Processing Data¶
DRS processes synchronized objects and allows you to add rules for selected objects.
Filtering Data¶
After a data filtering rule is added, update the source database to ensure data consistency. For example:
The filter criteria are met after the update. You need to continue the synchronization and perform the same update operation on the destination database. If no data is matched, the operation will be ignored, causing data inconsistency.
The filter criteria are not met after the update. You need to continue the synchronization and perform the same update operation on the destination database.
On the Data filtering page, select the table objects to be processed in the Object field.
In the Object area, select the table to be processed.
In the Filtering Criteria area, enter the filter criteria (only the part after WHERE in the SQL statement, for example, id=1), and click Verify.
Note
Each table has only one verification rule.
Up to 500 tables can be filtered at a time.
The filter expression cannot use the package, function, variable, or constant of a specific DB engine. It must comply with the general SQL standard. Enter the part following WHERE in the SQL statement (excluding WHERE and semicolons), for example, sid > 3 and sname like "G %". A maximum of 512 characters are allowed.
In SQL statements for setting filter criteria, keywords must be enclosed in backquotes, and the value of datatime (including date and time) must be enclosed in single quotation marks, for example, `update` > '2022-07-13 00:00:00' and age >10.
Filter criteria cannot be configured for large objects, such as CLOB, BLOB, and BYTEA.
You are not advised to set filter criteria for fields of approximate numeric types, such as FLOAT, DECIMAL, and DOUBLE.
Do not use fields containing special characters as a filter condition.
You are not advised to use non-idempotent expressions or functions as data processing conditions, such as SYSTIMESTAMP and SYSDATE, because the returned result may be different each time the function is called.
After the verification is successful, click Generate Processing Rule. The rule is displayed.
Click Next.
Processing Columns¶
On the Process Data page, select Processing Columns.
In the Object area, select the objects to be processed.
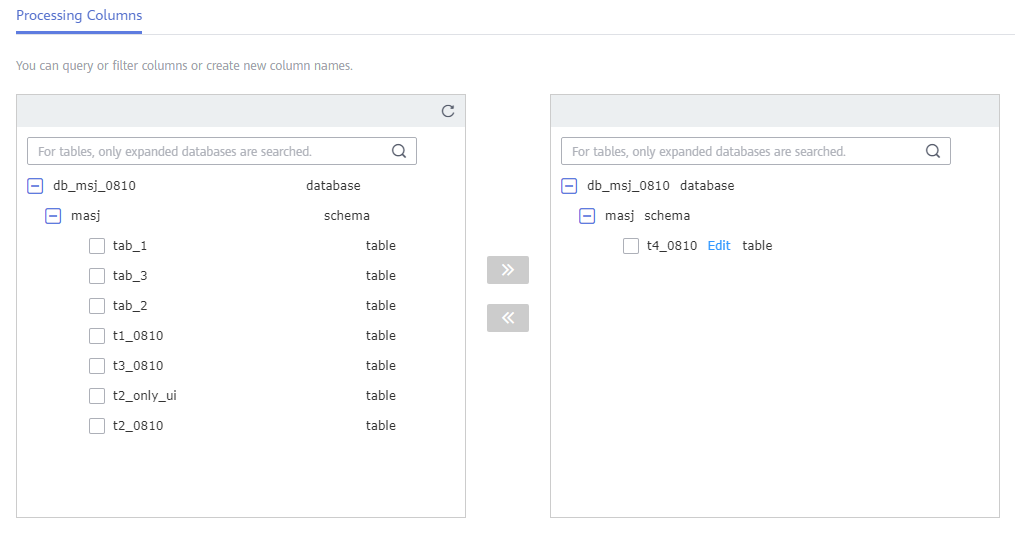
Figure 1 Processing Columns¶
Click Edit to the right of the selected object.
In the Edit Column dialog box, select the columns to be mapped and enter new column names.
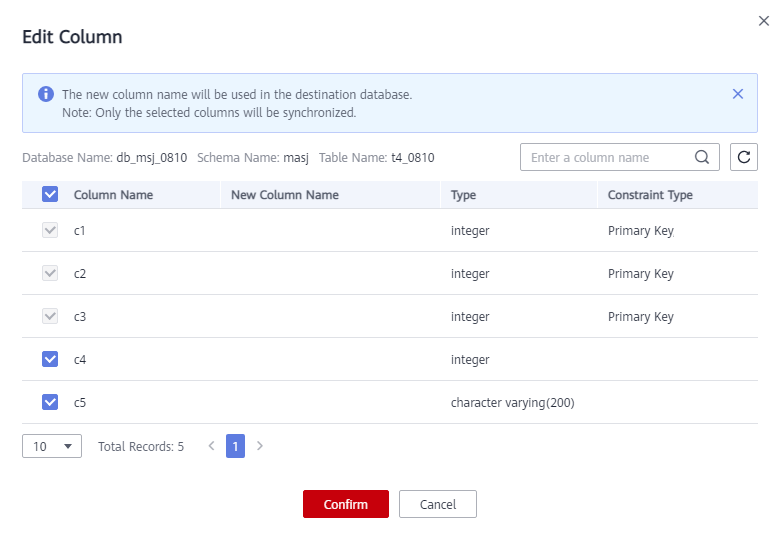
Figure 2 Edit Column¶
Note
You can query or filter columns or create new column names.
After the column name is edited, the column name of the destination database is changed to the new name.
The new column name cannot be the same as the original column name or an existing column name.
The column name in the synchronized table cannot be modified.
Only the selected columns can be synchronized.
MySQL to MySQL and MySQL to TaurusDB Cluster synchronizations do not support column mapping based on the partitioning column of a partitioned table.
GaussDB partition keys cannot be filtered.
Click Confirm.
Click Next.
Viewing Data Filtering Results¶
In the task list, click the task to be processed.
Click the Process Data tab to view data filtering records. Click
 in the upper right corner to refresh the record list.
in the upper right corner to refresh the record list.