Overview¶
Enhanced High-Speed Network¶
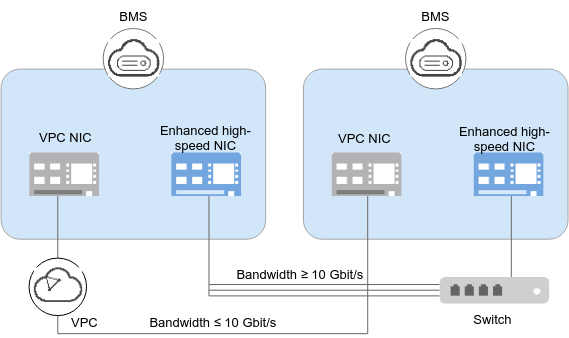
Figure 1 Enhanced high-speed network architecture¶
An enhanced high-speed network is a high-quality, high-speed, and low-latency internal network for BMSs to communicate with each other. It has the following features:
Networks for high-speed internal interconnection
Internal networks that you can customize
A total bandwidth greater than 10 Gbit/s
Hardware and software in high-speed networks are upgraded to provide enhanced high-speed networks. Figure 2 shows the architecture of the high-speed network and Figure 3 shows a comparison between the architectures of the high-speed network and enhanced high-speed network.
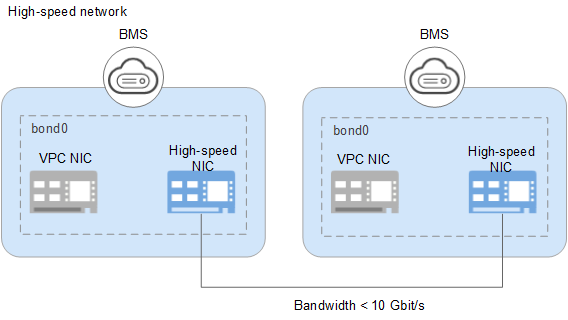
Figure 2 High-speed network architecture¶
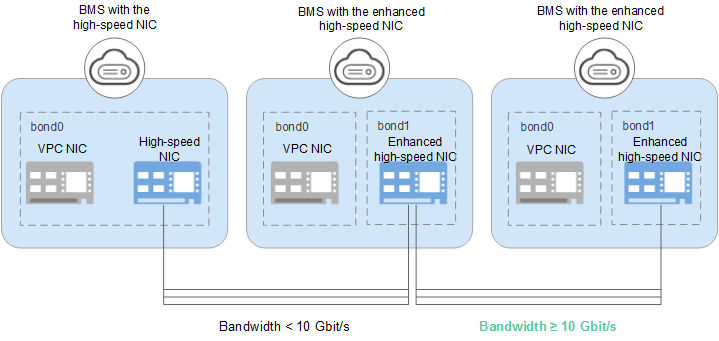
Figure 3 Comparison between the high-speed network and enhanced high-speed network¶
Compared with the high-speed network, the enhanced high-speed network has the following advantages:
View Enhanced High-Speed NICs¶
You can view the network interfaces of the enhanced high-speed network on the NICs tab page of the BMS details page.
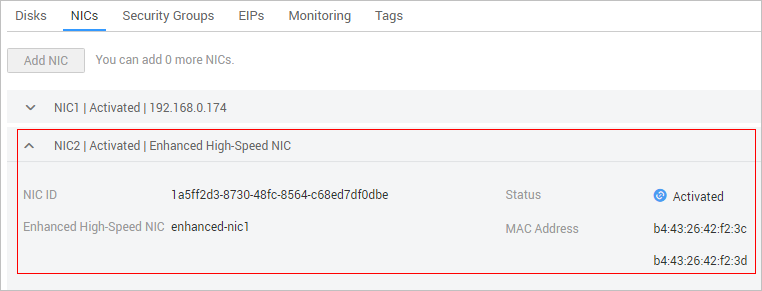
Figure 4 Viewing enhanced high-speed NICs¶
Application Scenarios¶
The enhanced high-speed NIC applies to the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: bonding
When bonding enhanced high-speed NICs, you can choose whether to configure VLANs based on network planning.
Do not configure VLANs.
If no VLAN is required, you can configure IP addresses and subnet masks directly when bonding enhanced high-speed NICs. After the configuration is complete, enhanced high-speed NICs on the same network can communicate with each other.
Configure VLANs.
If VLANs are required, you can configure VLAN sub-interfaces after bonding enhanced high-speed NICs.
Scenario 2: no bonding
If you use enhanced high-speed NICs directly without bonding them, you cannot configure VLANs or configure IP addresses or subnet masks. After the configuration is complete, enhanced high-speed NICs on the same network can communicate with each other.
Note
A single enhanced high-speed NIC also supports bonding.
Configuring an Enhanced High-Speed NIC (SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12) to Configuring an Enhanced High-Speed NIC (Windows Server) describe how to bond enhanced high-speed NICs in the OS. The configuration method varies depending on the OS.