String Functions¶
This section describes the following string functions:
LISTAGG¶
LISTAGG is used to order data in columns within each group specified in the ORDER BY clause and concatenates the order results.
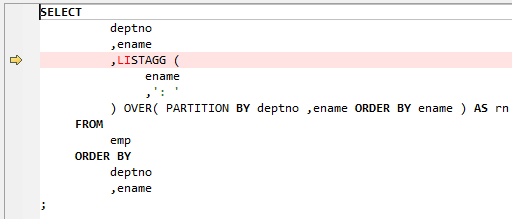
Figure 1 Input - Listagg¶
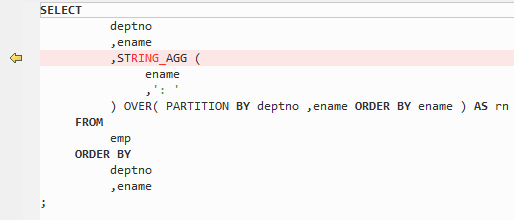
Figure 2 Output - Listagg¶
LISTAGG can be migrated after MigSupportForListAgg is set to false.
Input- LISTAGG
SELECT LISTAGG(BRANCH_ID, ',') WITHIN GROUP(ORDER BY AREA_ORDER) PRODUCTRANGE
FROM (SELECT DISTINCT VB.BRANCH_ID,
VB.VER_ID,
VB.AREA_ORDER
FROM SPMS_VERSION_BRANCH VB, SPMS_NODE_SET NS
WHERE VB.BRANCH_TYPE IN ('1', '3')
AND VB.AGENCY_BRANCH = NS.BRANCH_ID);
Output
SELECT LISTAGG (BRANCH_ID,',') WITHIN GROUP (
ORDER BY AREA_ORDER ) PRODUCTRANGE
FROM ( SELECT
DISTINCT VB.BRANCH_ID
,VB.VER_ID
,VB.AREA_ORDER
FROM
SPMS_VERSION_BRANCH VB
,SPMS_NODE_SET NS
WHERE VB.BRANCH_TYPE IN (
'1','3')
AND VB.AGENCY_BRANCH = NS.BRANCH_ID)
;
STRAGG¶
STRAGG is a string aggregate function used to collect values from multiple rows into a comma-separated string.
Input-STRAGG
SELECT DEPTNO,ENAME,STRAGG(ename) over (partition by deptno order by
ename RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING)
AS ENAME_STR FROM EMP;
Output
SELECT DEPTNO,ENAME,STRING_AGG (
ename,',') over( partition BY deptno ORDER BY
ename RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED
FOLLOWING ) AS ENAME_STR
FROM EMP
;
WM_CONCAT¶
WM_CONCAT is used to aggregate data from a number of rows into a single row, giving a list of data associated with a specific value.
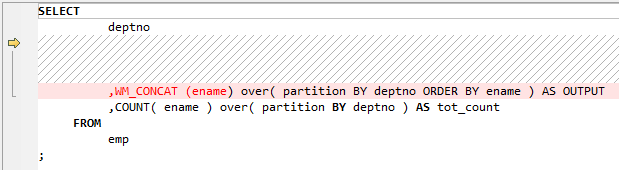
Figure 3 Input - WM_Concat¶
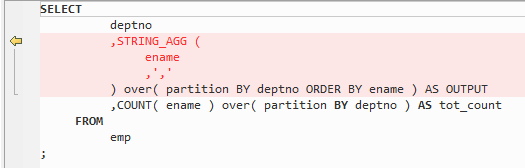
Figure 4 Output - WM_Concat¶
NVL2 and REPLACE¶
NVL2( expression, value1, value2) is a function used to determine the value returned by a query based on whether a specified expression is null or not. If the expression is not null, then NVL2 returns value1. If the expression is null, then NVL2 returns value 2.
Input - NVL2
NVL2(Expr1, Expr2, Expr3)
Output
DECODE(Expr1, NULL, Expr3, Expr2)
The REPLACE function is used to return char with every occurrence of search_string replaced with replacement_string. If replacement_string is omitted or null, then all occurrences of search_string are removed.
The REPLACE function in Oracle contains two mandatory parameters and one optional parameter. The REPLACE function in GaussDB(DWS) contains three mandatory parameters.
Input - Nested REPLACE
CREATE
OR REPLACE FUNCTION F_REPLACE_COMMA ( IS_STR IN VARCHAR2 ) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS BEGIN
IF
IS_STR IS NULL
THEN RETURN NULL ;
ELSE
RETURN REPLACE( REPLACE( IS_STR ,'a' ) ,CHR ( 10 ) ) ;
END IF ;
END F_REPLACE_COMMA ;
/
Output
CREATE
OR REPLACE FUNCTION F_REPLACE_COMMA ( IS_STR IN VARCHAR2 ) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS BEGIN
IF
IS_STR IS NULL
THEN RETURN NULL ;
ELSE
RETURN REPLACE( REPLACE( IS_STR ,'a' ,'' ) ,CHR ( 10 ) ,'' ) ;
END IF ;
end ;
/
Input - More than one REPLACE
SELECT
REPLACE( 'JACK and JUE' ,'J', '' ) "Changes"
,REPLACE( 'JACK1 and JUE' ,'J' ) "Changes1"
,REPLACE( 'JACK2 and JUE' ,'J' ) "Changes2"
FROM
DUAL
;
Output
SELECT
REPLACE( 'JACK and JUE' ,'J' ,'' ) "Changes"
,REPLACE( 'JACK1 and JUE' ,'J' ,'' ) "Changes1"
,REPLACE( 'JACK2 and JUE' ,'J' ,'' ) "Changes2"
FROM
DUAL
;
Input - REPLACE with Three parameters
SELECT
REPLACE( '123tech123' ,'123', '1')
FROM
dual
;
Output
SELECT
REPLACE( '123tech123' ,'123' , '1' )
FROM
dual
;
QUOTE¶
QUOTE allows the user to embed single-quotes in literal strings without having to resort to double quotes. That is, you can use single quotes to specify a literal string.
For example:
SELECT q'[I'm using quote operator in SQL statement]' "Quote (q) Operator" FROM dual;
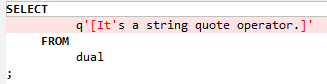
Figure 5 Input - Quote¶
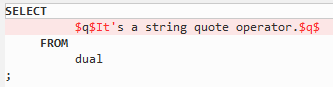
Figure 6 Output - Quote¶