Overview¶
DataArts Factory is a one-stop big data collaborative development platform that provides fully managed big data scheduling capabilities. It manages various big data services, making big data more accessible than ever before and helping you effortlessly build big data processing centers.
DataArts Factory used to be Data Lake Factory (DLF). Therefore, in this document, both Data Lake Factory and DLF can be used to refer to DataArts Factory.
Introduction to DataArts Factory¶
DataArts Factory enables a variety of operations such as data management, script development, job development, job scheduling, and monitoring, facilitating data analysis and processing.
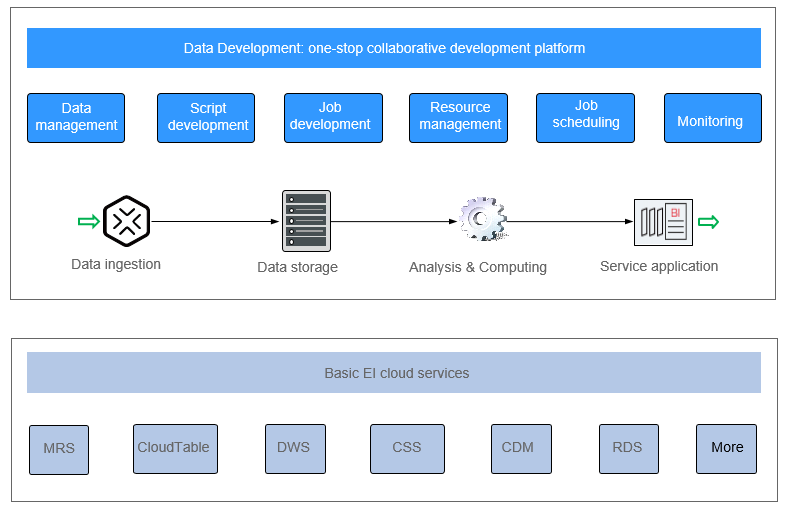
Figure 1 DataArts Factory architecture¶
Main Functions¶
Function | Description |
|---|---|
Data management |
|
Script development |
|
Job development |
|
Resource management | Supports unified management of file, jar, and archive resources used during script and job development. |
Job scheduling | Schedules jobs to run once or recursively and use events to trigger scheduling jobs. If the scheduling frequency is set to hour, the scheduling period can be based on interval hour or discrete hour. |
Monitoring |
|
Objects in DataArts Factory¶
Data connection: A data connection is a collection of information required for accessing data storage (computing) space, including the connection type, name, and login information.
Solution: A solution provides users with convenient and systematic management operations to better meet service requirements and objectives. Each solution can contain one or more business-related jobs, and one job can be used by multiple solutions.
Job: A job is composed of one or more nodes and can be executed to complete data operations.
Script: A script is an extension of a batch processing file. It is a program that stores text. Generally, a computer script program is a combination of a series of operations that control computers to perform operations. In the script program, certain logic branches can be implemented.
Node: A node defines the operations performed on data.
Resource: Resources refer to self-defined codes or text files that are uploaded by users and scheduled when node tasks are executed.
Expression: Node parameter values in a node job can be dynamically generated based on the running environment by using Expression Language (EL). EL uses simple arithmetic and logic to calculate and reference embedded objects, including job objects and tool objects.
Environment variable: An environment variable is an object with a specific name in the operating system. It contains information to be used by one or more applications.
PatchData: PatchData refers to the instance that is generated in a period of time by a periodically scheduled job.