DML¶
This section describes the migration syntax of Oracle DML. The migration syntax decides how the keywords/features are migrated.
For details, see the following topics:
SELECT¶
Overview
The Oracle SELECT statement starts a query, with an optional ORDER BY clause. The clause is used to retrieve records from one or more tables in a database.
Input - SELECT
SELECT col1, col2
FROM tab1;
Output
SELECT col1, col2
FROM tab1;
Order of Clauses
The HAVING clause must follow the GROUP BY clause. However, Oracle allows HAVING to be in front of or behind the GROUP BY clause. In the target database, the HAVING clause is moved to behind the GROUP BY clause.
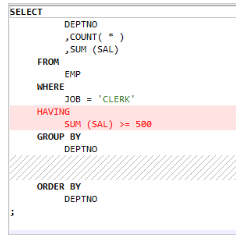
Figure 1 Input - Order of Clauses¶
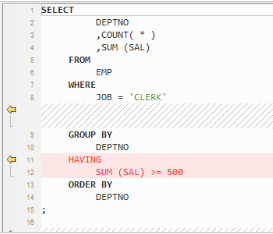
Figure 2 Output - Order of Clauses¶
Extended Group By Clause
The GROUP BY clause can be specified if you want the database to group the selected rows based on the value of expr(s). If this clause contains CUBE, ROLLUP, or GROUPING SETS extensions, then the database produces super-aggregate groupings in addition to the regular groupings. These features are not supported by GaussDB(DWS) but can be enabled using the UNION ALL operator.
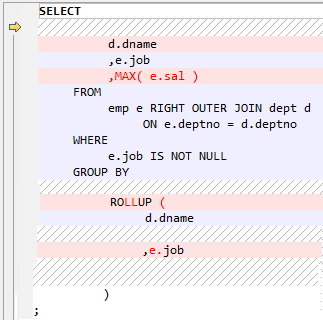
Figure 3 Input - Extended group by clause¶
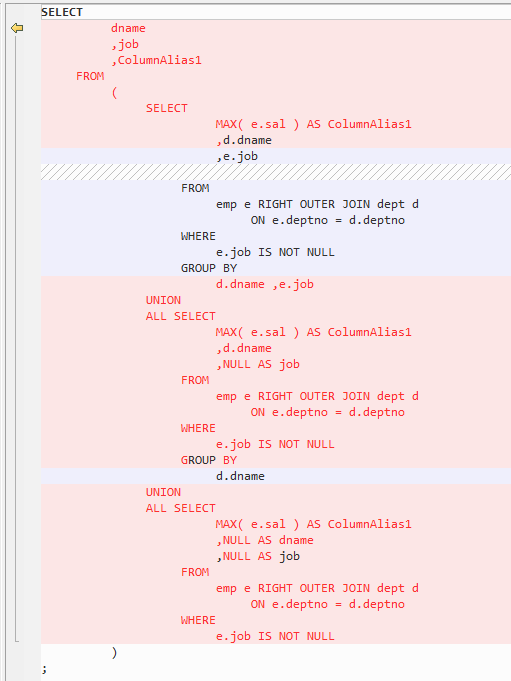
Figure 4 Output - Extended group by clause¶
GROUPING_ID and ROLLUP
GROUPING_ID returns a number that corresponds to the GROUPING bit vector associated with a row. GROUPING_ID is applicable only in a SELECT statement containing a GROUP BY extension, such as the ROLLUP operator and GROUPING function. In queries with multiple GROUP BY expressions, determining the GROUP BY level of a particular row requires multiple GROUPING functions, which may complicate SQL statements. In such scenarios, GROUPING_ID is used to avoid statement complexity.
Table Name Inside Brackets
Table names do not need to be specified within parentheses. However, allows using brackets.
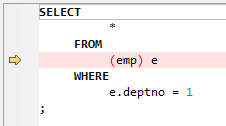
Figure 5 Input - Table name inside brackets¶
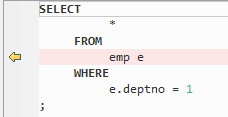
Figure 6 Output - Table name inside brackets¶
UNIQUE Keyword
Unique keyword is migrated as Distinct keyword.
