Restoring from a Cloud Server Backup¶
When disks on a server are faulty or their data is lost, you can use a backup to restore the server to its state when the backup was created.
Note
The system shuts down the server before restoring server data, and automatically starts up the server after the restoration is complete. If you deselect Start the server immediately after restoration, you need to manually start the server after the restoration is complete.
Constraints¶
When restoring from a cloud server backup, backup of a data disk cannot be restored to the system disk.
Data cannot be restored to servers in the Faulty state.
Prerequisites¶
Disks are running properly on the server whose data needs to be restored.
The server has at least one Available backup.
Procedure¶
Log in to the CBR console.
Log in to the management console.
Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region.Click
 and choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup type from the left navigation pane.
and choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup type from the left navigation pane.
Click the Backups tab. Locate the desired backup. For details, see Viewing a Backup.
Click Restore Server in the Operation column, as shown in Figure 1.
Important
The current server data will be overwritten by the data captured at the time of backup. The restoration cannot be undone.
Figure 1 Restoring a server
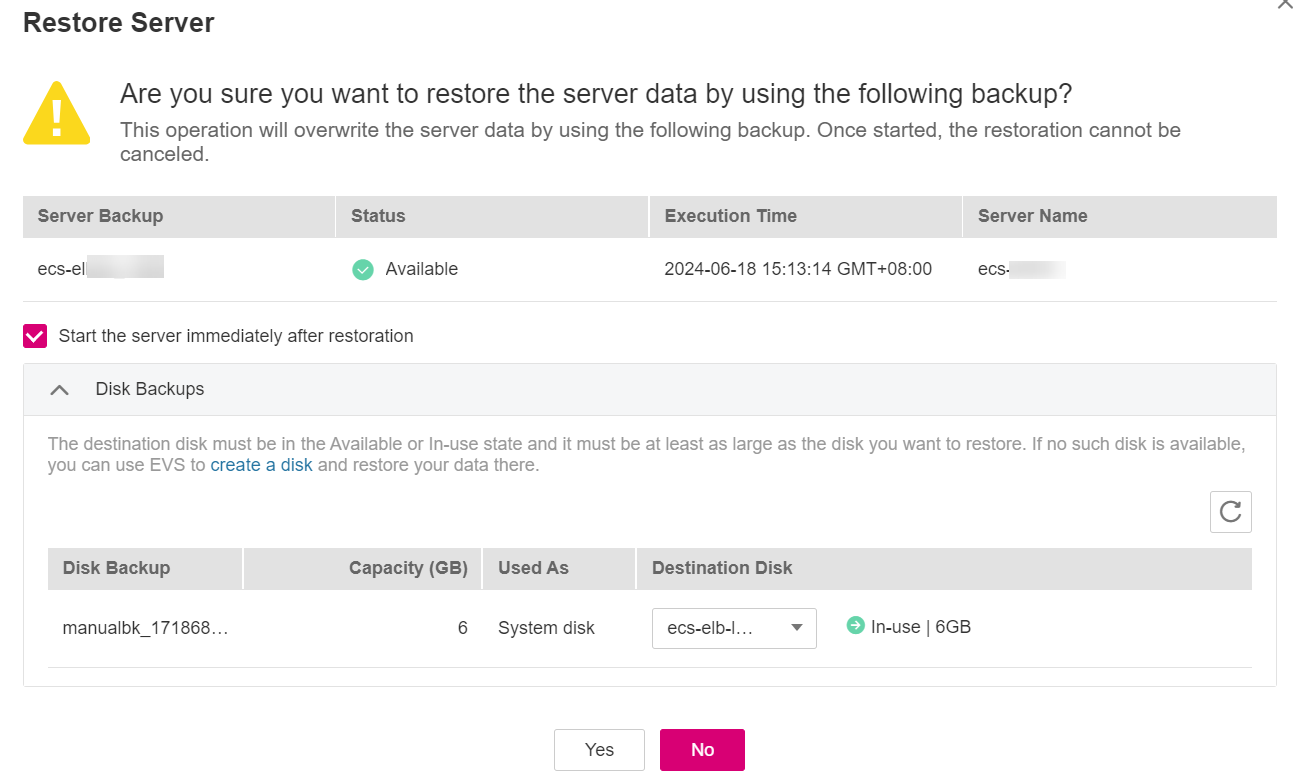
(Optional) Deselect Start the server immediately after restoration.
If you do so, manually start the server after the restoration is complete.
Important
Servers will be shut down during restoration, so you are advised to perform a restoration during off-peak hours.
In the Destination Disk drop-down list, select the target disk to which the backup will be restored.
Note
If the server has only one disk, the backup is restored to that disk by default.
If the server has multiple disks, the backup is restored to the original disks by default. You can also restore the backup to a different disk of at least the same size as the original disk.
When restoring from a cloud server backup, backup of a data disk cannot be restored to the system disk.
Important
If the number of disks to be restored is greater than the number of disks that were backed up, restoration may cause data inconsistency.
For example, if the Oracle data is scattered across multiple disks and only some of them are restored, data may become inconsistent and the application may fail to start.
Click Yes and confirm that the restoration is successful.
You can view the restoration status in the backup list. When the backup enters the Available state and no new restoration tasks failed, the restoration is successful. The data is restored to the state when that backup was created.
For details about how to view failed restoration tasks, see Managing Tasks.
Important
If you use a cloud server backup to restore a logical volume group, you need to attach the logical volume group again.
Due to Window limitations, data disks may fail to be displayed after a Windows server is restored. If this happens, manually bring these data disks online. For details, see Data Disks Are Not Displayed After a Windows Server Is Restored.