Overview¶
Background¶
When switching between old and new services, you may be challenged in ensuring the system service continuity. If a new service version is directly released to all users at a time, it can be risky because once an online accident or bug occurs, the impact on users is great. It could take a long time to fix the issue. Sometimes, the version has to be rolled back, which severely affects user experience.
Solution¶
Several release policies are developed for service upgrade: grayscale release, blue-green deployment, A/B testing, rolling upgrade, and batch suspension of release. Traffic loss or service unavailability caused by releases can be avoided as much as possible.
This document describes the principles and practices of grayscale release and blue-green deployment.
Grayscale release, also called canary release, is a smooth iteration mode for version upgrade. During the upgrade, some users use the new version, while other users continue to use the old version. After the new version is stable and ready, it gradually takes over all the live traffic. In this way, service risks brought by the release of the new version can be minimized, the impact of faults can be reduced, and quick rollback is supported.
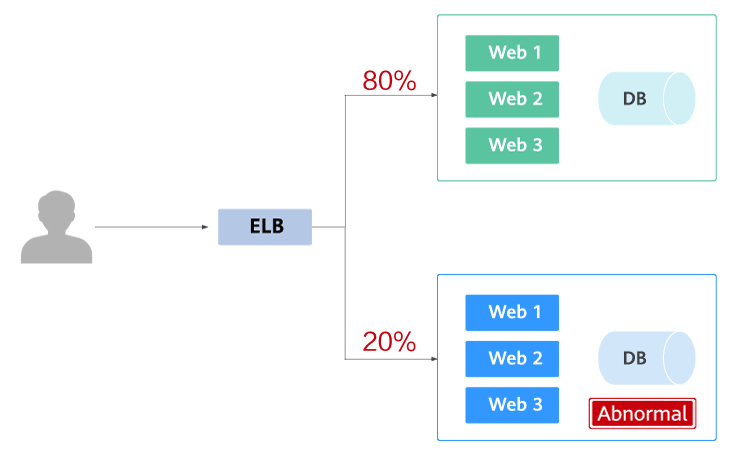
The following figure shows the general process of grayscale release. First, divide 20% of all service traffic to the new version. If the service version runs normally, gradually increase the traffic proportion and continue to test the performance of the new version. If the new version is stable, switch all traffic to it and bring the old version offline.
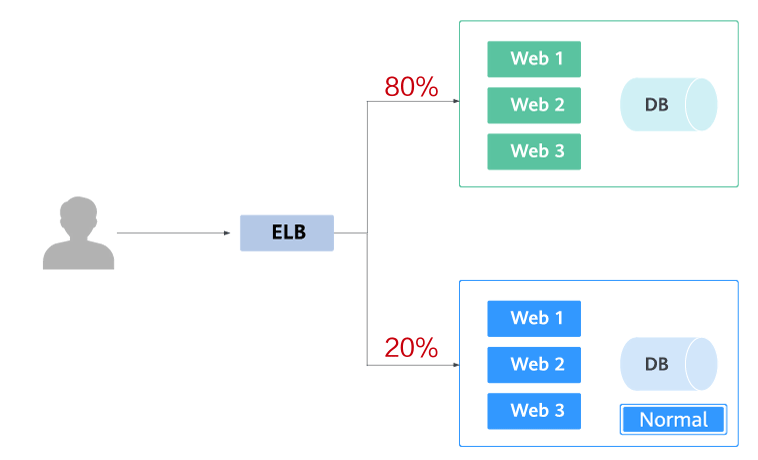
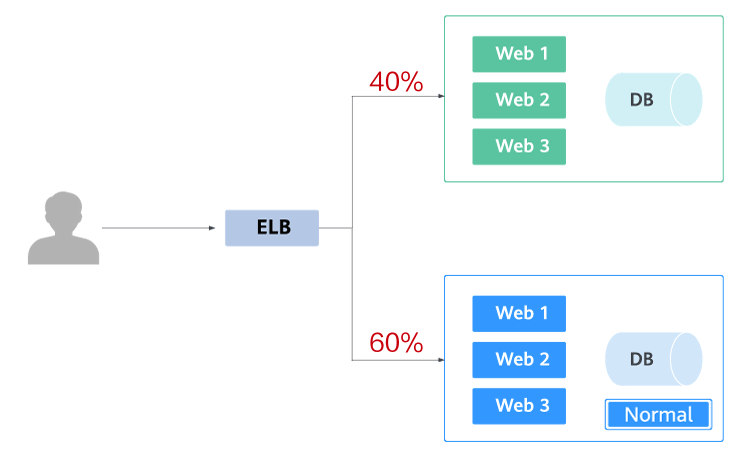
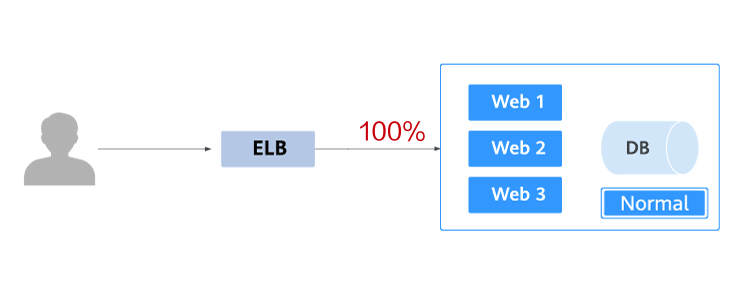
If an exception occurs in the new version when 20% of the traffic goes to the new version, you can quickly switch back to the old version.