Input - SELECT UNIQUE
SELECT UNIQUE a.item_id id, a.menu_id parent_id,a.serialno menu_order FROM ctp_menu_item_rel a WHERE a.item_id IN(SELECT UNIQUE id FROM ctp_temp_item_table);
Output
SELECT DISTINCT a.item_id id, a.menu_id parent_id,a.serialno menu_order FROM ctp_menu_item_rel a WHERE a.item_id IN(SELECT UNIQUE id FROM ctp_temp_item_table);
USERENY
Input - CLIENT_INFO
Returns user session information.
SELECT 1 FROM sp_ht ht WHERE ht.hth = pi_contract_number /* AND ht.contract_status = 2 --delete by leinian 2014-03-03(ECO) */ AND ht.contract_status IN ( 1, 2 ) /* add by leinian 2014-03-20(ECO) */ AND Nvl(ht.s3_pilot_flag, 'N') = 'N' AND NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM asms.asms_lookup_values alv WHERE alv.type_code = 'HTLX_LOAN' AND ht.htlx = alv.code) AND ht.duty_erp_ou_id = To_number(Nvl(Rtrim(Ltrim(Substr(Userenv( 'client_info'), 1, 8))), 218)) AND ht.source_code = 'ECONTRACT' AND ht.needing_engineering_service IS NOT NULL AND ht.khm != '28060' AND ht.htlx != '111' ;
Output
SELECT 1 FROM sp_ht ht WHERE ht.hth = pi_contract_number /* AND ht.contract_status = 2 --delete by leinian 2014-03-03(ECO) */ AND ht.contract_status IN ( 1 ,2 ) /* add by leinian 2014-03-20(ECO) */ AND Nvl( ht.s3_pilot_flag ,'N' ) = 'N' AND NOT EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM asms.asms_lookup_values alv WHERE alv.type_code = 'HTLX_LOAN' AND ht.htlx = alv.code ) AND ht.duty_erp_ou_id = To_number( Nvl( Rtrim( Ltrim( SUBSTR( MIG_ORA_EXT.USERENV ( 'client_info' ) ,1 ,8 ) ) ) ,218 ) ) AND ht.source_code = 'ECONTRACT' AND ht.needing_engineering_service IS NOT NULL AND ht.khm != '28060' AND ht.htlx != '111' ;
USERENV('CLIENT_INFO)
After the function in the package is converted, the function tag is not deleted. 4. The svproduct_is_for_pa function in sad_lookup_contract_pkg.bdy is used.
USERENV('CLIENT_INFO')
USERENV used during the migration process. Migration fails due to the tool.
SELECT 1 FROM sp_ht ht WHERE ht.hth = pi_contract_number /* AND ht.contract_status = 2 --delete by leinian 2014-03-03(ECO) */ AND ht.contract_status IN ( 1, 2 ) /* add by leinian 2014-03-20(ECO) */ AND Nvl(ht.s3_pilot_flag, 'N') = 'N' /* add by yangyirui 2012-09-10: S3 Data is not provided for the contract cutover. */ AND NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM asms.asms_lookup_values alv WHERE alv.type_code = 'HTLX_LOAN' AND ht.htlx = alv.code) AND ht.duty_erp_ou_id = To_number(Nvl(Rtrim(Ltrim(Substr(Userenv( 'client_info'), 1, 8))), 218)) AND ht.source_code = 'ECONTRACT' AND ht.needing_engineering_service IS NOT NULL AND ht.khm != '28060' AND ht.htlx != '111'
Input
Error message :client_info argument for USERENV function is not supported by the DSC. 4_sad_lookup_contract_pkg ================================ CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY SAD.sad_lookup_contract_pkg IS FUNCTION svproduct_is_for_pa(pi_contract_number IN VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS l_flag VARCHAR2(1) := 'N'; BEGIN FOR rec_lookup IN (SELECT 1 FROM asms.asms_lookup_values alv WHERE alv.type_code = 'HTLX_LOAN' AND alv.duty_erp_ou_id = to_number(nvl(rtrim(ltrim(substr(userenv('client_info'), 1, 8))), 218)) ) LOOP l_flag := 'Y'; END LOOP; RETURN l_flag; END svproduct_is_for_pa; END sad_lookup_contract_pkg; /
Output
CREATE OR replace FUNCTION sad_lookup_contract_pkg.Svproduct_is_for_pa ( pi_contract_number IN VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS l_flag VARCHAR2 ( 1 ) := 'N'; BEGIN FOR rec_lookup IN (SELECT 1 FROM asms.asms_lookup_values alv WHERE alv.type_code = 'HTLX_LOAN' AND alv.duty_erp_ou_id = To_number(Nvl( Rtrim(Ltrim(Substr( mig_ora_ext.Userenv ( 'client_info'), 1, 8)) ), 218) )) LOOP l_flag := 'Y'; END LOOP; RETURN l_flag; END; /
INSERT¶
Overview
The Oracle INSERT statement is used to insert a single record or multiple records into a table.
