Reinstalling the OS¶
Scenarios¶
If the OS of an ECS fails to start or requires optimization, reinstall the OS.
Notes¶
After the OS is reinstalled, the IP and MAC addresses of the ECS remain unchanged.
Reinstalling the OS clears the data in all partitions of the EVS system disk, including the system partition. Therefore, back up data before reinstalling the OS.
Reinstalling the OS does not affect data disks.
Do not perform any operations on the ECS immediately after its OS is reinstalled. Wait for several minutes until the system successfully injects the password or key. Otherwise, the injection may fail, and the ECS cannot be logged in to.
After the OS is reinstalled, the password for logging in to the ECS will be reset. To retrieve the password, perform the following operations:
For a Linux ECS, log in to it using the key and set a new password. For instructions about how to log in to an ECS using a key pair, see Remotely Logging In to a Linux ECS (Using an SSH Key Pair).
For a Windows ECS, retrieve the password by following the instructions provided in Obtaining the Password for Logging In to a Windows ECS.
You can choose to encrypt the system disk of an ECS during OS reinstallation.
Constraints¶
The EVS disk quotas must be greater than 0.
If the target ECS is created using a private image, ensure that the private image is available.
If an ECS OS is to be reinstalled using a full-ECS image, the ECS system disk can be encrypted.
Prerequisites¶
The target ECS is stopped.
The target ECS has a system disk attached.
Procedure¶
Log in to the management console.
Click
 in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.Under Computing, choose Elastic Cloud Server.
Locate the row containing the target ECS and choose More > Manage Image/Backup > Reinstall OS in the Operation column.
Only stopped ECSs support OS reinstallation. If the ECS is not stopped, stop it before proceeding with reinstallation.
(Optional) Select the Encrypted option to encrypt the system disk during OS reinstallation.
To enable encryption, click Create Xrole to assign KMS access permissions to EVS. If you have rights granting permission, assign the KMS access permissions to EVS. If you do not have the permission, contact the user having the security administrator rights to assign the KMS access permissions. For details, see Can All Users Use the Encryption Feature?
Encryption parameters are as follows:
Encryption: indicates that the EVS disk has been encrypted.
Create Xrole: assigns KMS access permissions to EVS to obtain KMS keys. After the permissions are assigned, follow-up operations do not require assigning permissions again.
Xrole Name: set to EVSAccessKMS, which means that permissions have been assigned to EVS to obtain KMS keys for encrypting or decrypting EVS disks.
KMS Key Name: specifies the name of the key used by the encrypted EVS disk. You can select an existing key, or click Create KMS Key and create a new one on the KMS console. The default value is evs/default.
KMS Key ID: specifies the ID of the key used by the encrypted data disk.
(Optional) Select a License Type (Use license from the system or Bring your own license (BYOL)) if the reinstalled OS running on your ECS is billed. For more details, see License Types.
The following OSs are billed:
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
Oracle Enterprise Linux
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Select the login mode.
If the target ECS uses key pair authentication, you can replace the original key pair.
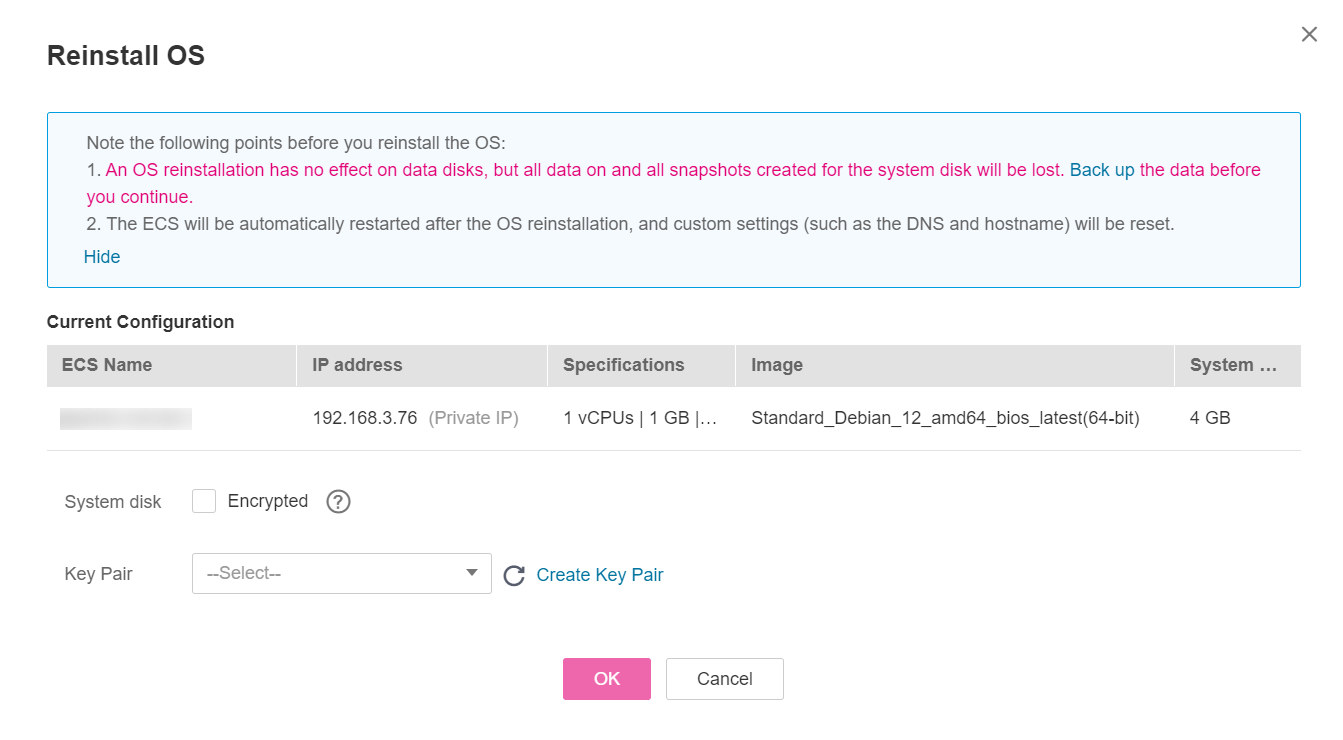
Figure 1 Reinstall OS¶
Click OK.
On the ECS OS Reinstallation page, confirm the settings, and click Submit.
After the request is submitted, the status Reinstalling is displayed. When this status disappears, the reinstallation is complete.
Note
A temporary ECS is created during the reinstallation process. After reinstallation, this ECS will be automatically deleted. Do not perform any operation on the temporary ECS during the reinstallation process.
Follow-up Procedure¶
If the reinstallation fails, perform steps 3 to 9 again to retry the OS installation.
If the second reinstallation attempt still fails, contact customer service for manual recovery at the backend.