Replica Set¶
A replica set consists of a set of mongod processes. It is a collection of nodes that help ensure data redundancy and reliability.
Note
For details about the mongod process, see the MongoDB official document.
A replica set consists of three nodes: primary, secondary, and hidden. The three-node architecture is set up automatically, and the three nodes automatically synchronize data with each other to ensure data reliability.
Primary node: Primary nodes are used to process both read and write requests.
Secondary node: Secondary nodes are used to process read requests only.
Hidden node: Hidden nodes are used to back up data.
You can perform operations on the primary and secondary nodes. If a primary node goes down or becomes faulty, the replica set elects a secondary node as a new primary node and continues normal operations. If there are no secondary nodes available, a hidden node will take over the role of the secondary node to ensure high availability. The following figure shows the replica set architecture.
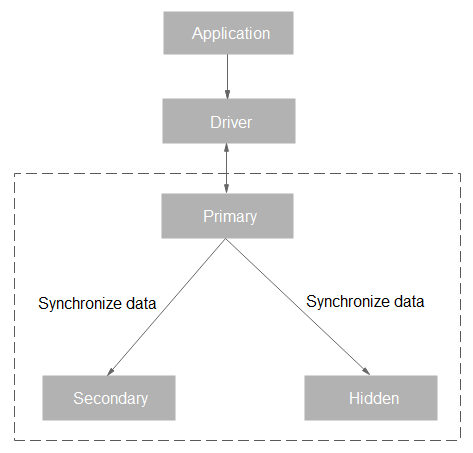
Figure 1 Replica set architecture¶
A driver handles all interactions between your application and the database in a language appropriate to the application. For details, see official documents.
You can perform multiple management and control tasks, such as creating instances, changing configurations, and backing up instances. The system flexibly controls and tracks tasks, and manages exceptions based on the operations delivered by you.
You can monitor performance information about DB instances, including basic metrics, storage space, access requests, and the number of operations.
DDS collects slow query logs and access control logs, recording DB instance running status.
You can back up DB instance data and upload them to OBS buckets. DDS supports automated and manual backup creation. Automated backups are kept for seven days by default.