PL/SQL¶
This section describes the migration syntax of Oracle PL/SQL. The migration syntax determines how the keywords and features are migrated.
PL/SQL combines the procedural features of SQL and programming languages.
SQL Commands
Currently, GaussDB(DWS) does not support set define off/on and spool off. After being converted by the DSC tool, related commands are commented out in the target database.
Oracle Syntax | Syntax After Migration |
|---|---|
set define off
spool ORACLE.log
create table product
(
product_id VARCHAR2(20),
product_name VARCHAR2(50)
);
spool off
| /*set define off;*/
/*spool ORACLE.log*/
CREATE TABLE product
(
product_id VARCHAR2(20),
product_name VARCHAR2(50)
);
/*spool off*/
|
For details, see the following topics:
Relational Operators with Spaces
EDITIONABLE¶
The EDITIONABLE keyword is not supported in GaussDB(DWS). So it needs to be removed from the destination database.
Input - EDITIONABLE
CREATE OR REPLACE EDITIONABLE PACKAGE "PACK1"."PACKAGE_SEND_MESSAGE"
AS
TYPE filelist IS REF CURSOR;
PROCEDURE get_message_info (in_userid IN VARCHAR2,
in_branchid IN VARCHAR2,
in_appverid IN VARCHAR2,
in_app_list_flag IN VARCHAR2,
in_filetype IN VARCHAR2,
in_filestate IN VARCHAR2,
o_retcode OUT VARCHAR2,
o_errormsg OUT VARCHAR2,
o_seq OUT VARCHAR2,
o_totalnum OUT NUMBER,
o_filelist OUT filelist);
Output
/*~~PACKAGE_SEND_MESSAGE~~*/
CREATE
SCHEMA PACKAGE_SEND_MESSAGE
;
Variable Assignment¶
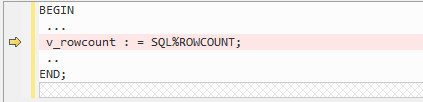
Figure 1 Input - PL/SQL¶
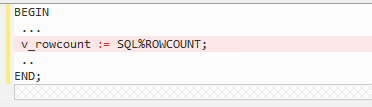
Figure 2 Output - PL/SQL¶
END¶
END with label is not supported in GaussDB(DWS), so, the label name is removed during migration.
Input - END with a procedure name
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE sp_ins_emp
…
…
...
END sp_ins_emp;
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE sp_ins_emp
…
…
...
END;
Input - END with a function name
CREATE FUNCTION fn_get_bal
…
…
...
END get_bal;
/
Output
CREATE FUNCTION fn_get_bal
…
…
...
END;
/
EXCEPTION Handling¶
GaussDB(DWS) does not support EXCEPTION handling. To migrate scripts, set the exceptionHandler parameter to True.
For DSC, this parameter must be set to the default value False.
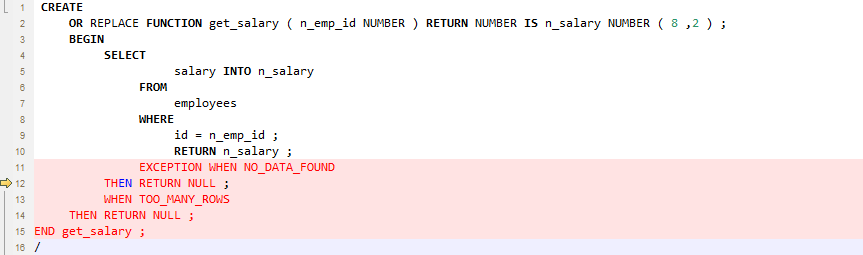
Figure 3 Input - EXCEPTION Handling¶
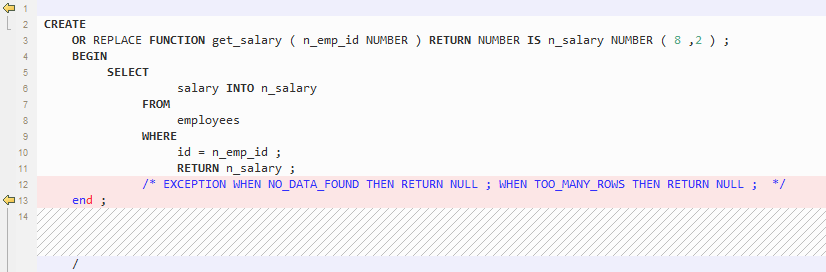
Figure 4 Output - EXCEPTION Handling¶
Subtransaction Handling¶
Subtransaction (that is commit and rollback statements in PL/SQL) is not supported. This parameter must be set to the default True.
