Migration Process¶
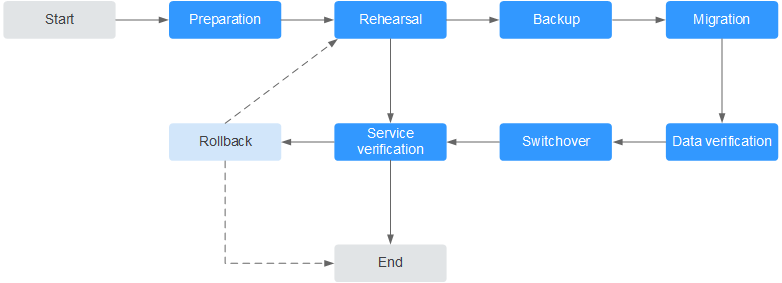
Figure 1 Migration flowchart¶
Evaluation¶
Collect the following information about the cached data to be migrated (based on Information to be collected for the migration):
Number of instances
Number of databases (DBs) configured for each instance
Number of keys in each DB
DBs used for your services
Space occupied by each instance
Redis version
Redis instance configurations (single-node, master/standby, or cluster)
Mapping relationships between your services and instances
Plan the following information about DCS instances based on the collected information:
Number of instances to be applied for
Specifications and type (single-node, master/standby, or cluster) of each instance
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), security groups, and subnets, and security groups, to which the instances and services belong
Note
redis-cli -h ${redis_address} -p ${port}
Run the following command to query the data distribution and obtain the IDs of DBs with data and the number of keys in each DB:
info keyspace
Query and record the number of keys in each DB for subsequent migration verification.
Run the following command to query the space occupied by the instance data. Check whether the available disk space of Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs) is sufficient for transition, and whether the instance specifications and remaining available memory are sufficient.
info memory
The occupied space can be obtained from the value of used_memory_human.
Preparation¶
After completing the evaluation, prepare the following items:
Mobile storage devices
These devices are used to copy and transfer data in case of network disconnection (in scenarios with data centers of enterprises).
Network resources
Create VPCs and subnets based on service planning.
Server resources
Apply for ECSs to bear Redis clients. The ECSs are used to export or import cached data.
Recommended ECS specifications are 8 vCPUs | 16 GB or higher.
DCS instances
Create DCS instances based on the migration planning. If the number of instances exceeds the default quota, submit a service ticket or contact customer service.
Related tools
Install the FTP tool and Redis migration tools.
Information to be collected
Collect the contact information of people involved in the migration, server addresses, login credentials, cache instance information, and DB information.
Overall migration plan
Formulate the overall migration plan, including the personnel arrangement, rehearsal, migration, verification, service switchover, and rollback solutions.
Break down each solution into executable operations and set milestones to mark the end of tasks.
Rehearsal¶
The rehearsal phase aims to:
Verify the feasibility of the migration tools and migration process.
Discover problems that may occur during migration and make effective improvements.
Evaluate the time required for migration.
Optimize the migration steps and verify the feasibility of concurrent implementation of some tasks to improve migration efficiency.
Backup¶
Before migration, back up related data, including but not limited to cached data and Redis configuration files, in case of emergency.
Migration¶
After conducting one or two rounds of migration rehearsal and solving problems found in the rehearsal, start data migration.
Break down the migration process into executable steps with specific start and end confirmation actions.
Data Verification¶
Check the following items:
The key distribution of each DB is consistent with the original or expected distribution.
Main keys.
Expiration time of keys.
Whether instances can be normally backed up and restored.
Service Switchover¶
After the data migration and verification, use the new instances for your services.
If DB IDs are changed, modify the ID configurations for your services.
If your services are migrated from data centers or cloud platforms provided by other vendors to this cloud as a whole, services and cached data can be migrated concurrently.
Service Verification¶
After the service switchover:
Verify the connectivity between your service applications and DCS instances.
Verify whether cached data can be normally added, deleted, modified, and queried.
If possible, perform pressure tests to ensure that the performance satisfies the peak service pressure.
Rollback¶
If your services are unavailable after the data migration because unexpected problems occur and cannot be solved in the short term, roll back your services.
Since source Redis data still exists, you only need to roll back your services and use the source Redis instances again.
After the rollback, you can continue to restart from the rehearsal or even preparation phase to solve the problems.
Information to be collected for the migration¶
The following table lists the information to be collected in the evaluation and preparation phases.
Migration Source | Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
Source Redis (List the information about all instances to be migrated.) | Source Redis IP address |
|
Redis instance password (if any) |
| |
Total data volume | Obtained from the value of used_memory_human by running the info memory command. Used to evaluate whether the migration solution, DCS instance specifications, and available disk space of ECSs meet requirements, and to estimate the time required for migration (service interruption duration). | |
IDs of DBs with data | Obtained by running the info keyspace command. Used to check whether the migration involves multiple DBs and non-AOF files. Some open-source tools can export and import data of only one DB at a time. For DCS instances, the single-node and master/standby types provide 256 DBs (DB 0 to DB 255), and the cluster type provides only one DB by default. | |
Number of keys in each DB | Used to verify the data integrity after migration. | |
Data type | The Cloud Data Migration (CDM) service supports two data formats: hash and string. If the source data contains data in other formats such as list and set, use a third-party migration tool. | |
ECS If a large number of instances are to be migrated, prepare multiple ECSs for concurrent migration. | EIP | Select ECSs that can communicate with DCS instances for data import to ensure network stability. Configure high-specification bandwidth to improve data transmission efficiency. |
Login credentials (username and password) |
| |
CPU and memory | Some migration tools support concurrent import through multiple threads. High-specification ECSs help improve import efficiency. | |
Available disk space | Sufficient available disk space needs to be reserved on the ECSs to store compressed files and decompressed cached data files. Note: To improve data transmission efficiency, compress large-size data files before transmitting them to ECSs. | |
DCS instances (Select appropriate instance specifications and quantities based on the number of source Redis instances and data volume.) | Instance connection address |
|
Instance connection port |
| |
Instance password |
| |
Instance type |
| |
Instance specifications and available memory |
| |
Network configurations | VPC | Plan VPCs in advance to ensure that your service applications and DCS instances are in same VPCs. |
Subnet |
| |
Whitelist or security group | DCS Redis 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, and 6.0 professional edition instances are deployed in different modes. Therefore, the access control methods vary. You can control access to your DCS instances by setting security groups or whitelists. For details, see How Do I Configure a Security Group? or Managing IP Address Whitelist. | |
... | ... | Other configurations. |