NOLOGGING
NOLOGGING is commented from the inserted script.
Oracle Syntax | Syntax After Migration |
|---|---|
INSERT INTO TBL_ORACLE NOLOGGING
SELECT emp_id, emp_name
FROM emp;
| INSERT INTO TBL_ORACLE /*NOLOGGING*/
SELECT emp_id, emp_name
FROM emp;
|
INSERT ALL
The Oracle INSERT ALL statement is used to add multiple rows using a single INSERT statement. The rows can be inserted into either a single table or multiple tables. The target query is converted as a common table expression (CTE).
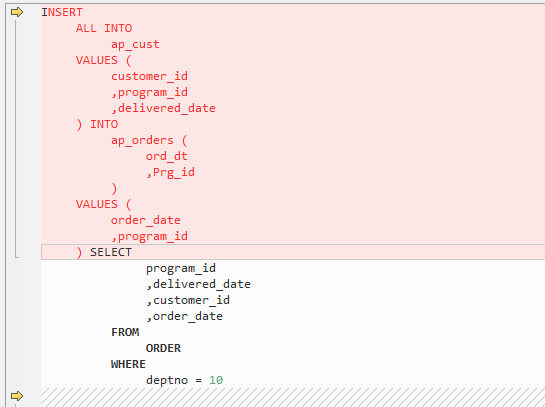
Figure 7 Input - INSERT ALL¶
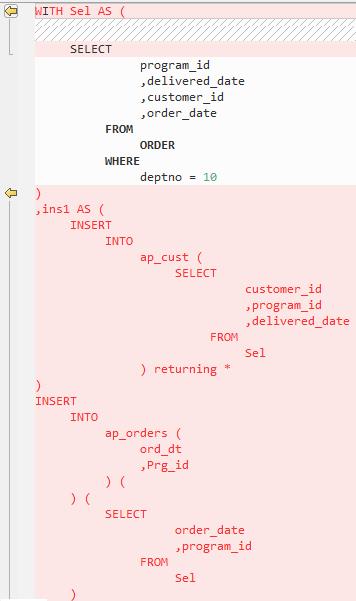
Figure 8 Output - Insert All¶
INSERT FIRST
The Oracle INSERT FIRST is used to execute an INSERT statement when the first condition is true; other statements are ignored. The target query is converted as a CTE.
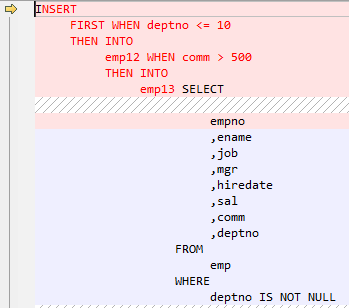
Figure 9 Input - Insert first¶

Figure 10 Output - Insert first¶
INSERT with Table Alias
The Oracle table aliases is used to clarify and improve readability when referring to a table in a query by assigning it a name or code. INSERT with table alias can be used with INSERT INTO statement. The tool supports the migration of INSERT INTO statements with table alias.