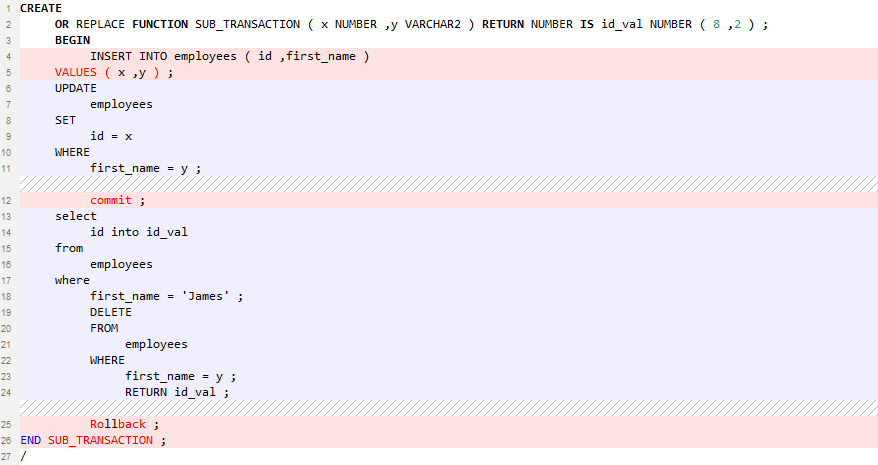
Figure 5 Input - Subtransaction Handling¶
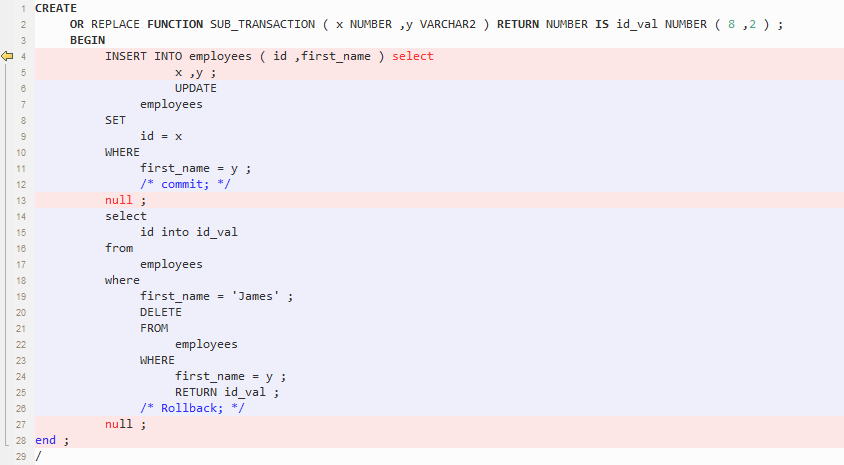
Figure 6 Output - Subtransaction Handling¶
STRING¶
The Oracle PL/SQL string type is not supported by GaussDB(DWS). This data type is handled by using VARCHAR.
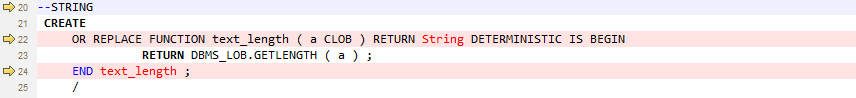
Figure 7 Input - STRING¶
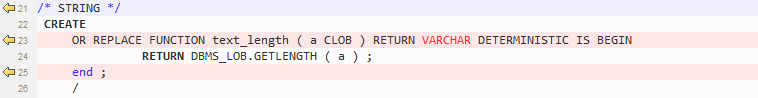
Figure 8 Output - STRING¶
LONG¶
LONG is migrated as TEXT.
