Master/Standby Redis¶
This section describes master/standby DCS Redis instances.
Note
You cannot upgrade the Redis version for an instance. For example, a master/standby DCS Redis 4.0 instance cannot be upgraded to a master/standby DCS Redis 5.0 instance. If your service requires the features of higher Redis versions, create a DCS Redis instance of a higher version and then migrate data from the old instance to the new one.
Features¶
Master/Standby DCS instances have higher availability and reliability than single-node DCS instances.
Master/Standby DCS instances have the following features:
Data persistence and high reliability
By default, data persistence is enabled by both the master and the standby node of a master/standby instance.
The standby node of a DCS Redis 3.0 instance is invisible to you. Only the master node provides data read/write operations.
The standby node of a Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instance is visible to you. You can read data from the standby node by connecting to it using the instance read-only address.
Data synchronization
Data in the master and standby nodes is kept consistent through incremental synchronization.
Note
After recovering from a network exception or node fault, master/standby instances perform a full synchronization to ensure data consistency.
Automatic master/standby switchover
If the master node becomes faulty, the instance is disconnected and unavailable for several seconds. The standby node takes over within 30 seconds without manual operations to resume stable services.
DR policies
Each master/standby DCS instance can be deployed across AZs with physically isolated power supplies and networks. Applications can also be deployed across AZs to achieve high availability for both data and applications.
Architecture of DCS Redis 3.0 Instances¶
Figure 1 shows the architecture of master/standby DCS Redis instances.
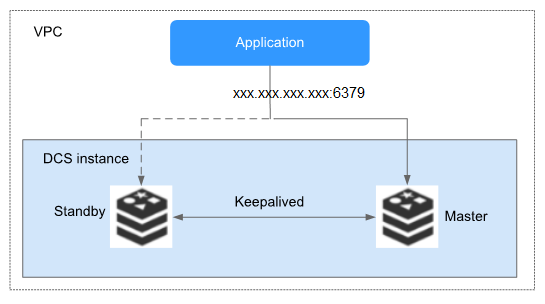
Figure 1 Master/Standby DCS instance architecture¶
Architecture description:
VPC
All server nodes of the instance run in the same VPC.
Note
For intra-VPC access, the client and the instance must be in the same VPC with specified security group rule configurations.
For details, see Security Group Configurations.
Application
The Redis client of the instance, which is the application running on the ECS.
DCS Redis instances are compatible with the Redis protocol, and can be accessed through open-source clients. For details about accessing DCS instances, see Accessing an Instance.
DCS instance
Indicates a master/standby DCS instance which has a master node and a standby node. By default, data persistence is enabled and data is synchronized between the two nodes.
DCS monitors the availability of the instance in real time. If the master node becomes faulty, the standby node becomes the master node and resumes service provisioning.
DCS Redis 3.0 instances are accessed through port 6379 by default. Port customization is not supported.
Architecture of Master/Standby DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 Instances¶
The following figure shows the architecture of a master/standby DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instance.
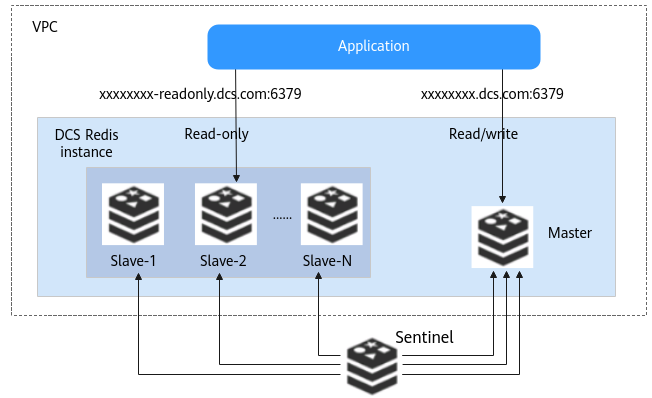
Figure 2 Architecture of a master/standby DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instance¶
Architecture description:
Each master/standby DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instance has two connection addresses. When connecting to such an instance, you can use the read/write domain name address to connect to the master node or use the read-only domain name address to connect to the standby node.
The connection addresses can be obtained on the instance details page on the DCS console.
Master/standby DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instances support Sentinels. Sentinels monitor the running status of the master and standby nodes. If the master node becomes faulty, a failover will be performed.
Sentinels are invisible to you and is used only in the service.
A standby node has the same specifications as a master node. A master/standby instance consists of a pair of master and standby nodes by default.
To access a DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instance, you can customize the port. If no port is specified, the default port 6379 will be used. In the architecture diagram, port 6379 is used. If you have customized a port, replace 6379 with the actual port.
Note
To implement read/write splitting using a master/standby instance, ensure that your client can distinguish between read and write requests. The client directs write requests to the read/write domain name and read requests to the read-only domain name.
Requests to the read-only domain name address may fail if the standby node of a master/standby DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instance is faulty. For higher reliability and lower latency, do not use the read-only address.