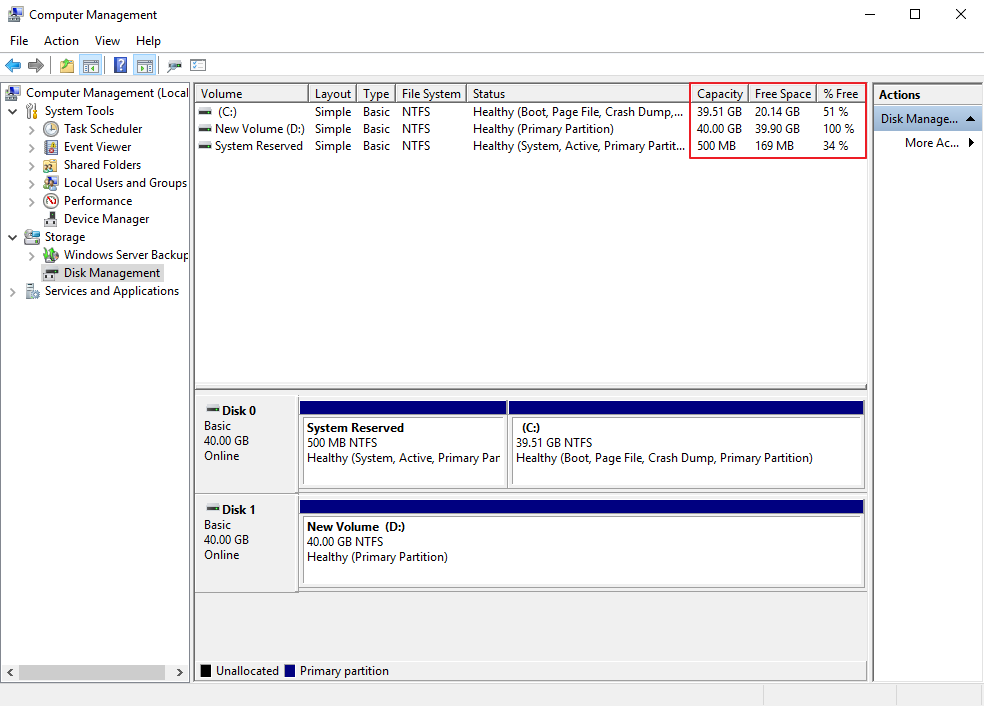
Figure 3 Disk list page¶
Installing Agent to View Disk Usage¶
Some disk monitoring metrics require that the agent to be installed.
For details about how to install the Agent on an ECS, see section "Installing and Configuring the Agent on a Linux ECS or BMS" in the Cloud Eye User Guide.
Metric | Parameter | Description | Value Range | Monitored Object & Dimension | Monitoring Period (Raw Data) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
disk_free | (Agent) Available Disk Space | Free space on the disks Unit: GB
| >= 0 | ECS - Mount point | 1 minute |
disk_total | (Agent) Disk Storage Capacity | Total space on the disks, including used and free Unit: GB
| >= 0 | ECS - Mount point | 1 minute |
disk_used | (Agent) Used Disk Space | Used space on the disks Unit: GB
| >= 0 | ECS - Mount point | 1 minute |
disk_usedPercent | (Agent) Disk Usage | Percentage of total disk space that is used, which is calculated as follows: Disk Usage = Used Disk Space/Disk Storage Capacity Unit: percent
| 0-100 | ECS - Mount point | 1 minute |