Input - LONG
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION fn_proj_det
( i_proj_cd INT )
RETURN LONG
IS
v_proj_det LONG;
BEGIN
SELECT proj_det
INTO v_proj_det
FROM project
WHERE proj_cd = i_proj_cd;
RETURN v_proj_det;
END;
/
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION fn_proj_det
( i_proj_cd INT )
RETURN TEXT
IS
v_proj_det TEXT;
BEGIN
SELECT proj_det
INTO v_proj_det
FROM project
WHERE proj_cd = i_proj_cd;
RETURN v_proj_det;
END;
/
RESULT_CACHE¶
When a function with result cache is called, Oracle executes the function, adds the result to the result cache, and then returns the function.
When the function call is repeated, Oracle fetches the results from the cache rather than re-executing the function.
Under certain scenarios, this caching behavior can result in significant performance gains.
The target database does not support this keyword, which will be removed from the target file.
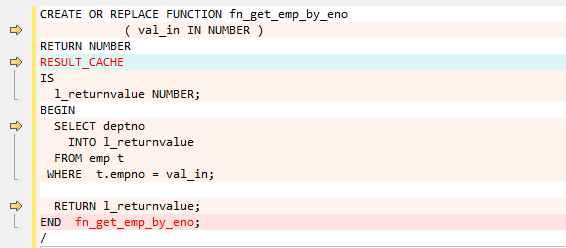
Figure 9 Input - RESULT_CACHE¶
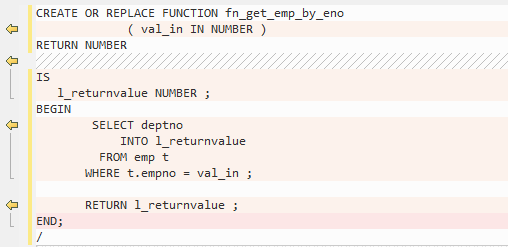
Figure 10 Output - RESULT_CACHE¶
Relational Operators with Spaces¶
The relational operators (<=, >=, !=) with spaces are not supported by GaussDB(DWS). DSC removes spaces between the operators.
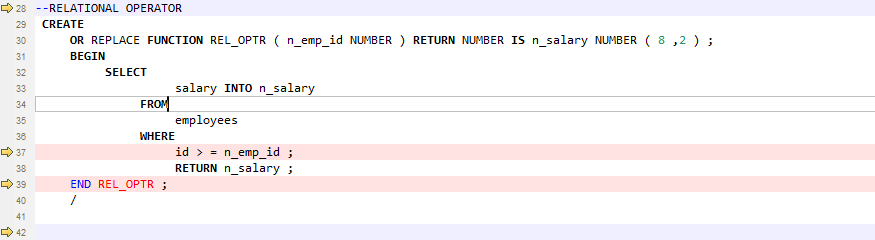
Figure 11 Input - Relational operator¶
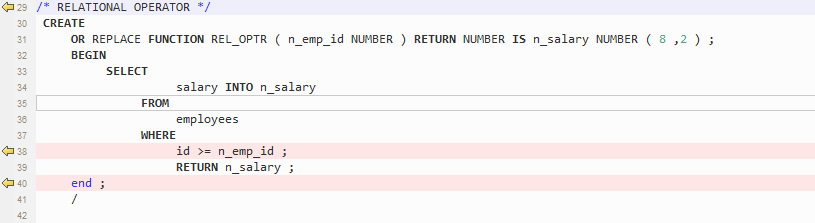
Figure 12 Output - Relational operator¶
Substitution Variables¶
Substitution variables are a feature of Oracle SQL*Plus tool. When a substitution variable is used in a statement, SQL*Plus requests an input value and rewrites the statement to include it. The rewritten statement is passed to the Oracle database. When the Oracle script input contains any substitution variables, the DSC displays the following message. Messages are recorded in the console and log files.
