What Are Inbound Bandwidth and Outbound Bandwidth?¶
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted in a given amount of time (generally one second). A larger bandwidth value indicates a stronger transmission capability. Bandwidth is classified into public bandwidth and private bandwidth.
Public bandwidth is the bandwidth consumed when data is transferred between cloud instances and the Internet. Public bandwidth is classified into inbound bandwidth and outbound bandwidth. For details the outbound bandwidth and inbound bandwidth, see Table 1.
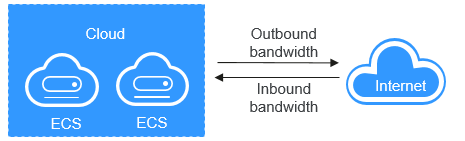
Figure 1 Inbound bandwidth and outbound bandwidth¶
Type | Description |
|---|---|
Outbound bandwidth | Bandwidth consumed when data is transferred from cloud to the Internet. For example, the outbound bandwidth is used when ECSs provide services accessible from the Internet and FTP clients download resources from the ECSs. |
Inbound bandwidth | Bandwidth consumed when data is transferred from the Internet to cloud. For example, the inbound bandwidth is used when resources are downloaded from the Internet to ECSs and FTP clients upload resources to the ECSs. |