Blogic Operations
Input - INSERT with Table Alias
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION myfct RETURN VARCHAR2 IS res VARCHAR2 ( 200 ) ; BEGIN res := 100 ; INSERT INTO emp18 RW ( RW.empno ,RW.ename ) SELECT res ,RWN.ename FROM emp16 RWN ; COMMIT ; RETURN res ; END ; /
Output
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION myfct RETURN VARCHAR2 IS res VARCHAR2 ( 200 ) ; BEGIN res := 100 ; INSERT INTO emp18 ( empno ,ename ) SELECT res ,RWN.ename FROM emp16 RWN ; /* COMMIT ; */ null ; RETURN res ; END ; /
Bulk Operations
Input - INSERT with Table Alias
INSERT INTO Public.emp14 ats ( ats.empno ,ats.ename ) VALUES ( 3 ,'Categories' ) ;
Output
INSERT INTO Public.emp14 ( empno ,ename ) SELECT 3 ,'Categories' ;
Input - INSERT with Table Alias
INSERT INTO "abc" . "emp18" wmc ( wmc.empno ,wmc.ename ) SELECT wmc.empno ,wm_concat (wmc.ename) AS eName FROM emp16 wmc GROUP BY empno ;
Output
INSERT INTO "abc" . "emp18" ( empno ,ename ) SELECT wmc.empno ,STRING_AGG ( wmc.ename ,',' ) AS eName FROM emp16 wmc GROUP BY empno ;
Input - INSERT with Table Alias
INSERT INTO emp14 "TABLE" ( "TABLE" .empno ,ename ) SELECT empno ,ename FROM emp12 WHERE emp12.salary > ( SELECT MAX( salary ) FROM emp13 "TABLE" WHERE "TABLE" .empno > 5 ) ;
Output
INSERT INTO emp14 ( empno ,ename ) SELECT empno ,ename FROM emp12 WHERE emp12.salary > ( SELECT MAX( salary ) FROM emp13 "TABLE" WHERE "TABLE" .empno > 5 ) ;
MERGE¶
MERGE is an ANSI-compliant SQL syntax operator used to select rows from one or more sources for updating or inserting a table or view. The criteria for updating or inserting the target table or view can be specified.
DSC uses multiple methods to migrate MERGE to SQL statements compatible with GaussDB(DWS).
Configure parameter mergeImplementation as follows:
Set to With by default. In this option, the target query is converted as a CTE.
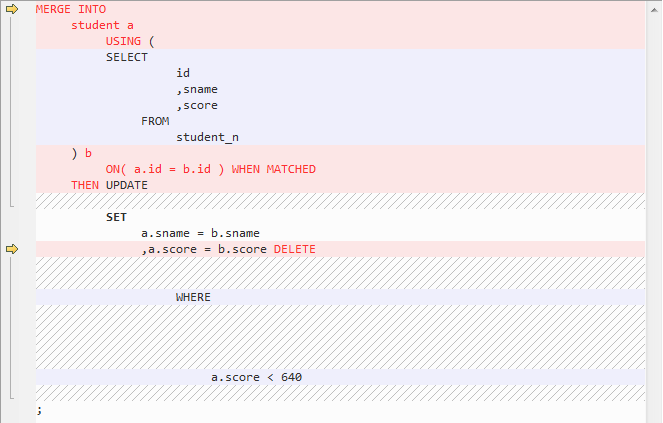
Figure 11 Input - MERGE¶
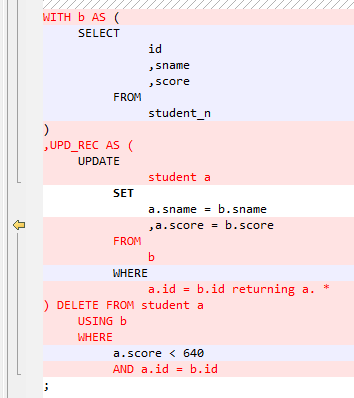
Figure 12 Output - MERGE¶
Set to SPLIT. In this option, the MERGE statement is split into multiple INSERT and UPDATE statements.
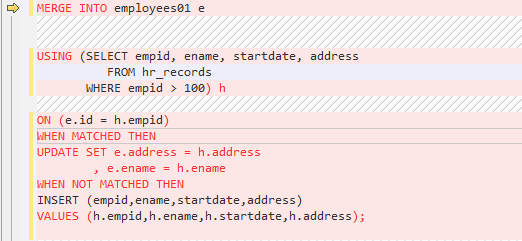
Figure 13 Input - MERGE¶
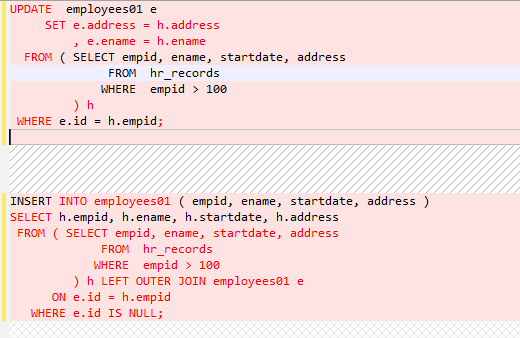
Figure 14 Output - MERGE¶