**************************************************************************
USER ATTENTION!!! Variable: &bbid should be substituted in the file : "/home/testmigration/V100R002C60/MigrationTool/Input/proc_frss_jczbsc.SQL" Variable: &wdbs should be substituted in the file : "/home/testmigration/V100R002C60/MigrationTool/Input/proc_frss_jczbsc.SQL" Variable: &batch_no should be substituted in the file : "/home/testmigration/V100R002C60/MigrationTool/Input/proc_frss_jczbsc.SQL"
**************************************************************************
PARALLEL_ENABLE¶
In Oracle, PARALLEL_ENABLE is used to enable parallel loading among partitions.
Input - PARALLEL_ENABLE
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION F_REPLACE_COMMA (IS_STR IN VARCHAR2)
RETURN VARCHAR2
parallel_enable
IS
BEGIN
IF IS_STR IS NULL THEN
RETURN NULL;
ELSE
RETURN REPLACE(REPLACE(IS_STR, CHR(13) || CHR(10), ''), ',', ', ');
END IF;
END F_REPLACE_COMMA;
/
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION F_REPLACE_COMMA (IS_STR IN VARCHAR2)
RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
BEGIN
IF IS_STR IS NULL THEN
RETURN NULL;
ELSE
RETURN REPLACE(REPLACE(IS_STR, CHR(13) || CHR(10), ''), ',', ', ');
END IF;
END;
/
PARALLEL Clause
PARALLEL should be commented.
Input
CREATE TABLE PRODUCT
( prod_id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY
, prod_code VARCHAR(5)
, prod_name VARCHAR(100)
, unit_price NUMERIC(6,2) NOT NULL )
PARALLEL 8;
Output
CREATE TABLE PRODUCT
( prod_id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY
, prod_code VARCHAR(5)
, prod_name VARCHAR(100)
, unit_price NUMERIC(6,2) NOT NULL )
/* PARALLEL 8 */;
TRUNCATE TABLE¶
The TRUNCATE TABLE statement in Oracle is used to remove all records from a table. It performs the same function as a DELETE statement without a WHERE clause. After truncating, the table will exist but it will be empty. DSC supports migration of TRUNCATE TABLE statements with static table names only. Migration of TRUNCATE TABLE statements with dynamic table names are not supported by the tool.
Note
The tool does not support migration of TRUNCATE TABLE statements with dynamic table names.
Example: l_table :='truncate table ' || itable_name
In this example, itable_name indicates a dynamic table name and is not supported by the DSC. The unsupported statements will be copied verbatim to the migrated scripts.
Input - TRUNCATE TABLE with Execute Immediate
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE schema1.proc1
AS
BEGIN
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'TRUNCATE TABLE QUERY_TABLE';
End proc1;
/
Output
CREATE
OR REPLACE PROCEDURE schema1.proc1 AS BEGIN
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'TRUNCATE TABLE schema1.QUERY_TABLE' ;
end ;
/
Input - TRUNCATE TABLE inside procedure
Note
Migration tool does not add schema names for dynamic PL/SQL statements.
CREATE
OR REPLACE PROCEDURE schemName.sp_dd_table ( itable_name VARCHAR2 ) IS l_table VARCHAR2 ( 255 ) ;
BEGIN
l_table :='truncate table ' || itable_name ;
---- dbms_utility.exec_ddl_statement(l_table);
dbms_output.put_line ( itable_name || ' ' || 'Truncated' ) ;
END sp_dd_table ;
/
Output
CREATE
OR REPLACE PROCEDURE schemName.sp_dd_table ( itable_name VARCHAR2 ) IS l_table VARCHAR2 ( 255 ) ;
BEGIN
l_table :='truncate table ' || itable_name ;
/*
dbms_utility.exec_ddl_statement(l_table); */
dbms_output.put_line ( itable_name || ' ' || 'Truncated' ) ;
end ;
/
ALTER SESSION¶
The ALTER SESSION statement in Oracle is used to set or modify the parameters and behavior of the database connection. The statement stays in effect until you disconnect from the database. The DSC supports the migration of ALTER SESSION as follows:
ALTER SESSION with ADVISE, ENABLE, DISABLE, CLOSE and FORCE clauses are migrated as commented scripts.
