What Are the Differences Between EIP, Private IP Address, and Virtual IP Address?¶
Different types of IP addresses have different functions.
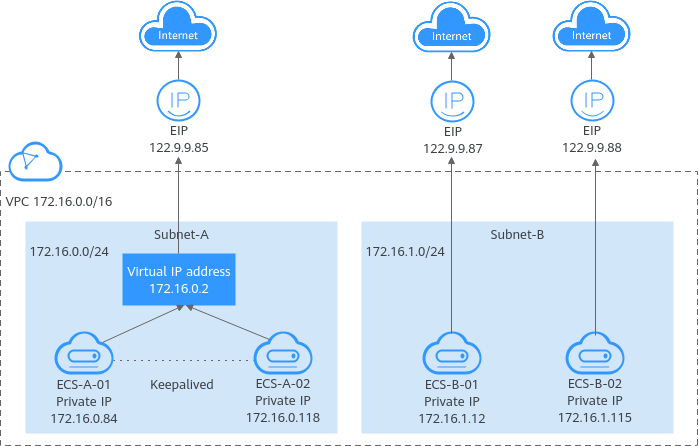
Figure 1 IP address architecture¶
IP Address Type | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
Private IP address | Private IP addresses come with your ECSs and belong to the VPC subnets of the ECSs. They are used for private communication on the cloud. |
|
Virtual IP address | A virtual IP address can be shared among multiple ECSs. Two ECSs can work as an active and standby pair to achieve high availability by using a virtual IP address and Keepalived. If the active ECS is faulty, the virtual IP address can be dynamically switched to the standby ECS to continue providing services. For more information about virtual IP addresses, see Virtual IP Address Overview. | Bind virtual IP address (172.16.0.2) both ECS-A-01 and ECS-A-02. The active/standby switchover of ECS-A-01 and ECS-A-02 can be implemented by using Keepalived. |
EIP | EIPs can be used by cloud resources for Internet access.
|
|