Creating a PTR Record¶
Scenarios¶
PTR records are used to prove credibility of IP addresses and domain names of email servers. To avoid being tracked, most spam senders use email servers whose IP addresses are dynamically allocated or not mapped to registered domain names. If you want to keep the spam out of your recipients' inbox, add a PTR record to map the email server IP address to a domain name. In this way, the email recipients can obtain the domain name by IP address and will know that the email server is trustworthy.
If you use an ECS as an email server, configure a PTR record to map the EIP of the ECS to the domain name.
Note
After an ECS is created and assigned with an EIP, a PTR record will be generated for the EIP by default in format of ecs-xx-xx-xx-xx.compute.xxx.com, where xx-xx-xx-xx indicates the EIP and xxx is the domain name provided by the cloud platform.
You can use any of the following methods to query the default PTR record for the EIP:
ping -a EIP
nslookup [-qt=ptr] EIP
dig -x EIP
The default PTR record may not be applicable in some scenarios. For example, the PTR record cannot be used as the domain name of an email server. In this case, create a PTR record for the EIP.
After the PTR record is created, the default record will be overwritten.
This following are operations for you to add a PTR record for a cloud resource, such as ECS.
Constraints¶
You can only configure PTR records for IP addresses with a 32-bit subnet mask.
Prerequisites¶
You have registered a domain name.
You have created an ECS and bound an EIP to it.
Procedure¶
Log in to the management console.
In the service list, choose Network > Domain Name Service.
The DNS console is displayed.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose PTR Records.
The PTR Records page is displayed.
Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.Click Create PTR Record.
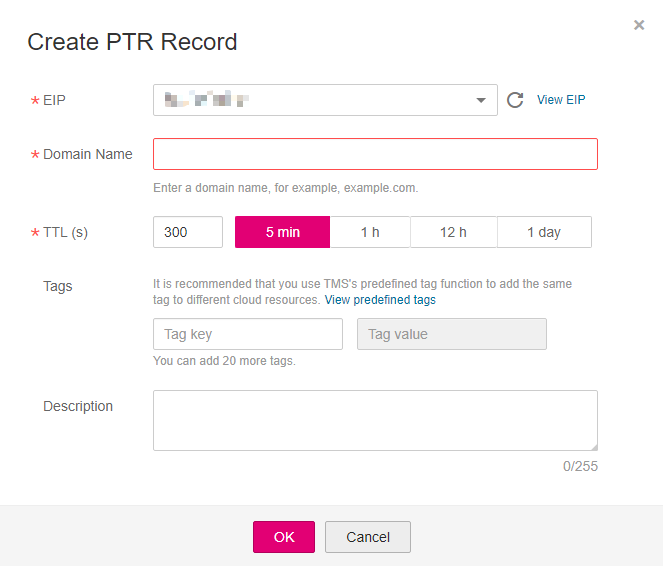
Figure 1 Creating a PTR record¶
Configure the parameters based on Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters for creating a PTR record¶ Parameter
Description
Example Value
EIP
EIP of another cloud resource, for example, ECS.
You can select an EIP from the drop-down list.
XX.XX.XX.XX
Domain Name
Domain name mapped to the EIP.
example.com
TTL (s)
Cache duration of the PTR record, in seconds
The default value is 300s.
300
Tag
(Optional) Identifier of the PTR record.
Each tag contains a key and a value. You can add a maximum of 20 tags to a PTR record.
For details about tag key and value requirements, see Table 2.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
(Optional) Supplementary information about the PTR record.
The description of the PTR record
Table 2 Tag key and value requirements¶ Parameter
Requirements
Example Value
Key
Cannot be left blank.
Must be unique for each resource.
Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and the following characters: _ . : = + - @
Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_.
example_key1
Value
Can be left blank.
Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and the following characters: _ . : = + - @
example_value1
Click OK.
You can view the created PTR record on the PTR Records page.

Figure 2 PTR Records¶
Note
If a domain name is mapped to multiple EIPs, you must create a PTR record for each EIP.
Verify that the PTR record has taken effect by running the following command on a PC connected to the Internet:
nslookup -qt=ptr EIP