ALTER SESSION with SET CLAUSE parameter (Example: NLS_DATE_FORMAT, NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE, and so on) are copied verbatim.
Note
The tool does not support migration of ALTER SESSION statements that have a variable for the command clause.
Example: EXECUTE IMMEDIATE ' alter session ' || command_val || 'parallel ' || type_value.
In this example, command_val is a variable and this is not supported by the DSC. The unsupported statements will be copied verbatim in the migrated scripts.
Input - ALTER SESSION
ALTER SESSION ENABLE PARALLEL DDL;
ALTER SESSION ADVISE COMMIT;
ALTER SESSION CLOSE DATABASE LINK local;
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT = 'YYYY MM DD HH24:MI:SS';
ALTER SESSION SET current_schema = 'isfc';
Output
/*ALTER SESSION ENABLE PARALLEL DDL;*/
/*ALTER SESSION ADVISE COMMIT;*/
/*ALTER SESSION CLOSE DATABASE LINK local;*/
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT = 'YYYY MM DD HH24:MI:SS';
ALTER SESSION SET current_schema = 'isfc';
Input - ALTER SESSION
CREATE OR REPLACE
PROCEDURE PUBLIC .TEST_CALL is
command_val varchar2 ( 1000 ) ;
type_value number ;
BEGIN
command_val := 'enable parallel ddl' ;
dbms_output.put_line ( mike ) ;
-- execute immediate 'ALTER SESSION DISABLE GUARD' ;
execute immediate 'ALTER SESSION ADVISE ROLLBACK' ;
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE ' alter session ' || command_val || 'parallel ' || type_value ;
END TEST_CALL;
/
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE
PROCEDURE PUBLIC.TEST_CALL is
command_val varchar2 ( 1000 ) ;
type_value number ;
BEGIN
command_val := 'enable parallel ddl' ;
dbms_output.put_line ( mike ) ;
/* execute immediate 'ALTER SESSION DISABLE GUARD' ; */
execute immediate '/*ALTER SESSION ADVISE ROLLBACK*/' ;
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'alter session ' || command_val || 'parallel ' || type_value ;
END ;
/
AUTONOMOUS¶
Input - AUTONOMOUS
CREATE OR REPLACE EDITIONABLE PACKAGE BODY "Pack1"."DEMO_PROC" is
PROCEDURE log(proc_name IN VARCHAR2, info IN VARCHAR2) IS
PRAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION;
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DEMO_PROC.log ( proc_name IN VARCHAR2 ,info IN VARCHAR2 ) IS
/*PRAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION;*/
Procedure Call¶
Procedure with no parameter needs to put () after procedure name while calling the same procedure.
