Overview¶
Definition¶
Distributed Database Middleware (DDM) is a MySQL-compatible, distributed middleware service designed for relational databases. It can resolve distributed scaling issues to break through capacity and performance bottlenecks of databases, helping handle highly concurrent access to massive volumes of data.
DDM uses a decoupled compute and storage architecture and provides functions such as database and table sharding, read/write splitting, elastic scaling, and sustainable O&M. Management of instance nodes has no impacts on your workloads. You can perform O&M on your databases and read and write data from and to them on the DDM console, just like as operating a single-node MySQL database.
Advantages¶
Automatic Database and Table Sharding
MySQL databases are usually deployed on single nodes. Once a fault occurs, all data may be lost, and your workloads are 100% affected.
DDM supports automatic database and table sharding to distribute data across multiple data nodes, so impacts on your services are greatly reduced once a fault occurs. It also supports explosive growth of services.
Read/Write Splitting
DDM can leverage data nodes. If there is still great query pressure after horizontal sharding, you can enable read/write splitting to speed up database processing and access, without the need to reconstruct your service system.
Elastic Scaling
MySQL databases can support only medium- and small-scale service systems because their CPU, memory, and network processing are limited by server configurations and their storage depends on the size of SSD or EVS disks.
DDM supports both compute and storage scaling. You can add nodes to a DDM instance or scale up its node class. Alternatively, increase shards or data nodes to distribute data from one large table to multiple tables or scale out storage resources as services grow, without worrying about O&M.
Service Architecture¶
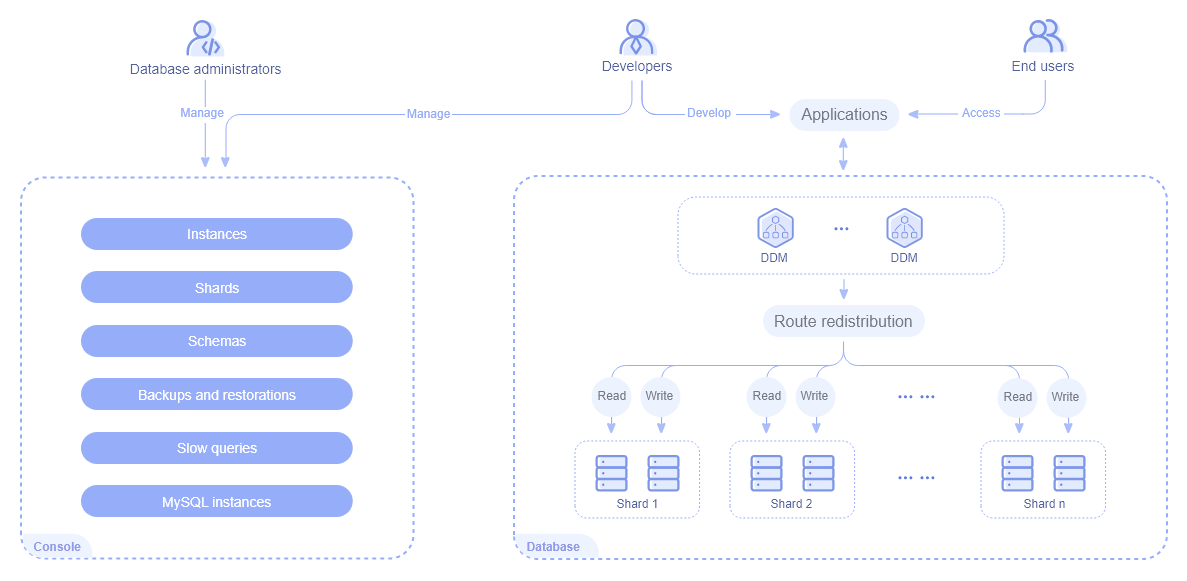
Figure 1 DDM service architecture¶
How DDM Works¶
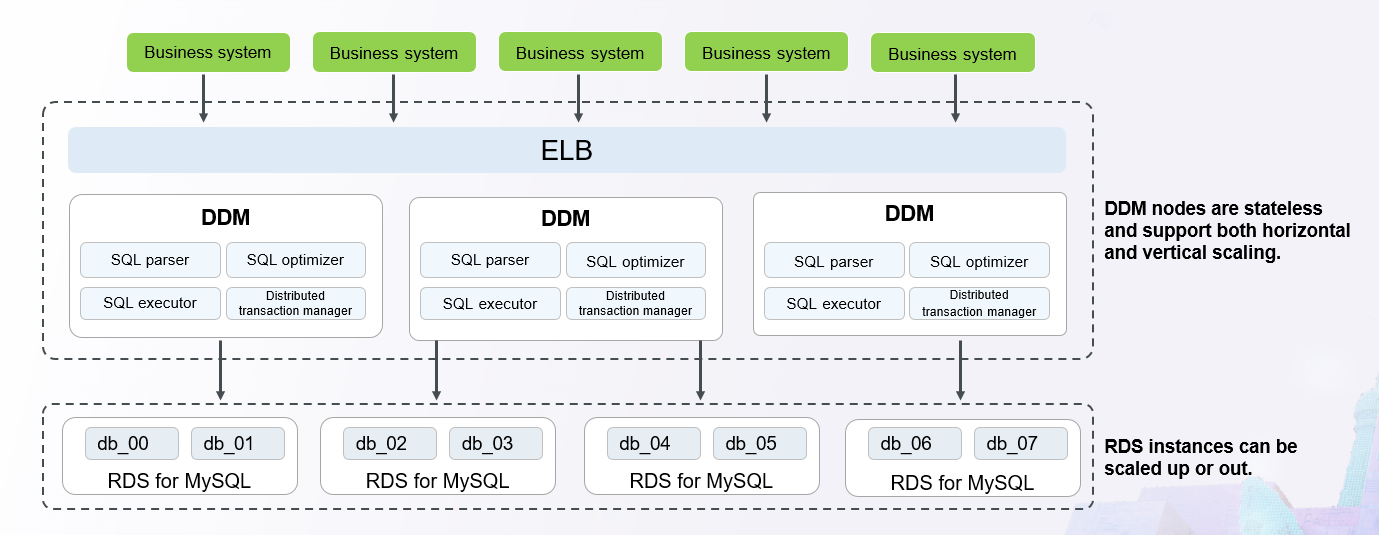
Figure 2 DDM working diagram¶