Scheduling Workloads¶
Volcano is a Kubernetes-based batch processing platform with high-performance general computing capabilities like task scheduling engine, heterogeneous chip management, and task running management. It provides end users with computing frameworks from multiple domains such as AI, big data, gene, and rendering. It also offers job scheduling, job management, and queue management for computing applications.
Kubernetes typically uses its default scheduler to schedule workloads. To use Volcano, specify Volcano for your workloads. For details about the Kubernetes scheduler, see Specify schedulers for pods.
Notes and Constraints¶
If you schedule a lot of workloads, Volcano will generate a significant number of logs. To prevent the node hosting Volcano from running out of disk space, use Volcano with LTS.
Using Volcano¶
When using Volcano to schedule workloads, you only need to configure schedulerName in the spec field of the pod and set the parameter to volcano. The following is an example:
Use YAML to create a queue.
apiVersion: scheduling.volcano.sh/v1beta1 kind: Queue metadata: name: q1 spec: reclaimable: true weight: 1
Set schedulerName in the spec field of the pod to volcano.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 4 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: annotations: # Submit the job to the q1 queue. scheduling.volcano.sh/queue-name: "q1" volcano.sh/preemptable: "true" labels: app: nginx spec: # Specify Volcano as the scheduler. schedulerName: volcano containers: - name: nginx image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: limits: cpu: 1 memory: 100Mi requests: cpu: 1 memory: 100Mi ports: - containerPort: 80
Additionally, Volcano supports the workload queues and preemption, which can be implemented through pod annotations. The following table lists the supported annotations.
Pod Annotations | Description |
|---|---|
scheduling.volcano.sh/queue-name: "<queue-name>" | Specifies the queue to which the workload belongs. <queue-name> indicates the queue name. |
volcano.sh/preemptable: "true" | Indicates whether a job can be preempted. If this function is enabled, the job can be preempted. Options:
|
You can obtain pod details to check whether the pod is scheduled by Volcano to the allocated queue.
Run the following command to check the pod details and obtain the scheduling.k8s.io/group-name value:
kubectl describe pod <pod_name>
The scheduling.k8s.io/group-name value of the pod is displayed.
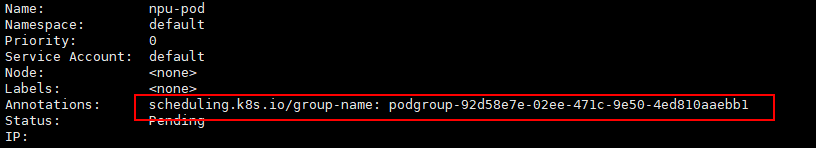
Check whether the pod is scheduled by Volcano to the allocated queue.
kubectl describe pg <group_name>
Command output:
Spec: Min Member: 1 Min Resources: Cpu: 100m Memory: 100Mi Queue: q1 Status: Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2023-05-30T01:54:43Z Reason: tasks in gang are ready to be scheduled Status: True Transition ID: 70be1d7d-3532-41e0-8324-c7644026b38f Type: Scheduled Phase: Running Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal Scheduled 0s (x3 over 2s) volcano pod group is ready