For example, pkg_etl.clear_temp_tables()
Input
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY IC_STAGE.pkg_etl
AS
PROCEDURE clear_temp_tables
IS
BEGIN
NULL;
END clear_temp_tables;
END pkg_etl;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY IC_STAGE.PKG_REVN_ARPU
AS
PROCEDURE AGGR_X_AGG00_REVN_DEALER (p_date PLS_INTEGER,
p_days PLS_INTEGER)
AS
v_start_date PLS_INTEGER;
v_curr_date PLS_INTEGER;
BEGIN
v_start_date := TO_CHAR (TO_DATE (p_date, 'yyyymmdd') - (p_days - 1), 'yyyymmdd');
v_curr_date := p_date;
WHILE (v_curr_date >= v_start_date)
LOOP
pkg_etl.clear_temp_tables;
pkg_dw.bind_variable ('v_curr_date', v_curr_date);
v_curr_date := TO_CHAR (TO_DATE (v_curr_date, 'yyyymmdd') - 1, 'yyyymmdd');
END LOOP;
END;
END PKG_REVN_ARPU;
/
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE IC_STAGE.pkg_etl#clear_temp_tables PACKAGE IS
BEGIN
NULL ;
END ;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE IC_STAGE.PKG_REVN_ARPU#AGGR_X_AGG00_REVN_DEALER
( p_date INTEGER
, p_days INTEGER )
PACKAGE
AS
v_start_date INTEGER;
v_curr_date INTEGER;
BEGIN
v_start_date := TO_CHAR( TO_DATE( p_date ,'yyyymmdd' ) - ( p_days - 1 ), 'yyyymmdd' ) ;
v_curr_date := p_date ;
WHILE ( v_curr_date >= v_start_date )
LOOP
pkg_etl#clear_temp_tables ( ) ;
pkg_dw.bind_variable ( 'v_curr_date' ,v_curr_date ) ;
v_curr_date := TO_CHAR( TO_DATE( v_curr_date ,'yyyymmdd' ) - 1,'yyyymmdd' ) ;
END LOOP ;
END ;
/
Function Name Having No Parameter Is Called
Function name which does not have any parameter, called by function name with parameter is not supported in EXCEPTION statement. For example, in SAD.SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB#error_msg ( ), error_msg is defined without parameter, as shown below:
CREATE
OR REPLACE FUNCTION SAD.SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB#func_name
RETURN VARCHAR2 IS MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME VARCHAR2 ( 30 ) := MIG_ORA_EXT.MIG_FN_GET_PKG_VARIABLE ( current_schema ( )
---
BEGIN
---
RETURN l_func_name ;
END ;
SCRIPTS: SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB.sql, SAD_CALC_ITEM_PRI_TEST_OB.sql
INPUT :
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY "SAD"."SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB" IS
PROCEDURE back_sad_cost_line_t(pi_contract_number IN VARCHAR2,
pi_quotation_id IN NUMBER,
pi_product_code IN VARCHAR2,
pi_process_batch_number IN NUMBER,
po_error_msg OUT VARCHAR2) IS
BEGIN
---
LOOP
INSERT INTO sad_cost_line_bak
(processing_batch_number,
contract_number,
product_code,
quotation_id,
item_code,
refresh_date,
split_date,
error_msg,
created_by,
creation_date,
last_updated_by,
last_update_date)
VALUES
(pi_process_batch_number,
cur_1.contract_number,
cur_1.product_code,
cur_1.quotation_id,
cur_1.item_code,
cur_1.refresh_date,
cur_1.split_date,
cur_1.error_msg,
cur_1.created_by,
cur_1.creation_date,
cur_1.last_updated_by,
cur_1.last_update_date);
END LOOP;
---
WHEN OTHERS THEN
po_error_msg := 'Others Exception raise in ' || func_name || ',' || SQLERRM;
END back_sad_cost_line_t;
END SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB;
OUTPUT :
CREATE
OR REPLACE PROCEDURE SAD.SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB#back_sad_cost_line_t ( pi_contract_number IN VARCHAR2
,pi_quotation_id IN NUMBER
,pi_product_code IN VARCHAR2
,pi_process_batch_number IN NUMBER
,po_error_msg OUT VARCHAR2 ) IS MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME VARCHAR2 ( 30 ) := MIG_ORA_EXT.MIG_FN_GET_PKG_VARIABLE ( current_schema ( )
