Cursor Loop¶
The use of cursors in WHILE and LOOP statements is called a cursor loop. Generally, OPEN, FETCH, and CLOSE statements are needed in cursor loop. The following describes a loop that is applicable to a static cursor loop without executing the four steps of a static cursor.
Syntax¶
Figure 1 shows the syntax diagram for the FOR AS loop.
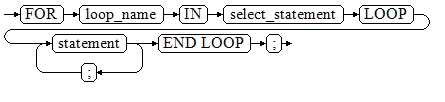
Figure 1 FOR_AS_loop::=¶
Precautions¶
The UPDATE operation for the queried table is not allowed in the loop statement.
The variable loop_name is automatically defined and is valid only in this loop. The type and value of loop_name are the same as those of the query result of select_statement.
The %FOUND, %NOTFOUND, and %ROWCOUNT attributes access the same internal variable in GaussDB(DWS). Transactions and anonymous blocks cannot be accessed by multiple cursors at the same time.
Examples¶
BEGIN
FOR ROW_TRANS IN
SELECT first_name FROM staffs
LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (ROW_TRANS.first_name );
END LOOP;
END;
/
-- Create a table:
CREATE TABLE integerTable1( A INTEGER) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(A);
CREATE TABLE integerTable2( B INTEGER) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(B);
INSERT INTO integerTable2 VALUES(2);
-- Multiple cursors share the parameters of cursor attributes:
DECLARE
CURSOR C1 IS SELECT A FROM integerTable1;--Declare the cursor.
CURSOR C2 IS SELECT B FROM integerTable2;
PI_A INTEGER;
PI_B INTEGER;
BEGIN
OPEN C1;-- Open the cursor.
OPEN C2;
FETCH C1 INTO PI_A; ---- The value of C1%FOUND and C2%FOUND is FALSE.
FETCH C2 INTO PI_B; ---- The value of C1%FOUND and C2%FOUND is TRUE.
-- Determine the cursor status:
IF C1%FOUND THEN
IF C2%FOUND THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Dual cursor share paremeter.');
END IF;
END IF;
CLOSE C1;-- Close the cursor.
CLOSE C2;
END;
/
-- Drop the temporary table:
DROP TABLE integerTable1;
DROP TABLE integerTable2;