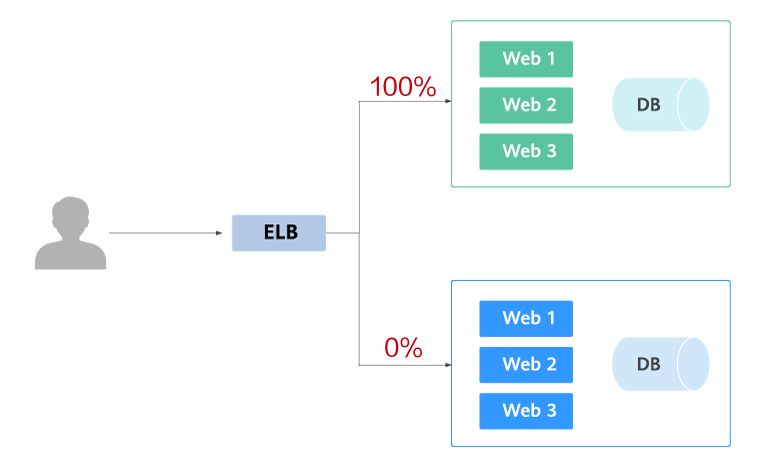
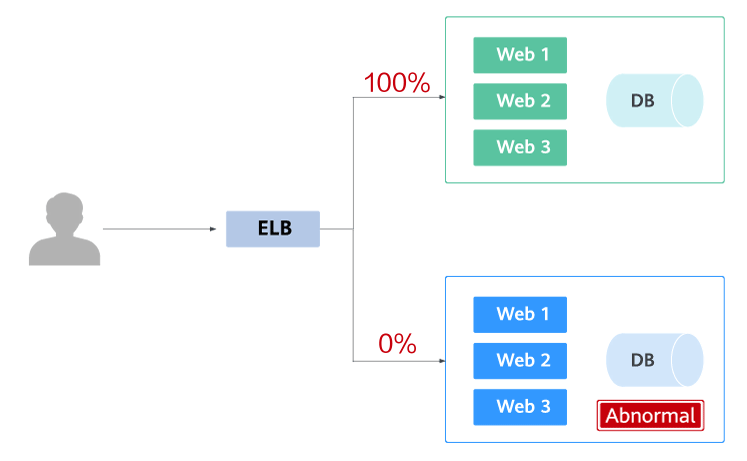
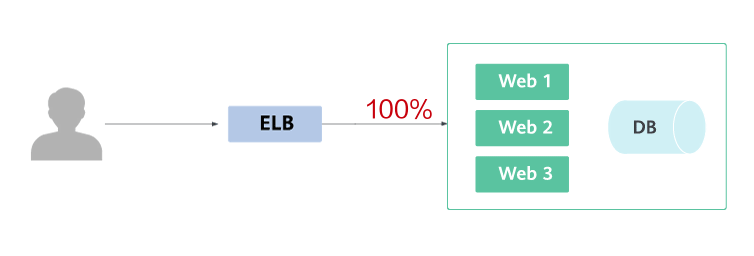
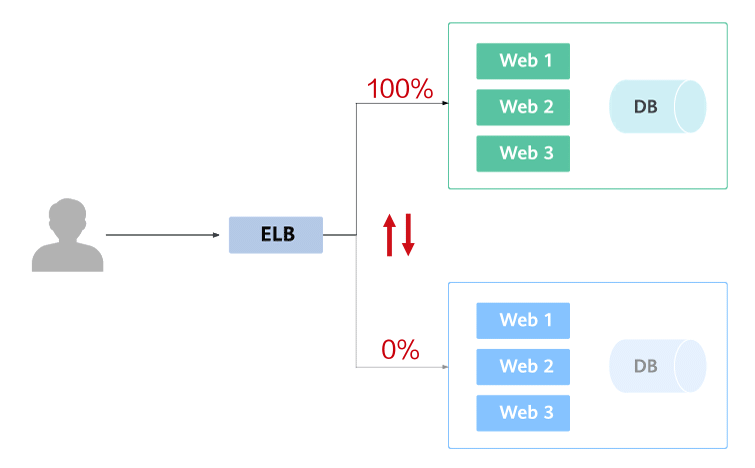
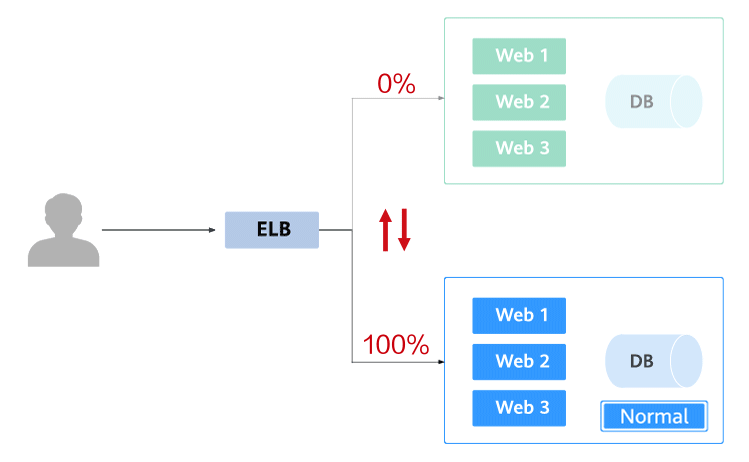
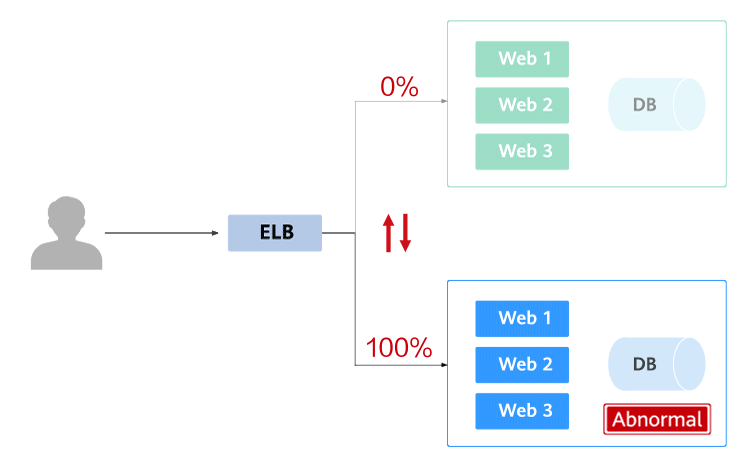
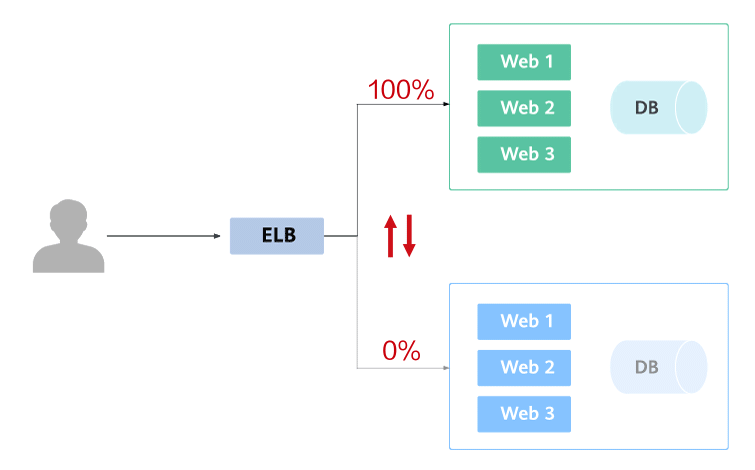
Blue-green deployment provides a zero-downtime, predictable manner for releasing applications to reduce service interruption during the release. A new version is deployed while the old version is retained. The two versions are online at the same time. The new and old versions work in hot backup mode. The route weight is switched (0 or 100) to enable different versions to go online or offline. If a problem occurs, the version can be quickly rolled back.