,'SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB'
,'g_func_name' ) ::VARCHAR2 ( 30 ) ;
ex_data_error
EXCEPTION ;
ex_prog_error
EXCEPTION ;
BEGIN
---
LOOP
INSERT INTO sad_cost_line_bak (
processing_batch_number
,contract_number
,product_code
,quotation_id
,item_code
,refresh_date
,split_date
,SAD.SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB#error_msg ( )
,created_by
,creation_date
,last_updated_by
,last_update_date
)
VALUES ( pi_process_batch_number ,cur_1.contract_number ,cur_1.product_code ,cur_1.quotation_id ,cur_1.item_code ,cur_1.refresh_date ,cur_1.split_date ,cur_1.error_msg ,cur_1.created_by ,cur_1.creation_date ,cur_1.last_updated_by ,cur_1.last_update_date ) ;
END LOOP ;
---
WHEN OTHERS THEN
po_error_msg := 'Others Exception raise in ' || SAD.SAD_CALC_ITEM_PKG_TEST_OB#func_name ( ) || ',' || SQLERRM ;
END ;
Input
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY SAD.bas_dml_lookup_pkg IS
g_pkg_name CONSTANT VARCHAR2(30) := 'bas_dml_ic_price_rule_pkg' ;
g_func_name VARCHAR2(100);
FUNCTION func_name
RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
l_func_name VARCHAR2(100) ;
BEGIN
l_func_name := g_pkg_name || '.' || g_func_name ;
RETURN l_func_name ;
END ;
PROCEDURE data_change_logs ( pi_table_name IN VARCHAR2
, pi_table_key_columns IN VARCHAR2
, po_error_msg OUT VARCHAR2
)
IS
BEGIN
g_func_name := 'insert_fnd_data_change_logs_t';
INSERT INTO fnd_data_change_logs_t
( logid, table_name, table_key_columns )
VALUES
( fnd_data_change_logs_t_s.NEXTVAL
, pi_table_name, pi_table_key_columns );
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
po_error_msg := 'Others Exception raise in ' || func_name || ',' || SQLERRM;
END data_change_logs;
END bas_dml_lookup_pkg;
/
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION SAD.bas_dml_lookup_pkg#func_name
RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_PKG_NAME VARCHAR2(30) := MIG_ORA_EXT.MIG_FN_GET_PKG_VARIABLE ( 'SAD', 'BAS_DML_LOOKUP_PKG', 'G_PKG_NAME' )::VARCHAR2(30) ;
MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME VARCHAR2(100) := MIG_ORA_EXT.MIG_FN_GET_PKG_VARIABLE ( 'SAD', 'BAS_DML_LOOKUP_PKG', 'G_FUNC_NAME' )::VARCHAR2(100) ;
l_func_name VARCHAR2(100) ;
BEGIN
l_func_name := MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_PKG_NAME || '.' || MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME ;
RETURN l_func_name ;
END ;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE SAD.bas_dml_lookup_pkg#data_change_logs ( pi_table_name IN VARCHAR2
, pi_table_key_columns IN VARCHAR2
, po_error_msg OUT VARCHAR2 )
IS
MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME VARCHAR2(30) := MIG_ORA_EXT.MIG_FN_GET_PKG_VARIABLE ( 'SAD' ,'BAS_DML_LOOKUP_PKG' ,'G_FUNC_NAME' )::VARCHAR2(30) ;
BEGIN
MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME := 'insert_fnd_data_change_logs_t' ;
INSERT INTO fnd_data_change_logs_t (
logid,table_name,table_key_columns )
VALUES ( NEXTVAL ( 'fnd_data_change_logs_t_s' )
, pi_table_name, pi_table_key_columns ) ;
MIG_ORA_EXT.MIG_FN_SET_PKG_VARIABLE ( 'SAD', 'BAS_DML_LOOKUP_PKG', 'G_FUNC_NAME', MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME ) ;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
po_error_msg := 'Others Exception raise in ' || SAD.bas_dml_lookup_pkg#func_name( ) || ',' || SQLERRM ;
MIG_ORA_EXT.MIG_FN_SET_PKG_VARIABLE ( 'SAD', 'BAS_DML_LOOKUP_PKG', 'G_FUNC_NAME', MIG_PV_VAL_DUMMY_G_FUNC_NAME ) ;
END ;
/